
- Smart Grid - Home
- Smart Grid Introduction
- What is an Electric Grid?
- Electric Grid Evolution
- What is a Smart Grid?
- Smart Grid - Functions
- Smart Grid - Characteristics
- Smart Grid - Advantages
- Smart Grid - Components
- Smart Grid - Challenges
- Smart Grid Technologies
- Smart Energy Resources
- Power System Automation
- Smart Substations
- Substation Automation
- Smart Grid - Feeder Automation
- Energy Management System
- Smart Grid - FACTS
- HVDC Transmission
- Wide Area Monitoring
- SCADA in Smart Grid
- Smart Grid - DMS
- Smart Grid - OMS
- Volt/VAR Control
- Smart Grid - FMSR
- Smart Grid - HEDT
- Phase Shifting Transformers
- Smart Grid - PHEV
- Advanced Metering Infrastructure
- Smart Meters - Introduction
- Smart Meters - AMI
- Smart Meters - AMIS
- Communication Architecture
- Drivers & Benefits
- Phasor Measurement Unit
- Intelligent Electronic Devices
- Power Quality Management
- Power Quality in Smart Grid
- Power Quality Issues
- Power Quality Monitoring Techniques
- Power Quality Conditioners
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)
- Power Quality Audit
- Smart Grid Communication
- Smart Grid Communication
- Communication Network
- Communication Technologies
- Broadband Over Power Line
- Internet Protocols
- Web Services in Smart Grid
- Cloud Computing
- Multi Agent System Technology
- IP Based Protocols
- Cyber Security
What is a Smart Grid?
A smart grid is nothing but a version of electric grid that combines an electric power supply system with digital communication and automation systems. It is developed to improve the reliability and efficiency of the existing electric grid.
Smart grids enable both companies and consumers to know the power consumption patterns to schedule their operations accordingly. In this chapter, we will discuss the definition, structure, components, and working of a smart grid. So, let start with the basic definition of smart grid.
Defining a Smart Grid
Smart grid is a new term in the field of electric engineering. It represents a power supply system that combines the energy delivery system with the modern digital communication technologies. Thus, a smart grid can be defined as a modern version of existing electrical system.
Smart grids are introduced as an integrated and interactive power supply network. In other words, we can say that
Smart Grid = Electric Grid + Information Technology
In a smart grid, the top-down one way power supply system is replaced by a decentralized power system. In which the total power generation capacity is decentralized and spread evenly around all parts of the electric grid. The power is not only generated by power plants, but it is produced by renewable end-user energy sources like solar power and can be fed back to the electric grid.
A smart grid is nothing but a digitally enabled electric grid that receives and distributes electricity, and also works on data and information related to the grid operation to determine the behavior of consumers to improve the efficiency, reliability, and sustainability of the power supply system.
Smart grids are equipped with two-way digital communication and computer processing system that enables the utility companies to manage their power supply system efficiently. It is also capable in providing data in real time and allows for quick balancing of supply and demand.
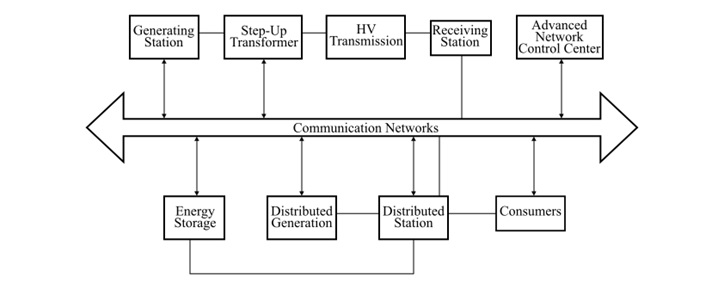
Components of a Smart Grid
A typical smart grid combines an ordinary electric grid with two-way digital communication technologies. For this, the following components are crucial −
Smart Meters
These are the devices used for recording energy utilization in real time. These meters are also capable in sending this information back to the utility company.
Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI)
It is the principal component of a smart grid that integrates smart meters, digital communication networks, and data management and processing systems.
Smart Sensors
These are the devices used for continuous monitoring of the operation of the electric grid to detect any kind of malfunctioning or faults. Smart sensors are installed at different locations across the grid.
Phase Measurement Units (PMUs)
These are the smart grid devices used for real-time monitoring of electricity waves travelling through the power network. These devices play a crucial role in improving the grid stability.
Distributed Energy Resources
These are the source of energy utilized for producing electricity from different locations. These resources include renewable energy sources like solar, wind, geothermal, biomass, etc. They are integrated with the main electric grid.
Energy Storage Systems
This is a new concept in smart grid technology. In smart grid, batteries and other energy storage systems are used to store electricity during low demand period and supply during high demand period to balance the supply and demand in the system.
Demand Response
It an automated system integrated into the electrical grid. The function of this system is to regulate the consumers power consumption depending on the supply conditions.
In addition to the traditional grids generating facilities and transmission network, a smart grid consists of three new components −
- Smart control and measuring devices
- Digital communication systems
- Computer software programs
The smart devices include computer controlled generators and other power sources as well as meters, monitors and intelligent electronic devices that gather information about the demand for power, its availability from various sources, the delivery capacity of each part of the grid and the flow of power throughout the system.
The computer software programs for the grid help to determine electricity efficiency and monitor the electrical functions of generators and consumers.
The digital communication and control is what makes the grid smart. Sensors that monitor and report conditions on the grid enable switches and other controls to respond instantly. Real time information permits system operators to predict, diagnose and reduce issues that have caused interruptions or serious power disturbances. With smart grid technologies end users have more control over their energy consumption and cost.
Role of Smart Grid
The smart grid is one of the most important and reliable concepts that can successfully implement the following −
- Optimized and efficient transmission of electricity with minimal losses.
- Fast restoration of electricity after fault and reduced down time.
- Reduced operational cost and hence the cost of electricity to consumers.
- Reduction in peak demand.
- Integration of renewable energy resources into the electric grid.
Why Do We Need a Smart Grid?
A smart grid empowers the electric grid by integrating it with two-way digital communication technologies. The primary objective of smart grid is to manage the energy system by monitoring its important data.
This data plays a vital role in meeting the overall electricity demand at all times. It provides a continuous communication between supplier and consumers to regulate the power generation to match the demand.
The continuous monitoring system of the smart grid helps in balancing the supply with demand.
How Does a Smart Grid Work ?
A smart grid works in the same way as an existing electric grid. The only difference is that smart grid provides real-time monitoring, controlling, and processing of grid data using computerized systems. It consists of several different segments for accomplishing different functions.
The operation of these segments of the smart grid is explained here −
Electricity Generation, Transmission, and Distribution
Smart grid consists of an electric power grid for generation, transmission, and distribution of electricity from the power plant to the end-consumers. This is similar to the existing electric power grid.
Data Collection
Smart grid consists of numerous types of smart sensors and meters installed across the grid. These devices monitor the electricity flow and grid conditions in real-time and transmit the data through communication network to the utility companys database management system. This data plays a vital role in improving the overall supply system.
Automated Response and Control System
Smart grid is equipped with an automated response and control mechanism to make decisions by using the grid data. For example, if a fault occurs in the system, the automated control system isolates the faulty part from rest of the network and supply the power through a new route to reduce the outages.
Renewable Energy Resources Integration
Smart grid works on the concept of decentralized power generation. These decentralized power plants are nothing but renewable energy resources which are integrated into the electric grid to ensure the constant power supply.
Consumer Intervention and Feedback
Smart grid provides a communication channel to involve consumers in the power system operation. This feature of the smart grid allows consumers to submit their feedback to improve the reliability and operation of the grid.
Smart Grid Characteristics
A Smart Grid would have the following fundamental characteristics −
Optimized Operation of the System
A smart grid allows consumers to play a part in optimizing the operation of the system and provides consumers with greater information and choice of supply.
Enables Demand Response and Demand-Side Management
A smart grid enables demand response and demand-side management through the integration of smart meters, smart appliances and consumer loads, micro-generation and electricity storage and by providing consumers with information related energy use and price.
Reduces the Environmental Impacts
Smart grids facilitate the connection and operation of generators of all sizes and technologies and accommodates intermittent generation and storage options. It accommodates and facilitates all renewable energy sources, distributed generation, residential micro-generation and storage options, thus significantly reducing the environmental impact of the whole electricity supply system. It also provide simplified interconnection just like plug-and-play.
Optimized and Efficient use of Assets
Smart grids optimize and efficiently operate assets by intelligent operation of the delivery system and pursuing efficient asset management. This includes utilizing assets depending on what is needed and when it is needed.
Improves Reliability and Security of Supply
Smart grids operate resiliently in disasters, physical or cyber-attacks and delivers enhanced levels of reliability and security of supplying energy. It assures and improves reliability and security of supply by anticipating and responding in a self-healing manner and strengthening the security of supply through enhanced transfer capabilities.
Advantages of Smart Grid
Listed below are some of the key advantages of a smart grid −
- Smart grids improve the reliability and efficiency of the electric power system.
- Smart grids integrate renewable energy resources into the grid for decentralized power generation and obtain continuous power supply.
- Smart grids provide tools and technologies to balance the supply and demand.
- Smart grids reduce the operational costs by automating the operations.
- Smart grids create a secure power infrastructure.
- Smart grids engage the consumers that is helpful in minimizing the energy wastage and cost.
- Smart grids create a sustainable energy system by integrating renewable energy sources.
Disadvantages of Smart Grid
Smart grids also have certain major disadvantages which are given below −
- Smart grids require a high upfront cost to implement the infrastructure.
- Smart grids are sensitive to cyber-attacks due to digitalization.
- Smart grids are relatively a complex power supply system in terms of technicality.
- Smart grids face difficulty in terms of public acceptance due to high initial cost and lack of awareness.
Difference between Smart Grid and Traditional Electric Grid
The following table highlights how a smart grid differs from a traditional electric grid −
| Key | Traditional Electric Grid | Smart Grid |
|---|---|---|
| Types of devices | Electromechanical type devices | Digital and microprocessor-based devices |
| Data communication | One-way communication | Two-way communication |
| Power generation | Centralized power generation | Decentralized power generation |
| Sensors | A few sensors (analog) are used | Digital sensors are installed throughout the system |
| Monitoring & restoration | Manual monitoring and restoration be provided | Automated monitoring and restoration be provided |
| Consumer involvement | No consumer involvement | Active involvement of consumer in grid operation |
| Protection system | Less efficient and slow protection system | Highly efficient, fast, and automated protection system |
| Effect on environment | Severe effects of grid operation on the environment | Relatively reduced effects on the environment. |
| Integration of renewable resources | Difficult to integrate renewable energy resources | Easy integration of renewable energy resources |
Conclusion
A smart grid is nothing but a power supply system that combines the existing electric grid with modern two-way digital communication system.
Smart grids have numerous advantages over the existing electric grid, but it is still facing several challenges in gaining public acceptance due to its high capital cost and lack of awareness.