
- Java - Home
- Java - Overview
- Java - History
- Java - Features
- Java Vs. C++
- JVM - Java Virtual Machine
- Java - JDK vs JRE vs JVM
- Java - Environment Setup
- Java - Hello World Program
- Java - Comments
- Java - Basic Syntax
- Java - Variables
- Java - Data Types
- Java - Type Casting
- Java - Unicode System
- Java - User Input
- Java - Date & Time
Java Operators
- Java - Operators
- Java - Arithmetic Operators
- Java - Assignment Operators
- Java - Relational Operators
- Java - Logical Operators
- Java - Bitwise Operators
- Java Operator Precedence & Associativity
- Java - Unary Operators
Java Control Statements
- Java - Decision Making
- Java - If Else Statement
- Java - Switch Statement
- Java - Loop Control
- Java - For Loop
- Java - For-Each Loop
- Java - While Loop
- Java - Do While Loop
- Java - Break Statement
- Java - Continue Statement
Object Oriented Programming
- Java - OOPs Concepts
- Java - Object & Classes
- Java - Class Attributes
- Java - Class Methods
- Java - Methods
- Java - Variables Scope
- Java - Constructors
- Java - Access Modifiers
- Java - Inheritance
- Java - Aggregation
- Java - Polymorphism
- Java - Overriding
- Java - Method Overloading
- Java - Dynamic Binding
- Java - Static Binding
- Java - Instance Initializer Block
- Java - Abstraction
- Java - Encapsulation
- Java - Interfaces
- Java - Packages
- Java - Inner Classes
- Java - Static Class
- Java - Anonymous Class
- Java - Singleton Class
- Java - Wrapper Classes
- Java - Enums
- Java - Enum Constructor
- Java - Enum Strings
Java Built-in Classes
- Java - Number
- Java - Boolean
- Java - Characters
- Java - Arrays
- Java - Multi-Dimensional Arrays
- Java - Final Arrays
- Java - Math Class
Java File Handling
- Java - Files
- Java - Create a File
- Java - Write to File
- Java - Read Files
- Java - Delete Files
- Java - Directories
- Java - I/O Streams
Java Error & Exceptions
- Java - Exceptions
- Java - try-catch Block
- Java - try-with-resources
- Java - Multi-catch Block
- Java - Nested try Block
- Java - Finally Block
- Java - throw Exception
- Java - Exception Propagation
- Java - Built-in Exceptions
- Java - Custom Exception
- Java - Chained Exception
Java Multithreading
- Java - Multithreading
- Java - Thread Life Cycle
- Java - Creating a Thread
- Java - Starting a Thread
- Java - Joining Threads
- Java - Naming Thread
- Java - Thread Scheduler
- Java - Thread Pools
- Java - Main Thread
- Java - Thread Priority
- Java - Daemon Threads
- Java - Thread Group
- Java - Shutdown Hook
Java Synchronization
- Java - Synchronization
- Java - Block Synchronization
- Java - Static Synchronization
- Java - Inter-thread Communication
- Java - Thread Deadlock
- Java - Interrupting a Thread
- Java - Thread Control
- Java - Reentrant Monitor
Java Networking
- Java - Networking
- Java - Socket Programming
- Java - URL Processing
- Java - URL Class
- Java - URLConnection Class
- Java - HttpURLConnection Class
- Java - Socket Class
- Java - Generics
Java Collections
Java Interfaces
- Java - List Interface
- Java - Queue Interface
- Java - Map Interface
- Java - SortedMap Interface
- Java - Set Interface
- Java - SortedSet Interface
Java Data Structures
Java Collections Algorithms
Advanced Java
- Java - Command-Line Arguments
- Java - Lambda Expressions
- Java - Sending Email
- Java - Applet Basics
- Java - Javadoc Comments
- Java - Autoboxing and Unboxing
- Java - File Mismatch Method
- Java - REPL (JShell)
- Java - Multi-Release Jar Files
- Java - Private Interface Methods
- Java - Inner Class Diamond Operator
- Java - Multiresolution Image API
- Java - Collection Factory Methods
- Java - Module System
- Java - Nashorn JavaScript
- Java - Optional Class
- Java - Method References
- Java - Functional Interfaces
- Java - Default Methods
- Java - Base64 Encode Decode
- Java - Switch Expressions
- Java - Teeing Collectors
- Java - Microbenchmark
- Java - Text Blocks
- Java - Dynamic CDS archive
- Java - Z Garbage Collector (ZGC)
- Java - Null Pointer Exception
- Java - Packaging Tools
- Java - Sealed Classes
- Java - Record Classes
- Java - Hidden Classes
- Java - Pattern Matching
- Java - Compact Number Formatting
- Java - Garbage Collection
- Java - JIT Compiler
Java Miscellaneous
- Java - Recursion
- Java - Regular Expressions
- Java - Serialization
- Java - Strings
- Java - Process API Improvements
- Java - Stream API Improvements
- Java - Enhanced @Deprecated Annotation
- Java - CompletableFuture API Improvements
- Java - Marker Interface
- Java - Streams
- Java - Datetime Api
- Java 8 - New Features
- Java 9 - New Features
- Java 10 - New Features
- Java 11 - New Features
- Java 12 - New Features
- Java 13 - New Features
- Java 14 - New Features
- Java 15 - New Features
- Java 16 - New Features
Java APIs & Frameworks
Java Class References
- Java - Scanner
- Java - Arrays
- Java - Strings
- Java - Date
- Java - ArrayList
- Java - Vector
- Java - Stack
- Java - PriorityQueue
- Java - LinkedList
- Java - ArrayDeque
- Java - HashMap
- Java - LinkedHashMap
- Java - WeakHashMap
- Java - EnumMap
- Java - TreeMap
- Java - IdentityHashMap
- Java - HashSet
- Java - EnumSet
- Java - LinkedHashSet
- Java - TreeSet
- Java - BitSet
- Java - Dictionary
- Java - Hashtable
- Java - Properties
- Java - Collection
- Java - Array
Java Useful Resources
Java - extends Keyword
Java extends is the keyword used to inherit the properties of a class. Following is the syntax of extends keyword.
Syntax
class Super {
.....
.....
}
class Sub extends Super {
.....
.....
}
Sample Code
Following is an example demonstrating Java inheritance. In this example, you can observe two classes namely Calculation and My_Calculation.
Using extends keyword, the My_Calculation inherits the methods addition() and Subtraction() of Calculation class.
Copy and paste the following program in a file with name My_Calculation.java
Example
class Calculation {
int z;
public void addition(int x, int y) {
z = x + y;
System.out.println("The sum of the given numbers:"+z);
}
public void Subtraction(int x, int y) {
z = x - y;
System.out.println("The difference between the given numbers:"+z);
}
}
public class My_Calculation extends Calculation {
public void multiplication(int x, int y) {
z = x * y;
System.out.println("The product of the given numbers:"+z);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
int a = 20, b = 10;
My_Calculation demo = new My_Calculation();
demo.addition(a, b);
demo.Subtraction(a, b);
demo.multiplication(a, b);
}
}
Output
Compile and execute the above code as shown below.
javac My_Calculation.java java My_Calculation
After executing the program, it will produce the following result −
The sum of the given numbers:30 The difference between the given numbers:10 The product of the given numbers:200
In the given program, when an object to My_Calculation class is created, a copy of the contents of the superclass is made within it. That is why, using the object of the subclass you can access the members of a superclass.
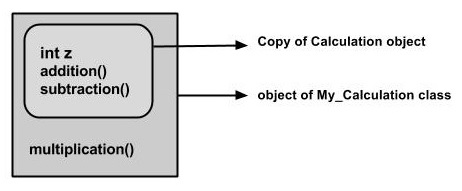
The Superclass reference variable can hold the subclass object, but using that variable you can access only the members of the superclass, so to access the members of both classes it is recommended to always create reference variable to the subclass.
If you consider the above program, you can instantiate the class as given below. But using the superclass reference variable ( cal in this case) you cannot call the method multiplication(), which belongs to the subclass My_Calculation.
Calculation demo = new My_Calculation(); demo.addition(a, b); demo.Subtraction(a, b);
Following is the example showcasing the same concept.
Example
class Calculation {
int z;
public void addition(int x, int y) {
z = x + y;
System.out.println("The sum of the given numbers:"+z);
}
public void Subtraction(int x, int y) {
z = x - y;
System.out.println("The difference between the given numbers:"+z);
}
}
public class My_Calculation extends Calculation {
public void multiplication(int x, int y) {
z = x * y;
System.out.println("The product of the given numbers:"+z);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
int a = 20, b = 10;
Calculation demo = new My_Calculation();
demo.addition(a, b);
demo.Subtraction(a, b);
}
}
Output
Compile and execute the above code as shown below.
javac My_Calculation.java java My_Calculation
After executing the program, it will produce the following result −
The sum of the given numbers:30 The difference between the given numbers:10
Note − A subclass inherits all the members (fields, methods, and nested classes) from its superclass. Constructors are not members, so they are not inherited by subclasses, but the constructor of the superclass can be invoked from the subclass.