
- Puppeteer - Home
- Puppeteer - Introduction
- Puppeteer - Element Handling
- Puppeteer - Usage of Google
- Puppeteer - NodeJS Installation
- Puppeteer VS Code Configuration
- Puppeteer - Installation
- Puppeteer - Basic Test
- Puppeteer - Non Headless Execution
- Comparison Between Puppeteer & Selenium
- Comparison Between Puppeteer & Protractor
- Comparison Between Puppeteer & Cypress
- Puppeteer - Browser Operations
- Puppeteer - Handling Tabs
- Puppeteer - Basic Commands
- Puppeteer - Firefox
- Puppeteer - Chrome
- Puppeteer - Handling Confirm Alerts
- Puppeteer - Handling Drop-downs
- Puppeteer - Locators
- Puppeteer - Xpath Functions
- Puppeteer - Xpath Attributes
- Puppeteer - Xpath Grouping
- Puppeteer - Absolute Xpath
- Puppeteer - Relative Xpath
- Puppeteer - Xpath Axes
- Puppeteer - Type Selector
- Name Selector & Class Name Selector
- Puppeteer - Id Selector
- Puppeteer - Attribute Selector
- Puppeteer - Handling Links/Button
- Handling Edit Boxes & Checkboxes
- Puppeteer - Handling Frames
- Puppeteer - Keyboard Simulation
- Puppeteer - Getting Element Text
- Puppeteer - Getting Element Attribute
- Puppeteer - Device Emulation
- Puppeteer - Disable JavaScript
- Puppeteer - Synchronization
- Puppeteer - Capture Screenshot
- Puppeteer Useful Resources
- Puppeteer - Quick Guide
- Puppeteer - Useful Resources
- Puppeteer - Discussion
Name Selector and Class Name Selector
Let us begin by learning about name selector.
Name Selector
Once we navigate to a webpage, we have to interact with the webelements available on the page like clicking a link/button, entering text within an edit box, and so on to complete our automation test case.
For this, our first job is to identify the element. If a value of the name attribute is used only one time in a page, we can use it as a name selector. If there are multiple elements with the same name, only the first matching element on the page shall be identified.
Syntax
The syntax for name selector is as follows −
const f = await page.$('[name="search"]')
Let us identify the edit box highlighted in the below image and enter text −
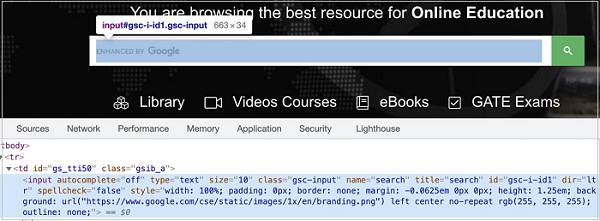
The element highlighted in the above image has the name attribute value as search. The name selector expression for the above element shall be [name="search"].
To begin, follow Steps 1 to 2 from the Chapter of Basic Test on Puppeteer which are as follows −
Step 1 − Create a new file within the directory where the node_modules folder is created (location where the Puppeteer and Puppeteer core have been installed).
The details on Puppeteer installation is discussed in the Chapter of Puppeteer Installation.
Right-click on the folder where the node_modules folder is created, then click on the New file button.
Step 2 − Enter a filename, say testcase1.js.
Step 3 − Add the below code within the testcase1.js file created.
//Puppeteer library
const pt= require('puppeteer')
async function selectorName(){
//launch browser in headless mode
const browser = await pt.launch()
//browser new page
const page = await browser.newPage();
//launch URL
await page.goto('https://www.tutorialspoint.com/index.htm')
//identify edit box with name
const f = await page.$('[name="search"]')
//enter text
f.type("Puppeteer")
//wait for sometime
await page.waitForTimeout(4000)
//browser close
await browser.close()
}
selectorName()
Step 4 − Execute the code with the command given below −
node <filename>
So in our example, we shall run the following command −
node testcase1.js
Class Name Selector
Once we navigate to a webpage, we have to interact with the webelements available on the page like clicking a link/button, entering text within an edit box, and so on to complete our automation test case.
For this, our first job is to identify the element. If a class name is used only one time in a page, we can use it as a class name selector. If there are multiple elements with the same class name, only the first matching element on the page shall be identified.
Syntax
The syntax for class name selector is as follows −
const n = await page.$(".txtloc")
In the below example, let us identify the highlighted element having class name heading and obtain its text - About Tutorialspoint.
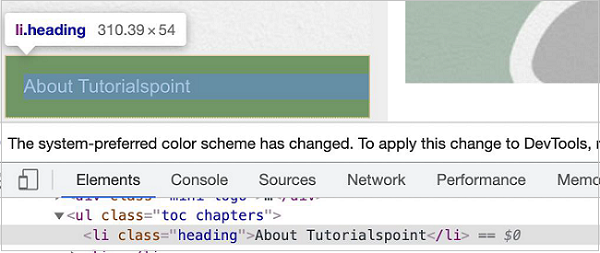
The id selector expression for the above element shall be .heading.
To begin, follow Steps 1 to 2 from the Chapter of Basic Test on Puppeteer which are as follows −
Step 1 − Create a new file within the directory where the node_modules folder is created (location where the Puppeteer and Puppeteer core have been installed).
The details on Puppeteer installation is discussed in the Chapter of Puppeteer Installation.
Right-click on the folder where the node_modules folder is created, then click on the New file button.

Step 2 − Enter a filename, say testcase1.js.

Step 3 − Add the below code within the testcase1.js file created.
//Puppeteer library
const pt= require('puppeteer')
async function getText(){
//launch browser in headless mode
const browser = await pt.launch()
//browser new page
const page = await browser.newPage()
//launch URL
await page.goto('https://www.tutorialspoint.com/about/about_careers.htm')
//identify element with class name
const f = await page.$(".heading")
//obtain text
const text = await (await f.getProperty('textContent')).jsonValue()
console.log("Text is: " + text)
}
getText()
Step 4 − Execute the code with the command given below −
node <filename>
So in our example, we shall run the following command −
node testcase1.js
After the command has been successfully executed, the text of the element - About Tutorialspoint gets printed in the console.