- Python - Home
- Python - Overview
- Python - History
- Python - Features
- Python vs C++
- Python - Hello World Program
- Python - Application Areas
- Python - Interpreter
- Python - Environment Setup
- Python - Virtual Environment
- Python - Basic Syntax
- Python - Variables
- Python - Private Variables
- Python - Data Types
- Python - Type Casting
- Python - Unicode System
- Python - Literals
- Python - Operators
- Python - Arithmetic Operators
- Python - Comparison Operators
- Python - Assignment Operators
- Python - Logical Operators
- Python - Bitwise Operators
- Python - Membership Operators
- Python - Identity Operators
- Python - Walrus Operator
- Python - Operator Precedence
- Python - Comments
- Python - User Input
- Python - Numbers
- Python - Booleans
- Python - Floating Points
- Python - Control Flow
- Python - Decision Making
- Python - If Statement
- Python - If else
- Python - Nested If
- Python - Conditional User Inputs
- Python - Match-Case Statement
- Python - Loops
- Python - for Loops
- Python - for-else Loops
- Python - While Loops
- Python - break Statement
- Python - continue Statement
- Python - pass Statement
- Python - Nested Loops
- Python Functions & Modules
- Python - Functions
- Python - Default Arguments
- Python - Keyword Arguments
- Python - Keyword-Only Arguments
- Python - Positional Arguments
- Python - Positional-Only Arguments
- Python - Arbitrary Arguments
- Python - Variables Scope
- Python - Function Annotations
- Python - Modules
- Python - Packing and Unpacking
- Python - Built in Functions
- Python Strings
- Python - Strings
- Python - Slicing Strings
- Python - Modify Strings
- Python - String Concatenation
- Python - String Formatting
- Python - Escape Characters
- Python - String Methods
- Python - String Exercises
- Python Lists
- Python - Lists
- Python - Access List Items
- Python - Change List Items
- Python - Add List Items
- Python - Remove List Items
- Python - Loop Lists
- Python - List Comprehension
- Python - Sort Lists
- Python - Copy Lists
- Python - Join Lists
- Python - List Methods
- Python - List Exercises
- Python Tuples
- Python - Tuples
- Python - Access Tuple Items
- Python - Update Tuples
- Python - Unpack Tuples
- Python - Loop Tuples
- Python - Join Tuples
- Python - Tuple Methods
- Python - Namedtuple
- Python - Tuple Exercises
- Python Sets
- Python - Sets
- Python - Access Set Items
- Python - Add Set Items
- Python - Remove Set Items
- Python - Loop Sets
- Python - Join Sets
- Python - Copy Sets
- Python - Set Operators
- Python - Set Methods
- Python - Set Exercises
- Python Dictionaries
- Python - Dictionaries
- Python - Access Dictionary Items
- Python - Change Dictionary Items
- Python - Add Dictionary Items
- Python - Remove Dictionary Items
- Python - Dictionary View Objects
- Python - Loop Dictionaries
- Python - Copy Dictionaries
- Python - Nested Dictionaries
- Python - Dictionary Methods
- Python - Dictionary Exercises
- Python Arrays
- Python - Arrays
- Python - Access Array Items
- Python - Add Array Items
- Python - Remove Array Items
- Python - Loop Arrays
- Python - Copy Arrays
- Python - Reverse Arrays
- Python - Sort Arrays
- Python - Join Arrays
- Python - Array Methods
- Python - Array Exercises
- Python File Handling
- Python - File Handling
- Python - Write to File
- Python - Read Files
- Python - Renaming and Deleting Files
- Python - Directories
- Python - File Methods
- Python - OS File/Directory Methods
- Python - OS Path Methods
- Object Oriented Programming
- Python - OOPs Concepts
- Python - Classes & Objects
- Python - Class Attributes
- Python - Class Methods
- Python - Static Methods
- Python - Constructors
- Python - Access Modifiers
- Python - Inheritance
- Python - Multiple Inheritance
- Python - Multilevel Inheritance
- Python - Polymorphism
- Python - Method Overriding
- Python - Method Overloading
- Python - Dynamic Binding
- Python - Dynamic Typing
- Python - Abstraction
- Python - Encapsulation
- Python - Interfaces
- Python - Packages
- Python - Inner Classes
- Python - Anonymous Class and Objects
- Python - Singleton Class
- Python - Wrapper Classes
- Python - Enums
- Python - Reflection
- Python - Data Classes
- Python Errors & Exceptions
- Python - Syntax Errors
- Python - Exceptions
- Python - try-except Block
- Python - try-finally Block
- Python - Raising Exceptions
- Python - Exception Chaining
- Python - Nested try Block
- Python - User-defined Exception
- Python - Logging
- Python - Assertions
- Python - Warnings
- Python - Built-in Exceptions
- Python - Debugger (PDB)
- Python Multithreading
- Python - Multithreading
- Python - Thread Life Cycle
- Python - Creating a Thread
- Python - Starting a Thread
- Python - Joining Threads
- Python - Naming Thread
- Python - Thread Scheduling
- Python - Thread Pools
- Python - Main Thread
- Python - Thread Priority
- Python - Daemon Threads
- Python - Synchronizing Threads
- Python Synchronization
- Python - Inter-thread Communication
- Python - Thread Deadlock
- Python - Interrupting a Thread
- Python Networking
- Python - Networking
- Python - Socket Programming
- Python - URL Processing
- Python - Generics
- Python Libraries
- NumPy Tutorial
- Pandas Tutorial
- SciPy Tutorial
- Matplotlib Tutorial
- Django Tutorial
- OpenCV Tutorial
- Python Miscellenous
- Python - Date & Time
- Python - Maths
- Python - Iterators
- Python - Generators
- Python - Generator Expressions
- Python - Lambda Expressions
- Python - Closures
- Python - Decorators
- Python - Recursion
- Python - Reg Expressions
- Python - PIP
- Python - Database Access
- Python - Weak References
- Python - Serialization
- Python - Templating
- Python - Output Formatting
- Python - Performance Measurement
- Python - Data Compression
- Python - CGI Programming
- Python - XML Processing
- Python - GUI Programming
- Python - Command-Line Arguments
- Python - Docstrings
- Python - JSON
- Python - Sending Email
- Python - Further Extensions
- Python - Tools/Utilities
- Python - Odds and Ends
- Python - GUIs
- Python Advanced Concepts
- Python - Abstract Base Classes
- Python - Custom Exceptions
- Python - Higher Order Functions
- Python - Object Internals
- Python - Memory Management
- Python - Metaclasses
- Python - Metaprogramming with Metaclasses
- Python - Mocking and Stubbing
- Python - Monkey Patching
- Python - Signal Handling
- Python - Type Hints
- Python - Automation Tutorial
- Python - Humanize Package
- Python - Context Managers
- Python - Coroutines
- Python - Descriptors
- Python - Diagnosing and Fixing Memory Leaks
- Python - Immutable Data Structures
- Python - Domain Specific Language (DSL)
- Python - Data Model
- Python Useful Resources
- Python - Questions & Answers
- Python - Interview Questions & Answers
- Python - Online Quiz
- Python - Quick Guide
- Python - Reference
- Python - Cheatsheet
- Python - Projects
- Python - Useful Resources
- Python - Discussion
- Python Compiler
- NumPy Compiler
- Matplotlib Compiler
- SciPy Compiler
Tkinter Checkbutton
The Checkbutton widget is used to display a number of options to a user as toggle buttons. The user can then select one or more options by clicking the button corresponding to each option.
You can also display images in place of text.
Syntax
Here is the simple syntax to create this widget −
w = Checkbutton ( master, option, ... )
Parameters
master − This represents the parent window.
options − Here is the list of most commonly used options for this widget. These options can be used as key-value pairs separated by commas.
| Sr.No. | Option & Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Activebackground Background color when the checkbutton is under the cursor. |
| 2 | Activeforeground Foreground color when the checkbutton is under the cursor. |
| 3 | Bg The normal background color displayed behind the label and indicator. |
| 4 | Bitmap To display a monochrome image on a button. |
| 5 | Bd The size of the border around the indicator. Default is 2 pixels. |
| 6 | Command A procedure to be called every time the user changes the state of this checkbutton. |
| 7 | Cursor If you set this option to a cursor name (arrow, dot etc.), the mouse cursor will change to that pattern when it is over the checkbutton. |
| 8 | disabledforeground The foreground color used to render the text of a disabled checkbutton. The default is a stippled version of the default foreground color. |
| 9 | Font The font used for the text. |
| 10 | Fg The color used to render the text. |
| 11 | Height The number of lines of text on the checkbutton. Default is 1. |
| 12 | Highlightcolor The color of the focus highlight when the checkbutton has the focus. |
| 13 | Image To display a graphic image on the button. |
| 14 | Justify If the text contains multiple lines, this option controls how the text is justified: CENTER, LEFT, or RIGHT. |
| 15 | Offvalue Normally, a checkbutton's associated control variable will be set to 0 when it is cleared (off). You can supply an alternate value for the off state by setting offvalue to that value. |
| 16 | Onvalue Normally, a checkbutton's associated control variable will be set to 1 when it is set (on). You can supply an alternate value for the on state by setting onvalue to that value. |
| 17 | Padx How much space to leave to the left and right of the checkbutton and text. Default is 1 pixel. |
| 18 | Pady How much space to leave above and below the checkbutton and text. Default is 1 pixel. |
| 19 | Relief With the default value, relief=FLAT, the checkbutton does not stand out from its background. You may set this option to any of the other styles. |
| 20 | Selectcolor The color of the checkbutton when it is set. Default is selectcolor="red". |
| 21 | Selectimage If you set this option to an image, that image will appear in the checkbutton when it is set. |
| 22 | State The default is state=NORMAL, but you can use state=DISABLED to gray out the control and make it unresponsive. If the cursor is currently over the checkbutton, the state is ACTIVE. |
| 23 | Text The label displayed next to the checkbutton. Use newlines ("\n") to display multiple lines of text. |
| 24 | Underline With the default value of -1, none of the characters of the text label are underlined. Set this option to the index of a character in the text (counting from zero) to underline that character. |
| 25 | Variable The control variable that tracks the current state of the checkbutton. Normally this variable is an IntVar, and 0 means cleared and 1 means set, but see the offvalue and onvalue options above. |
| 26 | Width The default width of a checkbutton is determined by the size of the displayed image or text. You can set this option to a number of characters and the checkbutton will always have room for that many characters. |
| 27 | Wraplength Normally, lines are not wrapped. You can set this option to a number of characters and all lines will be broken into pieces no longer than that number. |
Methods
Following are commonly used methods for this widget −
| Sr.No. | Method & Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | deselect() Clears (turns off) the checkbutton. |
| 2 | flash() Flashes the checkbutton a few times between its active and normal colors, but leaves it the way it started. |
| 3 | invoke() You can call this method to get the same actions that would occur if the user clicked on the checkbutton to change its state. |
| 4 | select() Sets (turns on) the checkbutton. |
| 5 | toggle() Clears the checkbutton if set, sets it if cleared. |
Example
Try the following example yourself −
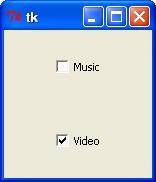
from tkinter import * import tkinter top = Tk() CheckVar1 = IntVar() CheckVar2 = IntVar() C1 = Checkbutton(top, text = "Music", variable = CheckVar1, \ onvalue = 1, offvalue = 0, height=5, \ width = 20, ) C2 = Checkbutton(top, text = "Video", variable = CheckVar2, \ onvalue = 1, offvalue = 0, height=5, \ width = 20) C1.pack() C2.pack() top.mainloop()
When the above code is executed, it produces the following result −