
- Cryptography - Home
- Cryptography - Origin
- Cryptography - History
- Cryptography - Principles
- Cryptography - Applications
- Cryptography - Benefits & Drawbacks
- Cryptography - Modern Age
- Cryptography - Traditional Ciphers
- Cryptography - Need for Encryption
- Cryptography - Double Strength Encryption
- Cryptosystems
- Cryptosystems
- Cryptosystems - Components
- Attacks On Cryptosystem
- Cryptosystems - Rainbow table attack
- Cryptosystems - Dictionary attack
- Cryptosystems - Brute force attack
- Cryptosystems - Cryptanalysis Techniques
- Types of Cryptography
- Cryptosystems - Types
- Public Key Encryption
- Modern Symmetric Key Encryption
- Cryptography Hash functions
- Key Management
- Cryptosystems - Key Generation
- Cryptosystems - Key Storage
- Cryptosystems - Key Distribution
- Cryptosystems - Key Revocation
- Block Ciphers
- Cryptosystems - Stream Cipher
- Cryptography - Block Cipher
- Cryptography - Feistel Block Cipher
- Block Cipher Modes of Operation
- Block Cipher Modes of Operation
- Electronic Code Book (ECB) Mode
- Cipher Block Chaining (CBC) Mode
- Cipher Feedback (CFB) Mode
- Output Feedback (OFB) Mode
- Counter (CTR) Mode
- Classic Ciphers
- Cryptography - Reverse Cipher
- Cryptography - Caesar Cipher
- Cryptography - ROT13 Algorithm
- Cryptography - Transposition Cipher
- Cryptography - Encryption Transposition Cipher
- Cryptography - Decryption Transposition Cipher
- Cryptography - Multiplicative Cipher
- Cryptography - Affine Ciphers
- Cryptography - Simple Substitution Cipher
- Cryptography - Encryption of Simple Substitution Cipher
- Cryptography - Decryption of Simple Substitution Cipher
- Cryptography - Vigenere Cipher
- Cryptography - Implementing Vigenere Cipher
- Modern Ciphers
- Base64 Encoding & Decoding
- Cryptography - XOR Encryption
- Substitution techniques
- Cryptography - MonoAlphabetic Cipher
- Cryptography - Hacking Monoalphabetic Cipher
- Cryptography - Polyalphabetic Cipher
- Cryptography - Playfair Cipher
- Cryptography - Hill Cipher
- Polyalphabetic Ciphers
- Cryptography - One-Time Pad Cipher
- Implementation of One Time Pad Cipher
- Cryptography - Transposition Techniques
- Cryptography - Rail Fence Cipher
- Cryptography - Columnar Transposition
- Cryptography - Steganography
- Symmetric Algorithms
- Cryptography - Data Encryption
- Cryptography - Encryption Algorithms
- Cryptography - Data Encryption Standard
- Cryptography - Triple DES
- Cryptography - Double DES
- Advanced Encryption Standard
- Cryptography - AES Structure
- Cryptography - AES Transformation Function
- Cryptography - Substitute Bytes Transformation
- Cryptography - ShiftRows Transformation
- Cryptography - MixColumns Transformation
- Cryptography - AddRoundKey Transformation
- Cryptography - AES Key Expansion Algorithm
- Cryptography - Blowfish Algorithm
- Cryptography - SHA Algorithm
- Cryptography - RC4 Algorithm
- Cryptography - Camellia Encryption Algorithm
- Cryptography - ChaCha20 Encryption Algorithm
- Cryptography - CAST5 Encryption Algorithm
- Cryptography - SEED Encryption Algorithm
- Cryptography - SM4 Encryption Algorithm
- IDEA - International Data Encryption Algorithm
- Public Key (Asymmetric) Cryptography Algorithms
- Cryptography - RSA Algorithm
- Cryptography - RSA Encryption
- Cryptography - RSA Decryption
- Cryptography - Creating RSA Keys
- Cryptography - Hacking RSA Cipher
- Cryptography - ECDSA Algorithm
- Cryptography - DSA Algorithm
- Cryptography - Diffie-Hellman Algorithm
- Data Integrity in Cryptography
- Data Integrity in Cryptography
- Message Authentication
- Cryptography Digital signatures
- Public Key Infrastructure
- Hashing
- MD5 (Message Digest Algorithm 5)
- SHA-1 (Secure Hash Algorithm 1)
- SHA-256 (Secure Hash Algorithm 256-bit)
- SHA-512 (Secure Hash Algorithm 512-bit)
- SHA-3 (Secure Hash Algorithm 3)
- Hashing Passwords
- Bcrypt Hashing Module
- Modern Cryptography
- Quantum Cryptography
- Post-Quantum Cryptography
- Cryptographic Protocols
- Cryptography - SSL/TLS Protocol
- Cryptography - SSH Protocol
- Cryptography - IPsec Protocol
- Cryptography - PGP Protocol
- Image & File Cryptography
- Cryptography - Image
- Cryptography - File
- Steganography - Image
- File Encryption and Decryption
- Cryptography - Encryption of files
- Cryptography - Decryption of files
- Cryptography in IoT
- IoT security challenges, Threats and Attacks
- Cryptographic Techniques for IoT Security
- Communication Protocols for IoT Devices
- Commonly Used Cryptography Techniques
- Custom Building Cryptography Algorithms (Hybrid Cryptography)
- Cloud Cryptography
- Quantum Cryptography
- DNA Cryptography
- One Time Password (OTP) algorithm in Cryptography
- Difference Between
- Cryptography - MD5 vs SHA1
- Cryptography - RSA vs DSA
- Cryptography - RSA vs Diffie-Hellman
- Cryptography vs Cryptology
- Cryptography - Cryptology vs Cryptanalysis
- Cryptography - Classical vs Quantum
- Cryptography vs Steganography
- Cryptography vs Encryption
- Cryptography vs Cyber Security
- Cryptography - Stream Cipher vs Block Cipher
- Cryptography - AES vs DES ciphers
- Cryptography - Symmetric vs Asymmetric
Data Encryption Standard
The Data Encryption Standard (DES) is a symmetric-key block cipher published by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).
DES is an implementation of a Feistel Cipher. It uses 16 round Feistel structure. The block size is 64-bit. Though, key length is 64-bit, DES has an effective key length of 56 bits, since 8 of the 64 bits of the key are not used by the encryption algorithm (function as check bits only). General Structure of DES is depicted in the following illustration −
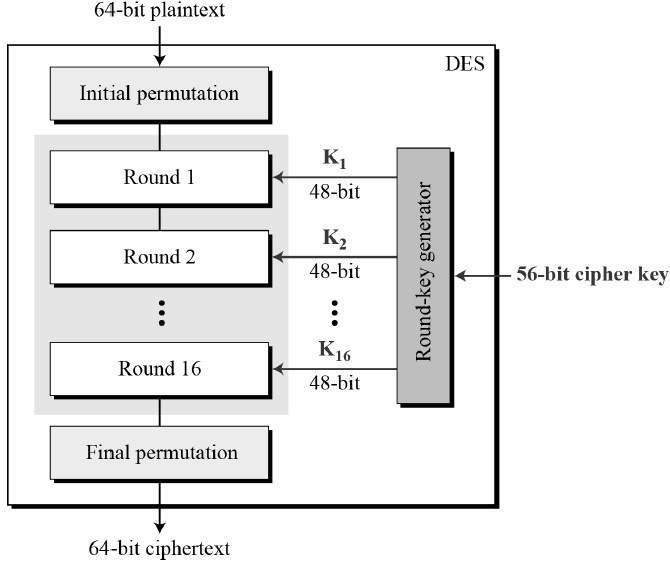
Since DES is based on the Feistel Cipher, all that is required to specify DES is −
- Round function
- Key schedule
- Any additional processing − Initial and final permutation
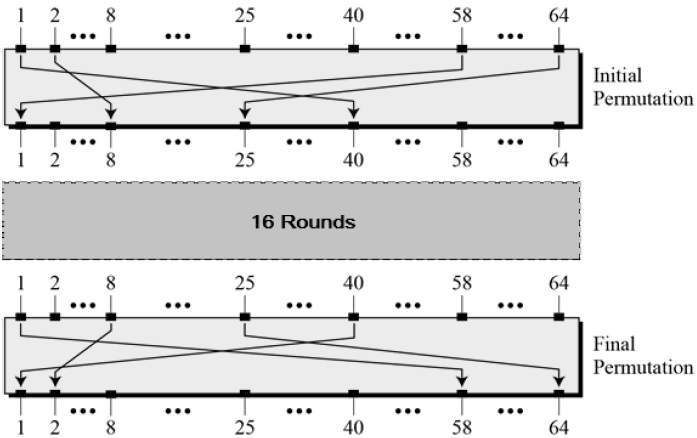
Initial and Final Permutation
The initial and final permutations are straight Permutation boxes (P-boxes) that are inverses of each other. They have no cryptography significance in DES. The initial and final permutations are shown as follows −
Round Function
The heart of this cipher is the DES function, f. The DES function applies a 48-bit key to the rightmost 32 bits to produce a 32-bit output.
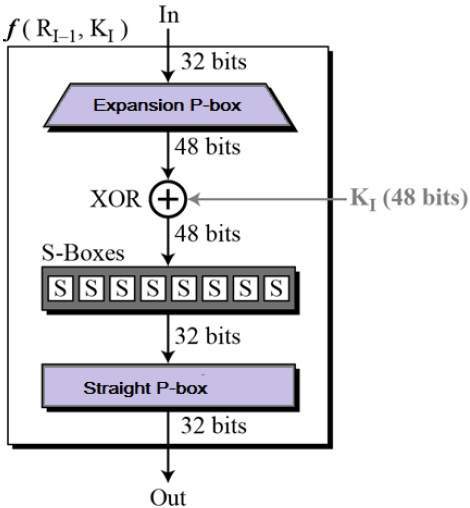
Expansion Permutation Box − Since right input is 32-bit and round key is a 48-bit, we first need to expand right input to 48 bits. Permutation logic is graphically depicted in the following illustration −
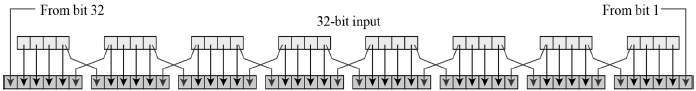
The graphically depicted permutation logic is generally described as table in DES specification illustrated as shown −
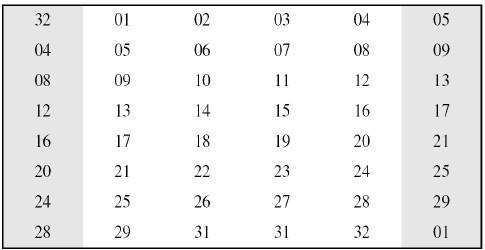
XOR (Whitener). − After the expansion permutation, DES does XOR operation on the expanded right section and the round key. The round key is used only in this operation.
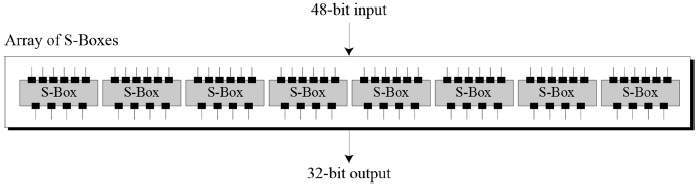
Substitution Boxes. − The S-boxes carry out the real mixing (confusion). DES uses 8 S-boxes, each with a 6-bit input and a 4-bit output. Refer the following illustration −
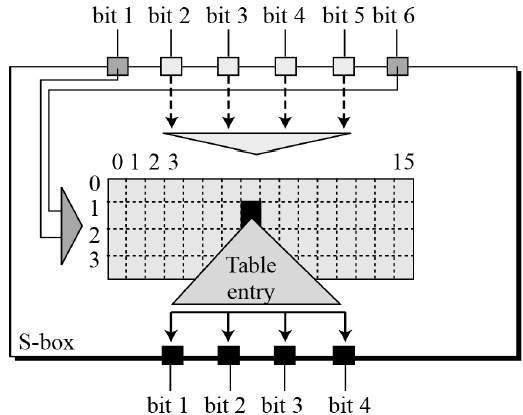
The S-box rule is illustrated below −
There are a total of eight S-box tables. The output of all eight s-boxes is then combined in to 32 bit section.
Straight Permutation − The 32 bit output of S-boxes is then subjected to the straight permutation with rule shown in the following illustration:
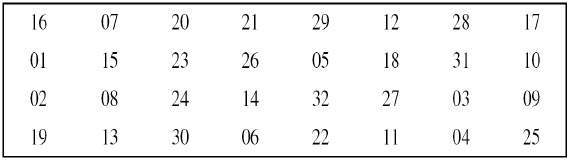
Key Generation
The round-key generator creates sixteen 48-bit keys out of a 56-bit cipher key. The process of key generation is depicted in the following illustration −
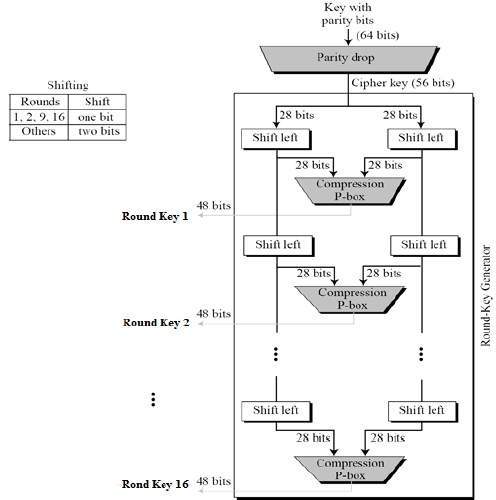
The logic for Parity drop, shifting, and Compression P-box is given in the DES description.
DES Analysis
The DES satisfies both the desired properties of block cipher. These two properties make cipher very strong.
Avalanche effect − A small change in plaintext results in the very great change in the ciphertext.
Completeness − Each bit of ciphertext depends on many bits of plaintext.
During the last few years, cryptanalysis have found some weaknesses in DES when key selected are weak keys. These keys shall be avoided.
DES has proved to be a very well designed block cipher. There have been no significant cryptanalytic attacks on DES other than exhaustive key search.