
- Smart Grid - Home
- Smart Grid Introduction
- What is an Electric Grid?
- Electric Grid Evolution
- What is a Smart Grid?
- Smart Grid - Functions
- Smart Grid - Characteristics
- Smart Grid - Advantages
- Smart Grid - Components
- Smart Grid - Challenges
- Smart Grid Technologies
- Smart Energy Resources
- Power System Automation
- Smart Substations
- Substation Automation
- Smart Grid - Feeder Automation
- Energy Management System
- Smart Grid - FACTS
- HVDC Transmission
- Wide Area Monitoring
- SCADA in Smart Grid
- Smart Grid - DMS
- Smart Grid - OMS
- Volt/VAR Control
- Smart Grid - FMSR
- Smart Grid - HEDT
- Phase Shifting Transformers
- Smart Grid - PHEV
- Advanced Metering Infrastructure
- Smart Meters - Introduction
- Smart Meters - AMI
- Smart Meters - AMIS
- Communication Architecture
- Drivers & Benefits
- Phasor Measurement Unit
- Intelligent Electronic Devices
- Power Quality Management
- Power Quality in Smart Grid
- Power Quality Issues
- Power Quality Monitoring Techniques
- Power Quality Conditioners
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)
- Power Quality Audit
- Smart Grid Communication
- Smart Grid Communication
- Communication Network
- Communication Technologies
- Broadband Over Power Line
- Internet Protocols
- Web Services in Smart Grid
- Cloud Computing
- Multi Agent System Technology
- IP Based Protocols
- Cyber Security
What is an Electric Grid?
An electric grid, also referred to as power grid, is nothing but an arrangement of various components like generating stations, transformers, and substations that is used for transporting electricity from one place to another, from its generation to final utilization.
Read this chapter to get a good understanding of Electric Grid and how they operate.
What is an Electric Grid?
An Electric grid is a large electrical network having interconnected components for generation and distribution of electricity across a wide area.
An electric grid includes the three main parties namely, utility companies, electricity suppliers, and end consumers. An electric grid consists of a complete infrastructure to produce electricity and deliver it to the consumers.
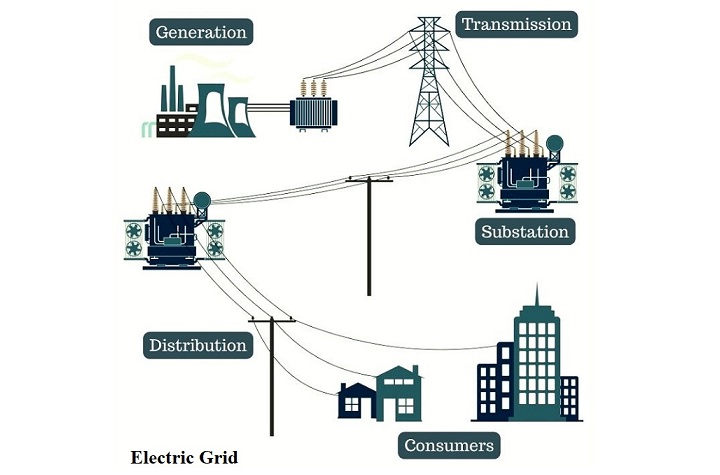
An electric grid does the following four things −
- It ensures the best utilization of energy resources.
- It provides higher power supply capacity.
- It makes the operation of whole power system economical.
- It improves the reliability of the power system.
Functions of Electric Grid
The following are some key functions of an electric grid −
Power Generation
It is the very first stage in an electric grid where the electricity is generated. Power generation involves the conversion of energy of coal, natural gas, nuclear substance, stored water, etc. into electrical energy. These days, power generation is also done by some renewable resources like solar, wind, geothermal, biomass, etc.
Transmission
It is the second stage in a power supply system. Transmission of electricity is the process of increasing the voltage level of generated electricity to a very high value and transport it to grid substations for further distribution.
Distribution
It is defined as the process of delivering electricity from substations to houses, commercial buildings, industries, etc. for utilization. It is done at relatively lower voltage level than generation and transmission.
Monitoring and Control
It is another important function of an electric grid. The flow of electricity through the networks is continuously monitored and regulated or controlled to ensure the balance between supply and demand.
Needs of Electric Grid
An electric grid is required for the following purposes −
- Improved Reliability − An electric grid provides a stable and uninterrupted supply of electricity to the end consumers. This improves the overall reliability of the power system.
- Improved Efficiency − Electric grid is also responsible for reducing the energy losses during generation, transmission, and distribution of electricity. This results in improved efficiency of the system.
- Enhanced Safety − Electric grid also ensures that electricity is safely delivered to the end consumers with a minimum risk of harms to people and infrastructure.
- Scalability − The demand of electricity is increasing day by day. Therefore, scalability of power system is another important need that electric grid must fulfill.
- Flexibility − Electric grid also plays an important role in integration of different types of power pants and loads. Hence, it must be flexible to provide this functionality.
Working of Electric Grid
An electric grid is a complex structure of several components which performs the following three major functions −
- Power Generation
- Power Transmission
- Power Distribution
Power generation is done by an arrangement of equipment called power plant. Power transmission is done to carry this power from power plants to substations. At the end, the power distribution is done from substations to end consumers like residential building, commercial buildings, and industrial settings.
The generation of electricity is accomplished by utility companies. The transmission and distribution of power is done by entities called grid operators which are basically regional entities.
The utility companies and grid operators continuously monitor the electric grid and maintain their balanced operation.
Types of Electric Grids
Depending on the functionality and technological features, the electric grids can be classified into the following two main types −
- Conventional/Traditional Grid
- Smart Grid
These two types of electric grids are explained below with their advantages and limitations.
Conventional Grid
It is also known as traditional or existing electric grid. The conventional electric grid is a type of an electric grid that uses a traditional power supply system for delivering electricity from power plants to the end consumers.
The conventional electric grid utilizes old technologies and manual operating systems. These electric grids are considered relatively less reliable due to limited monitoring and non-availability of real-time data. These are also ineffective to meet the increasing demand of electricity.
However, conventional electric grids have advantages such as less expensive, existing and mature technology, having a large number of active consumers, etc.
On the other hand, there are several down sides of the conventional grids which are listed below −
- Limited monitoring and control on the power supply
- Less reliable and efficient
- Higher energy losses during generation, transmission, and distribution
- Ineffective in handling peak load demand and increasing future demand of electricity
- Difficult to integrate with renewable energy resources
- More susceptible to power outages and security threats, etc.
Smart Grid
A smart grid, also termed as modern electric grid or digital electric grid, is an improved version of the traditional electric grid.
It is an integrated system of traditional electric grid and modern digital communication and control technologies.
Smart grid is an efficient, reliable and flexible electric grid used for generation, transmission, and distribution of electricity at lower cost and reduced energy losses.
Today, smart grid is becoming popular because of its following key advantages −
- Smart and remote metering technologies
- Remote monitoring of the system
- Two-way communication of information
- Real-time data availability of energy consumption
- Automated operation and control of the power system
- Easy and simple integration with renewable energy resources
- Able to meet the increasing demand of electricity, etc.
However, smart grid is relatively more expensive to implement as compared to conventional grid. But its overtime operational cost is lower than the conventional grid.
Components of Electric Grid
An electric grid consists of several important components. Some of the main components of an electric grid and their functions are given below −
- Power Plants − For generating electricity by using energy of different resources like fossil fuels, nuclear substances, water, solar energy, wind energy, geothermal energy, biomass, etc.
- Transmission Lines − For carrying electricity from power plants to substations over long distances. These can be overhead lines or underground cables.
- Transformers − For increasing or decreasing the voltage levels of electricity. These can be either step-up transformer or step-down transformer.
- Substations − For receiving electricity at high voltages and decrease the voltage for further distribution. Substations also performs switching and protection of the power system.
- Distribution Lines − Used for carrying electricity from substations to end consumers likes buildings and industries. These can also be overhead lines or underground cables.
An electric grid is a highly complex infrastructure for delivering electricity from power plants to consumers. In this chapter, we covered the basics of electric grid. In the next chapter, we will explain how electric grids evolved over time.