
- Java - Home
- Java - Overview
- Java - History
- Java - Features
- Java Vs. C++
- JVM - Java Virtual Machine
- Java - JDK vs JRE vs JVM
- Java - Environment Setup
- Java - Hello World Program
- Java - Comments
- Java - Basic Syntax
- Java - Variables
- Java - Data Types
- Java - Type Casting
- Java - Unicode System
- Java - User Input
- Java - Date & Time
Java Operators
- Java - Operators
- Java - Arithmetic Operators
- Java - Assignment Operators
- Java - Relational Operators
- Java - Logical Operators
- Java - Bitwise Operators
- Java Operator Precedence & Associativity
- Java - Unary Operators
Java Control Statements
- Java - Decision Making
- Java - If Else Statement
- Java - Switch Statement
- Java - Loop Control
- Java - For Loop
- Java - For-Each Loop
- Java - While Loop
- Java - Do While Loop
- Java - Break Statement
- Java - Continue Statement
Object Oriented Programming
- Java - OOPs Concepts
- Java - Object & Classes
- Java - Class Attributes
- Java - Class Methods
- Java - Methods
- Java - Variables Scope
- Java - Constructors
- Java - Access Modifiers
- Java - Inheritance
- Java - Aggregation
- Java - Polymorphism
- Java - Overriding
- Java - Method Overloading
- Java - Dynamic Binding
- Java - Static Binding
- Java - Instance Initializer Block
- Java - Abstraction
- Java - Encapsulation
- Java - Interfaces
- Java - Packages
- Java - Inner Classes
- Java - Static Class
- Java - Anonymous Class
- Java - Singleton Class
- Java - Wrapper Classes
- Java - Enums
- Java - Enum Constructor
- Java - Enum Strings
Java Built-in Classes
- Java - Number
- Java - Boolean
- Java - Characters
- Java - Arrays
- Java - Multi-Dimensional Arrays
- Java - Final Arrays
- Java - Math Class
Java File Handling
- Java - Files
- Java - Create a File
- Java - Write to File
- Java - Read Files
- Java - Delete Files
- Java - Directories
- Java - I/O Streams
Java Error & Exceptions
- Java - Exceptions
- Java - try-catch Block
- Java - try-with-resources
- Java - Multi-catch Block
- Java - Nested try Block
- Java - Finally Block
- Java - throw Exception
- Java - Exception Propagation
- Java - Built-in Exceptions
- Java - Custom Exception
- Java - Chained Exception
Java Multithreading
- Java - Multithreading
- Java - Thread Life Cycle
- Java - Creating a Thread
- Java - Starting a Thread
- Java - Joining Threads
- Java - Naming Thread
- Java - Thread Scheduler
- Java - Thread Pools
- Java - Main Thread
- Java - Thread Priority
- Java - Daemon Threads
- Java - Thread Group
- Java - Shutdown Hook
Java Synchronization
- Java - Synchronization
- Java - Block Synchronization
- Java - Static Synchronization
- Java - Inter-thread Communication
- Java - Thread Deadlock
- Java - Interrupting a Thread
- Java - Thread Control
- Java - Reentrant Monitor
Java Networking
- Java - Networking
- Java - Socket Programming
- Java - URL Processing
- Java - URL Class
- Java - URLConnection Class
- Java - HttpURLConnection Class
- Java - Socket Class
- Java - Generics
Java Collections
Java Interfaces
- Java - List Interface
- Java - Queue Interface
- Java - Map Interface
- Java - SortedMap Interface
- Java - Set Interface
- Java - SortedSet Interface
Java Data Structures
Java Collections Algorithms
Advanced Java
- Java - Command-Line Arguments
- Java - Lambda Expressions
- Java - Sending Email
- Java - Applet Basics
- Java - Javadoc Comments
- Java - Autoboxing and Unboxing
- Java - File Mismatch Method
- Java - REPL (JShell)
- Java - Multi-Release Jar Files
- Java - Private Interface Methods
- Java - Inner Class Diamond Operator
- Java - Multiresolution Image API
- Java - Collection Factory Methods
- Java - Module System
- Java - Nashorn JavaScript
- Java - Optional Class
- Java - Method References
- Java - Functional Interfaces
- Java - Default Methods
- Java - Base64 Encode Decode
- Java - Switch Expressions
- Java - Teeing Collectors
- Java - Microbenchmark
- Java - Text Blocks
- Java - Dynamic CDS archive
- Java - Z Garbage Collector (ZGC)
- Java - Null Pointer Exception
- Java - Packaging Tools
- Java - Sealed Classes
- Java - Record Classes
- Java - Hidden Classes
- Java - Pattern Matching
- Java - Compact Number Formatting
- Java - Garbage Collection
- Java - JIT Compiler
Java Miscellaneous
- Java - Recursion
- Java - Regular Expressions
- Java - Serialization
- Java - Strings
- Java - Process API Improvements
- Java - Stream API Improvements
- Java - Enhanced @Deprecated Annotation
- Java - CompletableFuture API Improvements
- Java - Marker Interface
- Java - Streams
- Java - Datetime Api
- Java 8 - New Features
- Java 9 - New Features
- Java 10 - New Features
- Java 11 - New Features
- Java 12 - New Features
- Java 13 - New Features
- Java 14 - New Features
- Java 15 - New Features
- Java 16 - New Features
Java APIs & Frameworks
Java Class References
- Java - Scanner
- Java - Arrays
- Java - Strings
- Java - Date
- Java - ArrayList
- Java - Vector
- Java - Stack
- Java - PriorityQueue
- Java - LinkedList
- Java - ArrayDeque
- Java - HashMap
- Java - LinkedHashMap
- Java - WeakHashMap
- Java - EnumMap
- Java - TreeMap
- Java - IdentityHashMap
- Java - HashSet
- Java - EnumSet
- Java - LinkedHashSet
- Java - TreeSet
- Java - BitSet
- Java - Dictionary
- Java - Hashtable
- Java - Properties
- Java - Collection
- Java - Array
Java Useful Resources
Final Arrays in Java
In Java, when we use the final keyword for a variable, it means we are referring to the variable as a constant. When we use the final keyword for an array, it means we cannot reassign it to point to a new array; it's referred to as a final array in Java.
What do we mean by Final Array?
If we declare an array as final, then its reference to the array cannot be changed. But we can change/modify the elements inside the final array.
Declaring a Final Array
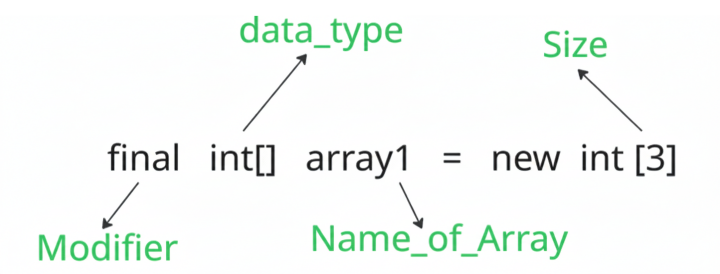
In Java, we can declare a final array by just adding the final keyword at the start of the array declaration as follows:
final dataType[] name_of_Array = new dataType[size];
For example:
final int[] array1 = new int [3]
Initializing a Final Array
We can initialize values to a Final array in three different ways, they are as follows:
Direct Initialization
In Java, we can directly initialize the values of a final array when declaring it. The following is the syntax for direct initialization of a final array:
final dataType[] name_of_Array = {value_1, value_2_,value_3 ...};
By Indexing
In Java, we can initialize the values of a final array by specifying the index of the element. The following is the syntax for initializing a value of a final array by indexing:
name_of_Array [Index] = value;
Using For Loops
In Java, we can initialize the values of a final array using for loops, in which the loop is used to iterate over the elements. The following is the syntax for initializing the value of a final array using for loops:
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
name_of_Array [i] = value;
}
}
Example
Below is an example for declaring a final array and initializing its values using different methods in Java:
public class Demo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// Using direct initialization
final int[] array1 = {1, 2, 3};
System.out.println("Using direct initialization");
for (int i = 0; i < array1.length; i++) {
System.out.print(array1[i] + " ");
}
// Using indexing
final String[] array2 = new String[3];
array2[0] = "Welcome";
array2[1] = "to";
array2[2] = "TutorialsPoint";
System.out.println("\n\nUsing indexing ");
for (int i = 0; i < array2.length; i++) {
System.out.print(array2[i] + " ");
}
// Using for loop
final double[] array3 = new double[3];
for (int i = 0; i < array3.length; i++) {
array3[i] = (i + 1) * 1.5;
}
System.out.println("\n\nUsing for loop");
for (int i = 0; i < array3.length; i++) {
System.out.print(array3[i] + " ");
}
}
}
Output
Using direct initialization 1 2 3 Using indexing Welcome to TutorialsPoint Using for loop 1.5 3.0 4.5
Modifying a Final Array
In Java, we can modify the elements of a final array by providing the index of the element to be changed. But we cannot change the reference of the array, which means reassigning the final array is not allowed in Java.
Example
Below is an example of modifying an element in a final array in Java:
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final int[] myArray = {10, 20, 30};
System.out.println("Array before modification: " + Arrays.toString(myArray));
myArray[0] = 100;
System.out.println("Array before modification: " + Arrays.toString(myArray));
}
}
Output
Array before modification: [10, 20, 30] Array before modification: [100, 20, 30]
Example
Below is an example of reassigning the final array, which will throw a compilation Error:
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final int[] myArray1 = {10, 20, 30};
int[] myArray2 = {4,5,6};
System.out.println("Array before modification: " + Arrays.toString(myArray1));
myArray1 = myArray2;
System.out.println("Array before modification: " + Arrays.toString(myArray));
}
}
Output
The above code throws an error when we try to reassign the final array.
Demo.java:7: error: cannot assign a value to final variable myArray1
myArray1 = myArray2;
^
1 error