
- Java - Home
- Java - Overview
- Java - History
- Java - Features
- Java Vs. C++
- JVM - Java Virtual Machine
- Java - JDK vs JRE vs JVM
- Java - Environment Setup
- Java - Hello World Program
- Java - Comments
- Java - Basic Syntax
- Java - Variables
- Java - Data Types
- Java - Type Casting
- Java - Unicode System
- Java - User Input
- Java - Date & Time
Java Operators
- Java - Operators
- Java - Arithmetic Operators
- Java - Assignment Operators
- Java - Relational Operators
- Java - Logical Operators
- Java - Bitwise Operators
- Java Operator Precedence & Associativity
- Java - Unary Operators
Java Control Statements
- Java - Decision Making
- Java - If Else Statement
- Java - Switch Statement
- Java - Loop Control
- Java - For Loop
- Java - For-Each Loop
- Java - While Loop
- Java - Do While Loop
- Java - Break Statement
- Java - Continue Statement
Object Oriented Programming
- Java - OOPs Concepts
- Java - Object & Classes
- Java - Class Attributes
- Java - Class Methods
- Java - Methods
- Java - Variables Scope
- Java - Constructors
- Java - Access Modifiers
- Java - Inheritance
- Java - Aggregation
- Java - Polymorphism
- Java - Overriding
- Java - Method Overloading
- Java - Dynamic Binding
- Java - Static Binding
- Java - Instance Initializer Block
- Java - Abstraction
- Java - Encapsulation
- Java - Interfaces
- Java - Packages
- Java - Inner Classes
- Java - Static Class
- Java - Anonymous Class
- Java - Singleton Class
- Java - Wrapper Classes
- Java - Enums
- Java - Enum Constructor
- Java - Enum Strings
Java Built-in Classes
- Java - Number
- Java - Boolean
- Java - Characters
- Java - Arrays
- Java - Multi-Dimensional Arrays
- Java - Final Arrays
- Java - Math Class
Java File Handling
- Java - Files
- Java - Create a File
- Java - Write to File
- Java - Read Files
- Java - Delete Files
- Java - Directories
- Java - I/O Streams
Java Error & Exceptions
- Java - Exceptions
- Java - try-catch Block
- Java - try-with-resources
- Java - Multi-catch Block
- Java - Nested try Block
- Java - Finally Block
- Java - throw Exception
- Java - Exception Propagation
- Java - Built-in Exceptions
- Java - Custom Exception
- Java - Chained Exception
Java Multithreading
- Java - Multithreading
- Java - Thread Life Cycle
- Java - Creating a Thread
- Java - Starting a Thread
- Java - Joining Threads
- Java - Naming Thread
- Java - Thread Scheduler
- Java - Thread Pools
- Java - Main Thread
- Java - Thread Priority
- Java - Daemon Threads
- Java - Thread Group
- Java - Shutdown Hook
Java Synchronization
- Java - Synchronization
- Java - Block Synchronization
- Java - Static Synchronization
- Java - Inter-thread Communication
- Java - Thread Deadlock
- Java - Interrupting a Thread
- Java - Thread Control
- Java - Reentrant Monitor
Java Networking
- Java - Networking
- Java - Socket Programming
- Java - URL Processing
- Java - URL Class
- Java - URLConnection Class
- Java - HttpURLConnection Class
- Java - Socket Class
- Java - Generics
Java Collections
Java Interfaces
- Java - List Interface
- Java - Queue Interface
- Java - Map Interface
- Java - SortedMap Interface
- Java - Set Interface
- Java - SortedSet Interface
Java Data Structures
Java Collections Algorithms
Advanced Java
- Java - Command-Line Arguments
- Java - Lambda Expressions
- Java - Sending Email
- Java - Applet Basics
- Java - Javadoc Comments
- Java - Autoboxing and Unboxing
- Java - File Mismatch Method
- Java - REPL (JShell)
- Java - Multi-Release Jar Files
- Java - Private Interface Methods
- Java - Inner Class Diamond Operator
- Java - Multiresolution Image API
- Java - Collection Factory Methods
- Java - Module System
- Java - Nashorn JavaScript
- Java - Optional Class
- Java - Method References
- Java - Functional Interfaces
- Java - Default Methods
- Java - Base64 Encode Decode
- Java - Switch Expressions
- Java - Teeing Collectors
- Java - Microbenchmark
- Java - Text Blocks
- Java - Dynamic CDS archive
- Java - Z Garbage Collector (ZGC)
- Java - Null Pointer Exception
- Java - Packaging Tools
- Java - Sealed Classes
- Java - Record Classes
- Java - Hidden Classes
- Java - Pattern Matching
- Java - Compact Number Formatting
- Java - Garbage Collection
- Java - JIT Compiler
Java Miscellaneous
- Java - Recursion
- Java - Regular Expressions
- Java - Serialization
- Java - Strings
- Java - Process API Improvements
- Java - Stream API Improvements
- Java - Enhanced @Deprecated Annotation
- Java - CompletableFuture API Improvements
- Java - Marker Interface
- Java - Streams
- Java - Datetime Api
- Java 8 - New Features
- Java 9 - New Features
- Java 10 - New Features
- Java 11 - New Features
- Java 12 - New Features
- Java 13 - New Features
- Java 14 - New Features
- Java 15 - New Features
- Java 16 - New Features
Java APIs & Frameworks
Java Class References
- Java - Scanner
- Java - Arrays
- Java - Strings
- Java - Date
- Java - ArrayList
- Java - Vector
- Java - Stack
- Java - PriorityQueue
- Java - LinkedList
- Java - ArrayDeque
- Java - HashMap
- Java - LinkedHashMap
- Java - WeakHashMap
- Java - EnumMap
- Java - TreeMap
- Java - IdentityHashMap
- Java - HashSet
- Java - EnumSet
- Java - LinkedHashSet
- Java - TreeSet
- Java - BitSet
- Java - Dictionary
- Java - Hashtable
- Java - Properties
- Java - Collection
- Java - Array
Java Useful Resources
Java - break Statement
The Java break statement is used to exit a loop immediately and transfer control to the next statement after the loop. It has two main usages: when encountered inside a loop, it terminates the loop instantly, and in a switch statement, it is used to exit a specific case (covered in the next chapter).
Syntax of break Statement
The syntax of a break is a single statement inside any loop or switch case −
break;
Flow Diagram of break Statement
See the following image to know how break statement works to stop the execution of a loop:
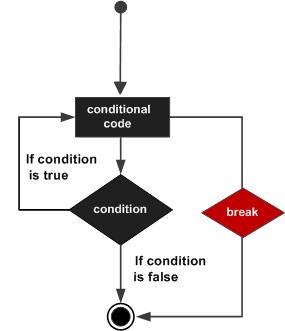
Using break with while Loop
You can use the break statement can be used with the while loop to stop its execution.
Example
In this example, we're showing the use of a break statement to break a while loop to print numbers starting from 10 to 14 which will otherwise print element till 19. Here we've initialized an int variable x with a value of 10. Then in while loop, we're checking x as less than 20 and within while loop, we're printing the value of x and incrementing the value of x by 1. While loop will run until x becomes 15. Once x is 15, break statement will break the while loop and program exits.
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int x = 10;
while( x < 20 ) {
if(x == 15){
break;
}
System.out.print("value of x : " + x );
x++;
System.out.print("\n");
}
}
}
Output
value of x : 10 value of x : 11 value of x : 12 value of x : 13 value of x : 14
Using break with for Loop
You can also use the break statement can be used with the for loop to stop its execution.
Example
In this example, we're showing the use of a break statement within a for loop to print few elements of an array instead of all elements. Here we're creating an array of integers as numbers and initialized it some values. We've created a variable named index to represent index of the array within for loop, check it against size of the array and incremented it by 1. Within for loop body, we're printing element of the array using index notation. Once 30 is encountered as value, break statement breaks the flow of for loop and program quits.
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int [] numbers = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
for(int index = 0; index < numbers.length; index++) {
if(numbers[index] == 30){
break;
}
System.out.print("value of item : " + numbers[index] );
System.out.print("\n");
}
}
}
Output
value of item : 10 value of item : 20
Using break with an Infinite Loop
An infinite loop executes loop statements indefinitely. To stop the execution of an infinite loop, you can use the break statement inside a condition. When the program encounters the specified condition, the break statement terminates the loop.
Example
In this example, we're showing the use of break statement to break an infinite loop using while loop. It will keep printing the numbers until the value of x becomes 15.
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int x = 10;
while( true ) {
System.out.print("value of x : " + x );
x++;
if(x == 15) {
break;
}
System.out.print("\n");
}
}
}
Output
value of item : 10 value of item : 11 value of item : 12 value of item : 13 value of item : 14
Using break with switch Statement
The break statement is used in a switch statement to exit a case once it has been executed. Without the break statement, execution continues to the next case until a break is encountered or the switch block ends.
Example
In this example, we demonstrate the use of the break statement inside a switch statement. The program prints the corresponding day name based on the given day number.
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int day = 3;
switch (day) {
case 1:
System.out.println("Monday");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("Tuesday");
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("Wednesday");
break;
case 4:
System.out.println("Thursday");
break;
case 5:
System.out.println("Friday");
break;
case 6:
System.out.println("Saturday");
break;
case 7:
System.out.println("Sunday");
break;
default:
System.out.println("Invalid day");
}
}
}
Output
When the above code is compiled and executed, it produces the following result −
Wednesday