C - Hello World
Every learner aspiring to become a professional software developer starts with writing a Hello World program in the programming language he/she is learning. In this chapter, we shall learn how to write a Hello World program in C language.
Hello World in C Language
Before writing the Hello World program, make sure that you have the C programming environment set up in your computer. This includes the GCC compiler, a text editor, and preferably an IDE for C programming such as CodeBlocks.
Example
The first step is to write the source code for the Hello World program. Open a text editor on your computer. On Windows, open Notepad or Notepad++, enter the following code and save it as "hello.c".
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
/* my first program in C */
printf("Hello World! \n");
return 0;
}
Output
Run the code and check its output −
Hello World!
The Step-by-Step Execution of a C Program
Let us understand how the above program works in a step-by-step manner.
Step 1
The first statement in the above code is the #include statement that imports the stdio.h file in the current C program. This is called a preprocessor directive. This header file contains the definitions of several library functions used for stand IO operations. Since we shall be calling the printf() function which is defined in the stdio.h library, we need to include it in the first step.
Step 2
Every C program must contain a main() function. The main() function in this program prints the "Hello World" message on the console terminal.
Inside the main() function, we have inserted a comment statement that is ultimately ignored by the compiler; it is for the documentation purpose.
The next statement calls the printf() function. In C, every statement must terminate with a semicolon symbol (;), failing which the compiler reports an error.
The printf() function, imported from the stdio.h library file, echoes the Hello World string to the standard output stream. In case of Windows, the standard output stream is the Command prompt terminal and in case of Linux it is the Linux terminal.
In C, every function needs to have a return value. If the function doesnt return anything, its value is void. In the example above, the main() function has int as its return value. Since the main() function doesnt need to return anything, it is defined to return an integer "0". The "return 0" statement also indicates that the program has been successfully compiled and run.
Step 3
Next, we need to compile and build the executable from the source code ("hello.c").
If you are using Windows, open the command prompt in the folder in which "hello.c" has been saved. The following command compiles the source code −
gcc -c hello.c -o hello.o
The -c option specifies the source code file to be compiled. This will result in an object file with the name hello.o if the C program doesnt have any errors. If it contains errors, they will be displayed. For example, if we forget to put the semicolon at the end of the printf() statement, the compilation result will show the following error −
helloworld.c: In function 'main':
helloworld.c:6:30: error: expected ';' before 'return'
printf("Hello, World! \n")
^
;
helloworld.c:8:4:
return 0;
To build an executable from the compiled object file, use the following command −
gcc -o hello.exe hello.o
The hello.exe is now ready to be run from the command prompt that displays the Hello World message in the terminal.
C:\Users\user>hello Hello World!
On Ubuntu Linux, the object file is first given executable permission before running it by prefixing "./" to it.
$ chmod a+x a.o $ ./a.o
You can also use an IDE such as CodeBlocks to enter the code, edit, debug and run the Hello World program more conveniently.
Using CodeBlocks IDE for C Programming
CodeBlocks is one the most popular IDEs for C/C++ development. Install it if you have not already done and open it. Create a new file from the File menu, enter the following code and save it as "hello.c".
Example
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
/* my first program in C */
printf("Hello World! \n");
return 0;
}
Output
Run the code and check its output −
Hello World!
Choose Build and Run option from the Build menu as shown below −
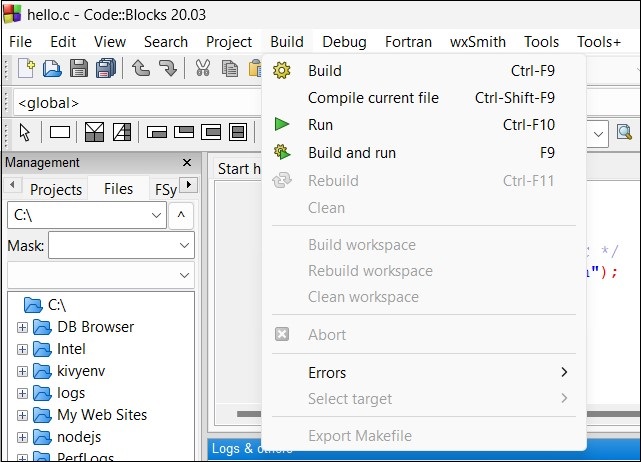
You can also use the F9 shortcut for the same. If the program is error-free, the Build Log tab shows the following messages −
gcc.exe -c C:\Users\mlath\hello.c -o C:\Users\mlath\hello.o gcc.exe -o C:\Users\mlath\hello.exe C:\Users\mlath\hello.o Process terminated with status 0 (0 minute(s), 0 second(s)) 0 error(s), 0 warning(s) (0 minute(s), 0 second(s)) Checking for existence: C:\Users\mlath \hello.exe Executing: '"C:\Program Files\CodeBlocks/cb_console_runner.exe" "C:\Users\mlath\hello.exe"' (in 'C:\Users\mlath\Documents')
In a separate command prompt window, the output will be displayed −
Hello World! Process returned 0 (0x0) execution time : 0.236 s Press any key to continue.
If the code contains errors, the build log tab echoes them. For instance, if we miss the trailing semicolon in the printf() statement, the log will be as below −
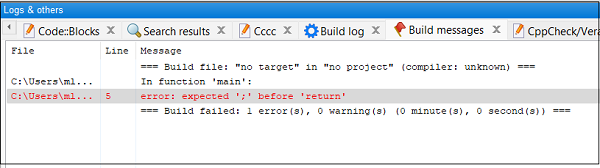
You can use any other IDE to run the C program. You will need to follow the documentation of the respective IDE for the purpose.
Running the Hello World successfully also confirms that the C programming environment is working properly on your computer.
