
- Digital Electronics - Home
- Digital Electronics Basics
- Types of Digital Systems
- Types of Signals
- Logic Levels And Pulse Waveforms
- Digital System Components
- Digital Logic Operations
- Digital Systems Advantages
- Number Systems
- Number Systems
- Binary Numbers Representation
- Binary Arithmetic
- Signed Binary Arithmetic
- Octal Arithmetic
- Hexadecimal Arithmetic
- Complement Arithmetic
- Base Conversions
- Base Conversions
- Binary to Decimal Conversion
- Decimal to Binary Conversion
- Binary to Octal Conversion
- Octal to Binary Conversion
- Octal to Decimal Conversion
- Decimal to Octal Conversion
- Hexadecimal to Binary Conversion
- Binary to Hexadecimal Conversion
- Hexadecimal to Decimal Conversion
- Decimal to Hexadecimal Conversion
- Octal to Hexadecimal Conversion
- Hexadecimal to Octal Conversion
- Binary Codes
- Binary Codes
- 8421 BCD Code
- Excess-3 Code
- Gray Code
- ASCII Codes
- EBCDIC Code
- Code Conversion
- Error Detection & Correction Codes
- Logic Gates
- Logic Gates
- AND Gate
- OR Gate
- NOT Gate
- Universal Gates
- XOR Gate
- XNOR Gate
- CMOS Logic Gate
- OR Gate Using Diode Resistor Logic
- AND Gate vs OR Gate
- Two Level Logic Realization
- Threshold Logic
- Boolean Algebra
- Boolean Algebra
- Laws of Boolean Algebra
- Boolean Functions
- DeMorgan's Theorem
- SOP and POS Form
- POS to Standard POS Form
- Minimization Techniques
- K-Map Minimization
- Three Variable K-Map
- Four Variable K-Map
- Five Variable K-Map
- Six Variable K-Map
- Don't Care Condition
- Quine-McCluskey Method
- Min Terms and Max Terms
- Canonical and Standard Form
- Max Term Representation
- Simplification using Boolean Algebra
- Combinational Logic Circuits
- Digital Combinational Circuits
- Digital Arithmetic Circuits
- Multiplexers
- Multiplexer Design Procedure
- Mux Universal Gate
- 2-Variable Function Using 4:1 Mux
- 3-Variable Function Using 8:1 Mux
- Demultiplexers
- Mux vs Demux
- Parity Bit Generator and Checker
- Comparators
- Encoders
- Keyboard Encoders
- Priority Encoders
- Decoders
- Arithmetic Logic Unit
- 7-Segment LED Display
- Code Converters
- Code Converters
- Binary to Decimal Converter
- Decimal to BCD Converter
- BCD to Decimal Converter
- Binary to Gray Code Converter
- Gray Code to Binary Converter
- BCD to Excess-3 Converter
- Excess-3 to BCD Converter
- Adders
- Half Adders
- Full Adders
- Serial Adders
- Parallel Adders
- Full Adder using Half Adder
- Half Adder vs Full Adder
- Full Adder with NAND Gates
- Half Adder with NAND Gates
- Binary Adder-Subtractor
- Subtractors
- Half Subtractors
- Full Subtractors
- Parallel Subtractors
- Full Subtractor using 2 Half Subtractors
- Half Subtractor using NAND Gates
- Sequential Logic Circuits
- Digital Sequential Circuits
- Clock Signal and Triggering
- Latches
- Shift Registers
- Shift Register Applications
- Binary Registers
- Bidirectional Shift Register
- Counters
- Binary Counters
- Non-binary Counter
- Design of Synchronous Counter
- Synchronous vs Asynchronous Counter
- Finite State Machines
- Algorithmic State Machines
- Flip Flops
- Flip-Flops
- Conversion of Flip-Flops
- D Flip-Flops
- JK Flip-Flops
- T Flip-Flops
- SR Flip-Flops
- Clocked SR Flip-Flop
- Unclocked SR Flip-Flop
- Clocked JK Flip-Flop
- JK to T Flip-Flop
- SR to JK Flip-Flop
- Triggering Methods:Flip-Flop
- Edge-Triggered Flip-Flop
- Master-Slave JK Flip-Flop
- Race-around Condition
- A/D and D/A Converters
- Analog-to-Digital Converter
- Digital-to-Analog Converter
- DAC and ADC ICs
- Realization of Logic Gates
- NOT Gate from NAND Gate
- OR Gate from NAND Gate
- AND Gate from NAND Gate
- NOR Gate from NAND Gate
- XOR Gate from NAND Gate
- XNOR Gate from NAND Gate
- NOT Gate from NOR Gate
- OR Gate from NOR Gate
- AND Gate from NOR Gate
- NAND Gate from NOR Gate
- XOR Gate from NOR Gate
- XNOR Gate from NOR Gate
- NAND/NOR Gate using CMOS
- Full Subtractor using NAND Gate
- AND Gate Using 2:1 MUX
- OR Gate Using 2:1 MUX
- NOT Gate Using 2:1 MUX
- Memory Devices
- Memory Devices
- RAM and ROM
- Cache Memory Design
- Programmable Logic Devices
- Programmable Logic Devices
- Programmable Logic Array
- Programmable Array Logic
- Field Programmable Gate Arrays
- Digital Electronics Families
- Digital Electronics Families
- CPU Architecture
- CPU Architecture
Arithmetic Logic Unit in Digital Electronics
The Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) is the fundamental component in a computing system like a computer. It is basically the actual data processing element within the central processing unit (CPU) in a computing system. It performs all the arithmetic and logical operations and forms the backbone of modern computer technology.
In this chapter, we will explain the working of the arithmetic logic unit, along with its main components, their functions, and the importance of the ALU in the field of digital system designs.
What is Arithmetic Logic Unit?
Arithmetic Logic Unit abbreviated as ALU is considered as the engine or heart of every central processing unit (CPU). ALU is basically a combination logic circuit that can perform arithmetic and logical operation on digital data (data in binary format). It can also execute instructions given to a computing system like a digital computer.
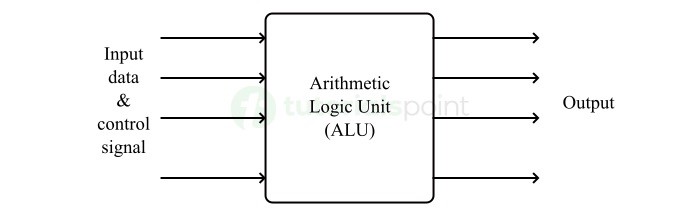
Within the complex architecture of a digital computing system, the arithmetic logic unit or ALU plays an important role as it executes and processes all the instructions, performs calculations, manipulates binary data, and performs various decision-making operations.
The development of arithmetic logic unit begins with the need for efficient, high speed, and accurate data processing and computation. With the advancement in electronics technologies, ALU has become a highly sophisticated digital data processing device that can handle a large number of complex instructions and computational tasks.
Todays ALU provides high accuracy, precision, and significantly fast processing speed in computing operations.
Features of Arithmetic Logic Unit
Here are some key features of arithmetic logic unit −
- The ALU can perform all arithmetic and logic operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, logical comparisons, etc.
- It can also perform bitwise and mathematical operations on binary numbers.
- It contains two segments namely, AU (arithmetic unit) and LU (logic unit) to perform arithmetic operations and logical operations respectively.
- It is the computational powerhouse within a central processing unit (CPU).
- ALU is the part of every CPU where actual data processing takes place.
- ALU is responsible for interpreting the code instructions based on which operations to be performed on the input data.
- Once the data processing is completed, the ALU sends the outcomes to the memory unit or output unit.
Main Components of Arithmetic Logic Unit
The arithmetic logic unit consists of various functional parts that are responsible for performing specific operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, comparison, and more. Some of the key components of the arithmetic logic unit are explained below −
Arithmetic Unit
The main components used in the arithmetic unit (AU) segment of the arithmetic logic unit are as follows −
Adder
The adder or binary adder is one of the important components of the arithmetic logic unit. It performs the addition of two or more binary numbers. To accomplish this operation, it performs a series of logical and arithmetic operations. Some common types of adders used in the arithmetic ogic unit are half-adder, full-adder, parallel adder, and ripple carry adder. Each type of adder is designed and optimized to perform a specific computing operation.
Subtractor
The subtractor is another digital combinational circuit designed to perform subtraction of binary numbers. In most arithmetic logic unit, the subtractor uses 2s complement arithmetic to perform subtraction on binary numbers.
Multiplier and Divider
In more complex and advanced arithmetic logic units, dedicated multiplier and divider circuits are also implemented to perform multiplication and division on binary numbers. These circuits use advanced processing techniques like iterative or parallel processing to accomplish these operations.
Logic Unit
The logic unit (LU) of the ALU comprises the components responsible for performing Boolean or comparison operations. The following are some main components of the logic unit of an ALU −
Logic Gates
The logic gates like AND, OR, NOT, NAND, NOR, XOR, and XNOR are the key components of logic unit. These are standard logic circuits that can manipulate input data based on some predefined logical instructions and generate a desired output.
Each logic gate can perform a specific logical operation. However, different types of logic gates can be connected together in a specific manner to perform complex logical operations.
Type of Logic Gate
The brief overview of each type of logic gate is explained here −
- AND Gate − It performs the Boolean multiplication on input binary data. Its output is logic 1 or true, only when all its inputs are logic 1 or true.
- OR Gate − The OR gate performs the Boolean addition of input binary data. It generates a logic 1 or true output, if any of its inputs is logic 1 or true.
- NOR Gate − The NOT gate performs the inversion operation. It gives a logic 1 or true output when its input is logic 0 or false and vice-versa.
- NAND Gate − The NAND gate performs the NOTed AND operation and produces a logic 1 or true output when both inputs or any of the inputs is logic 0 or false.
- NOR Gate − The NOR gate performs the NOTed OR operation and generates a logic 1 or true output when all its inputs are logic 0 or false.
- XOR Gate − The XOR gate performs the exclusive OR operation and produces a logic 1 or true output when its both inputs are dissimilar. Hence, it is used as inequality detector.
- XNOR Gate − The XNOR gate performs the exclusive NOR operation and gives a logic 1 or true output when both its inputs are similar. Thus, it is used as an equality detector.
This is all about structure and components of the arithmetic logic unit. Let us now understand what functions an ALU can perform.
Functions of Arithmetic Logic Unit
The arithmetic logic unit can perform a wide range of functions and operations in digital computing systems. Some important functions that an arithmetic logic unit perform are explained below −
Arithmetic Operations
The arithmetic operations are one of the primary functions that the arithmetic logic unit performs. This category of operations includes addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division of binary numbers. All these operations form the basis of mathematical computations that the arithmetic logic unit can perform.
Logical Operations
The arithmetic logic unit can also perform various logical operations such as AND operation, OR operation, NOT operation, etc. These logical operations form the basis of decision making and data manipulation processes.
Comparison Operations
The arithmetic logic unit also facilitates to perform various comparison operations such as equal to, not equal to, less than, greater than, etc. These comparison operations are essential in decision making processes.
Shift Operations
The arithmetic logic unit can also perform shift operations on binary numbers such as left shift and right shift. These operations are important in multiplication and division operations. The shift operations can manipulate binary data at bit level and hence optimize the arithmetic calculations.
Working of Arithmetic Logic Unit
The working of the arithmetic logic unit depends on a combination of input data and control signals. In other words, the arithmetic logic unit receives the input data and control signals and then interpret these data and signals to perform specific operations.
Let us understand the working of the arithmetic logic unit in detail by breaking it down in sub-components.
Receiving Input Data and Control Signals
The arithmetic logic unit receives the input data from the user and a set of control signals that specifies the operation to be performed. The data is received through the input data path while the control signals are received from the control unit.
Execution of Operation
Once the arithmetic logic unit received the input data and control signals, it selects an appropriate functional component among arithmetic unit, logic unit, comparison unit, or shift unit to perform the specific operation. Once the operation completes, the ALU sends the results to the memory unit for storage or output unit.
Significance of Arithmetic Logic Unit
In the field of digital electronics and computing technology, the arithmetic logic unit plays an important role because of the following reasons −
- It can perform the arithmetic, logical, and comparison operations with very high accuracy, precision, and efficiency.
- It can also perform complex data processing and decision-making operations.
- ALU can execute complex processing tasks at a very high speed that results in better performance and higher efficiency.
- ALU introduces versatility as it can execute a wide range of computational tasks.
Conclusion
This is all about arithmetic logic unit (ALU) which is an important combinational logic circuit in digital electronics and modern computing systems. It acts as the heart of central processing unit (CPU) and executes all kinds of operations including arithmetic, logical, and comparison operations. In a digital computing system, the arithmetic logic unit acts as a primary functional unit that processes the input data based on the instructions. In this chapter, we have studied all the important concepts related to the arithmetic logic unit.