
- Python - Home
- Python - Overview
- Python - History
- Python - Features
- Python vs C++
- Python - Hello World Program
- Python - Application Areas
- Python - Interpreter
- Python - Environment Setup
- Python - Virtual Environment
- Python - Basic Syntax
- Python - Variables
- Python - Private Variables
- Python - Data Types
- Python - Type Casting
- Python - Unicode System
- Python - Literals
- Python - Operators
- Python - Arithmetic Operators
- Python - Comparison Operators
- Python - Assignment Operators
- Python - Logical Operators
- Python - Bitwise Operators
- Python - Membership Operators
- Python - Identity Operators
- Python - Walrus Operator
- Python - Operator Precedence
- Python - Comments
- Python - User Input
- Python - Numbers
- Python - Booleans
- Python - Floating Points
- Python - Control Flow
- Python - Decision Making
- Python - If Statement
- Python - If else
- Python - Nested If
- Python - Conditional User Inputs
- Python - Match-Case Statement
- Python - Loops
- Python - for Loops
- Python - for-else Loops
- Python - While Loops
- Python - break Statement
- Python - continue Statement
- Python - pass Statement
- Python - Nested Loops
- Python Functions & Modules
- Python - Functions
- Python - Default Arguments
- Python - Keyword Arguments
- Python - Keyword-Only Arguments
- Python - Positional Arguments
- Python - Positional-Only Arguments
- Python - Arbitrary Arguments
- Python - Variables Scope
- Python - Function Annotations
- Python - Modules
- Python - Packing and Unpacking
- Python - Built in Functions
- Python Strings
- Python - Strings
- Python - Slicing Strings
- Python - Modify Strings
- Python - String Concatenation
- Python - String Formatting
- Python - Escape Characters
- Python - String Methods
- Python - String Exercises
- Python Lists
- Python - Lists
- Python - Access List Items
- Python - Change List Items
- Python - Add List Items
- Python - Remove List Items
- Python - Loop Lists
- Python - List Comprehension
- Python - Sort Lists
- Python - Copy Lists
- Python - Join Lists
- Python - List Methods
- Python - List Exercises
- Python Tuples
- Python - Tuples
- Python - Access Tuple Items
- Python - Update Tuples
- Python - Unpack Tuples
- Python - Loop Tuples
- Python - Join Tuples
- Python - Tuple Methods
- Python - Namedtuple
- Python - Tuple Exercises
- Python Sets
- Python - Sets
- Python - Access Set Items
- Python - Add Set Items
- Python - Remove Set Items
- Python - Loop Sets
- Python - Join Sets
- Python - Copy Sets
- Python - Set Operators
- Python - Set Methods
- Python - Set Exercises
- Python Dictionaries
- Python - Dictionaries
- Python - Access Dictionary Items
- Python - Change Dictionary Items
- Python - Add Dictionary Items
- Python - Remove Dictionary Items
- Python - Dictionary View Objects
- Python - Loop Dictionaries
- Python - Copy Dictionaries
- Python - Nested Dictionaries
- Python - Dictionary Methods
- Python - Dictionary Exercises
- Python Arrays
- Python - Arrays
- Python - Access Array Items
- Python - Add Array Items
- Python - Remove Array Items
- Python - Loop Arrays
- Python - Copy Arrays
- Python - Reverse Arrays
- Python - Sort Arrays
- Python - Join Arrays
- Python - Array Methods
- Python - Array Exercises
- Python File Handling
- Python - File Handling
- Python - Write to File
- Python - Read Files
- Python - Renaming and Deleting Files
- Python - Directories
- Python - File Methods
- Python - OS File/Directory Methods
- Python - OS Path Methods
- Object Oriented Programming
- Python - OOPs Concepts
- Python - Classes & Objects
- Python - Class Attributes
- Python - Class Methods
- Python - Static Methods
- Python - Constructors
- Python - Access Modifiers
- Python - Inheritance
- Python - Multiple Inheritance
- Python - Multilevel Inheritance
- Python - Polymorphism
- Python - Method Overriding
- Python - Method Overloading
- Python - Dynamic Binding
- Python - Dynamic Typing
- Python - Abstraction
- Python - Encapsulation
- Python - Interfaces
- Python - Packages
- Python - Inner Classes
- Python - Anonymous Class and Objects
- Python - Singleton Class
- Python - Wrapper Classes
- Python - Enums
- Python - Reflection
- Python - Data Classes
- Python Errors & Exceptions
- Python - Syntax Errors
- Python - Exceptions
- Python - try-except Block
- Python - try-finally Block
- Python - Raising Exceptions
- Python - Exception Chaining
- Python - Nested try Block
- Python - User-defined Exception
- Python - Logging
- Python - Assertions
- Python - Warnings
- Python - Built-in Exceptions
- Python - Debugger (PDB)
- Python Multithreading
- Python - Multithreading
- Python - Thread Life Cycle
- Python - Creating a Thread
- Python - Starting a Thread
- Python - Joining Threads
- Python - Naming Thread
- Python - Thread Scheduling
- Python - Thread Pools
- Python - Main Thread
- Python - Thread Priority
- Python - Daemon Threads
- Python - Synchronizing Threads
- Python Synchronization
- Python - Inter-thread Communication
- Python - Thread Deadlock
- Python - Interrupting a Thread
- Python Networking
- Python - Networking
- Python - Socket Programming
- Python - URL Processing
- Python - Generics
- Python Libraries
- NumPy Tutorial
- Pandas Tutorial
- SciPy Tutorial
- Matplotlib Tutorial
- Django Tutorial
- OpenCV Tutorial
- Python Miscellenous
- Python - Date & Time
- Python - Maths
- Python - Iterators
- Python - Generators
- Python - Generator Expressions
- Python - Lambda Expressions
- Python - Closures
- Python - Decorators
- Python - Recursion
- Python - Reg Expressions
- Python - PIP
- Python - Database Access
- Python - Weak References
- Python - Serialization
- Python - Templating
- Python - Output Formatting
- Python - Performance Measurement
- Python - Data Compression
- Python - CGI Programming
- Python - XML Processing
- Python - GUI Programming
- Python - Command-Line Arguments
- Python - Docstrings
- Python - JSON
- Python - Sending Email
- Python - Further Extensions
- Python - Tools/Utilities
- Python - Odds and Ends
- Python - GUIs
- Python Advanced Concepts
- Python - Abstract Base Classes
- Python - Custom Exceptions
- Python - Higher Order Functions
- Python - Object Internals
- Python - Memory Management
- Python - Metaclasses
- Python - Metaprogramming with Metaclasses
- Python - Mocking and Stubbing
- Python - Monkey Patching
- Python - Signal Handling
- Python - Type Hints
- Python - Automation Tutorial
- Python - Humanize Package
- Python - Context Managers
- Python - Coroutines
- Python - Descriptors
- Python - Diagnosing and Fixing Memory Leaks
- Python - Immutable Data Structures
- Python - Domain Specific Language (DSL)
- Python - Data Model
- Python Useful Resources
- Python - Questions & Answers
- Python - Interview Questions & Answers
- Python - Online Quiz
- Python - Quick Guide
- Python - Reference
- Python - Cheatsheet
- Python - Projects
- Python - Useful Resources
- Python - Discussion
- Python Compiler
- NumPy Compiler
- Matplotlib Compiler
- SciPy Compiler
Python - Environment Setup
First step in the journey of learning Python is to install it on your machine. Today most computer machines, especially having Linux OS, have Python pre-installed. However, it may not be the latest version.
In this section, we shall learn to install the latest version of Python, Python 3.11.2, on Linux, Windows and Mac OS.
Latest version of Python for all the operating system environments can be downloaded from PSFâs official website.
Install Python on Ubuntu Linux
To check whether Python is already installed, open the Linux terminal and enter the following command −
user@ubuntu20:~$ python3 --version
In Ubuntu Linux, the easiest way to install Python is to use apt â Advanced Packaging Tool. It is always recommended to update the list of packages in all the configured repositories.
user@ubuntu20:~$ sudo apt update
Even after the update, the latest version of Python may not be available for install, depending upon the version of Ubuntu you are using. To overcome this, add the deadsnakes repository.
user@ubuntu20:~$ sudo apt-get install software-properties-common user@ubuntu20:~$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:deadsnakes/ppa
Update the package list again.
user@ubuntu20:~$ sudo apt update
To install the latest Python 3.11 version, enter the following command in the terminal −
user@ubuntu20:~$ sudo apt-get install python3.11
Check whether it has been properly installed.
user@ubuntu20:~$ python3.11
Python 3.11.2 (main, Feb 8 2023, 14:49:24) [GCC 9.4.0] on linux
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> print ("Hello World")
Hello World
>>>
Install Python on Windows
It may be noted that Pythonâs version 3.10 onwards cannot be installed on Windows 7 or earlier operating systems.
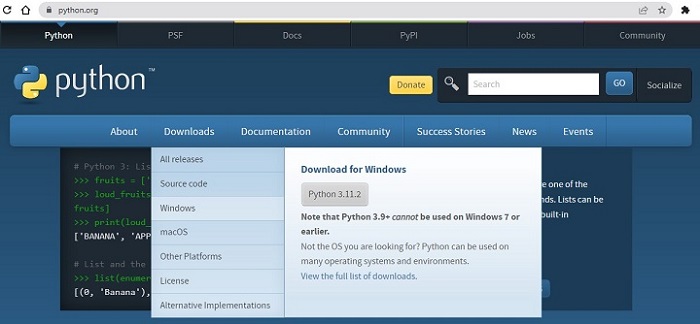
The recommended way to install Python is to use the official installer. Linn to the latest stable version is given on the home page itself. It is also found at https://www.python.org/downloads/windows/.
You can find embeddable packages and installers for 32 as well as 64-bit architecture.
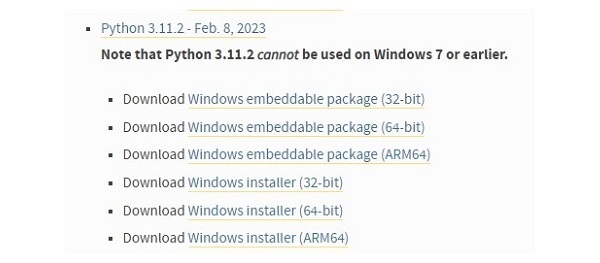
Let us download 64-bit Windows installer −
(https://www.python.org/ftp/python/3.11.2/python-3.11.2-amd64.exe)
Double click on the file where it has been downloaded to start the installation.

Although you can straight away proceed by clicking the Install Now button, it is advised to choose the installation folder with a relatively shorter path, and tick the second check box to update the PATH variable.
Accept defaults for rest of the steps in this installation wizard to complete the installation.
Open the Window Command Prompt terminal and run Python to check the success of installation.
C:\Users\Acer>python Python 3.11.2 (tags/v3.11.2:878ead1, Feb 7 2023, 16:38:35) [MSC v.1934 64 bit (AMD64)] on win32 Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information. >>>
Pythonâs standard library has an executable module called IDLE â short for Integrated Development and Learning Environment. Find it from Window start menu and launch.
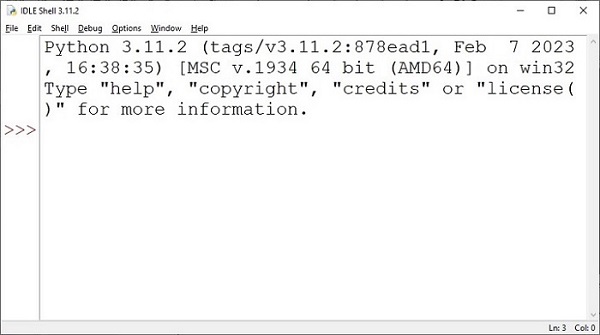
IDLE contains Python shell (interactive interpreter) and a customizable multi-window text editor with features such as syntax highlighting, smart indent, auto completion etc. It is cross-platform so works the same on Windows, MacOS and Linux. It also has a debugger with provision to set breakpoints, stepping, and viewing of global and local namespaces.
Install Python on MacOS
Earlier versions of MacOS used to have Python 2.7 pre-installed in it. However, now that the version no longer supported, it has been discontinued. Hence, you need to install Python on your own.
On a Mac computer, Python can be installed by two methods −
Using the official installer
Manual installation with homebrew
You can find macOS 64-bit universal2 installer on the downloads page of the official website −
https://www.python.org/ftp/python/3.11.2/python-3.11.2-macos11.pkg
The installation process is more or less similar to that on Windows. Usually, accepting the default options during the wizard steps should do the work.
The frequently required utilities such as PIP and IDLE are also installed by this installation wizard.
Alternately, you can opt for the installation from command line. You need to install Homebrew, Macâs package manager, if it is not already available. You can follow the instructions for installation at https://docs.brew.sh/Installation.
After that, open the terminal and enter the following commands −
brew update && brew upgrade brew install python3
Latest version of Python will now be installed.
Install Python from Source Code
If you are an experienced developer, with good knowledge of C++ and Git tool, you can follow the instructions in this section to build Python executable along with the modules in the standard library.
You must have the C compiler for the OS that you are on. In Ubuntu and MacOS, gcc compiler is available. For Windows, you should install Visual Studio 2017 or later.
Steps to Build Python on Linux/Mac
Download the source code of Pythonâs latest version either from Pythonâs official website or its GitHub repository.
Extract the files with the command −
tar -xvzf /home/python/Python-3.11.2.tgz
Alternately, clone the main branch of Pythonâs GitHub repository. (You should have git installed)
git clone -b main https://github.com/python/cpython
A configure script comes in the source code. Running this script will create the makefile.
./configure --enable-optimizations
Followed by this, use the make tool to build the files and then make install to put the final files in /usr/bin/ directory.
make make install
Python has been successfully built from the source code.
If you use Windows, make sure you have Visual Studio 2017 and Git for Windows installed. Clone the Python source code repository by the same command as above.
Open the windows command prompt in the folder where the source code is placed. Run the following batch file
PCbuild\get_externals.bat
This downloads the source code dependencies (OpenSSL, Tk etc.)
Open Visual Studio and PCbuild/sbuild.sln solution, and build (press F10) the debug folder shows python_d.exe which is the debug version of Python executable.
To build from command prompt, use the following command −
PCbuild\build.bat -e -d -p x64
Thus, in this chapter, you learned how to install Python from the pre-built binaries as well as from the source code.
Setting Up the PATH
When the Python software is installed, it should be accessible from anywhere in the file system. For this purpose, the PATH environment variable needs to be updated. A system PATH is a string consisting of folder names separated by semicolon (;). Whenever an executable program is invoked from the command line, the operating system searches for it in the folders listed in the PATH variable. We need to append Pythonâs installation folder to the PATH string.
In case of Winows operating system, if you have enabled âadd python.exe to system pathâ option on the first screen of the installation wizard, the path will be automatically updated. To do it manually, open Environment Variables section from Advanced System Settings.
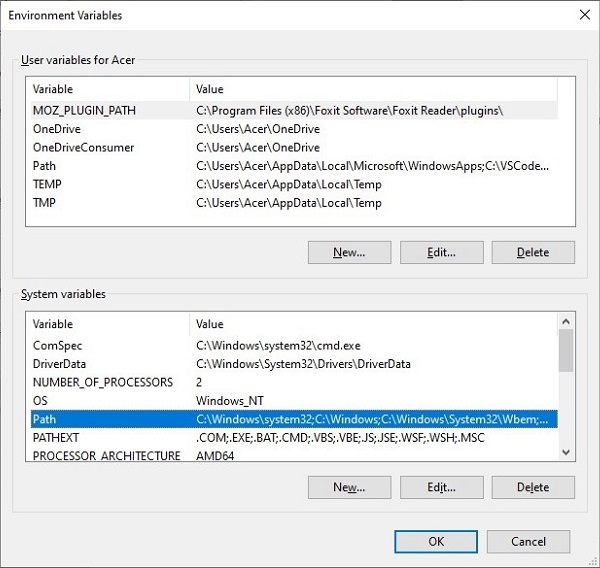
Edit the Path variable, and add a new entry. Enter the name of the installation folder in which Python has been installed, and press OK.
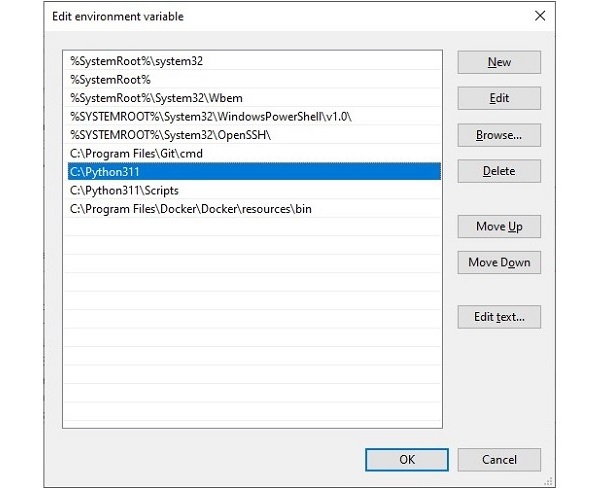
To add the Python directory to the path for a particular session in Linux −
In the bash shell (Linux) − type export PATH="$PATH:/usr/bin/python3.11" and press Enter.
Python Command Line Options
We know that interactive Python interpreter can be invoked from the terminal simply by calling Python executable. Note that no additional parameters or options are needed to start the interactive session.
user@ubuntu20:~$ python3.11
Python 3.11.2 (main, Feb 8 2023, 14:49:24) [GCC 9.4.0] on linux
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> print ("Hello World")
Hello World
>>>
Python interpreter also responds to the following command line options −
-c <command>
Interpreters execute one or more statements in a string, separated by newlines (;) symbol.
user@ubuntu20:~$ python3 -c "a=2;b=3;print(a+b)" 5
-m <module-name>
Interpreter executes the contents of named module as the __main__ module. Since the argument is a module name, you must not give a file extension (.py).
Consider the following example. Here, the timeit module in standard library has a command line interface. The -s option sets up the arguments for the module.
C:\Users\Acer>python -m timeit -s "text = 'sample string'; char = 'g' 'char in text'" 5000000 loops, best of 5: 49.4 nsec per loop
<script>
Interpreter executes the Python code contained in script with .py extension, which must be a filesystem path (absolute or relative).
Assuming that a text file with the name hello.py contains print (âHello Worldâ) statement is present in the current directory. The following command line usage of script option.
C:\Users\Acer>python hello.py Hello World
? Or -h or âhelp
This command line option prints a short description of all command line options and corresponding environment variables and exit.
-V or --version
This command line option prints the Python version number
C:\Users\Acer>python -V Python 3.11.2 C:\Users\Acer>python --version Python 3.11.2
Python Environment Variables
The operating system uses path environment variable to search for any executable (not only Python executable). Python specific environment variables allow you to configure the behaviour of Python. For example, which folder locations to check to import a module. Normally Python interpreter searches for the module in the current folder. You can set one or more alternate folder locations.
Python environment variables may be set temporarily for the current session or may be persistently added in the System Properties as in case of path variable.
PYTHONPATH
As mentioned above, if you want the interpreter should search for a module in other folders in addition to the current, one or more such folder locations are stored as PYTHONPATH variable.
First, save hello.py script in a folder different from Pythonâs installation folder, let us say c:\modulepath\hello.py
To make the module available to the interpreter globally, set PYTHONPATH
C:\Users\Acer>set PYTHONPATH= c:\modulepath C:\Users\Acer>echo %PYTHONPATH% c:\modulepath
Now you can import the module even from any directory other than c:\modulepath directory.
>>> import hello Hello World >>>
PYTHONHOME
Set this variable to change the location of the standard Python libraries. By default, the libraries are searched in /usr/local/pythonversion in case of Linux and instalfolder\lib in Windows. For example, c:\python311\lib.
PYTHONSTARTUP
Usually, this variable is set to a Python script, which you intend to get automatically executed every time Python interpreter starts.
Let us create a simple script as follows and save it as startup.py in the Python installation folder −
print ("Example of Start up file")
print ("Hello World")
Now set the PYTHONSTARTUP variable and assign name of this file to it. After that start the Python interpreter. It shows the output of this script before you get the prompt.
F:\311_2>set PYTHONSTARTUP=startup.py F:\311_2>echo %PYTHONSTARTUP% startup.py F:\311_2>python Python 3.11.2 (tags/v3.11.2:878ead1, Feb 7 2023, 16:38:35) [MSC v.1934 64 bit (AMD64)] on win32 Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information. Example of Start up file Hello World >>>
PYTHONCASEOK
This environment is available for use only on Windows and MacOSX, not on Linux. It causes Python to ignore the cases in import statement.
PYTHONVERBOSE
If this variable is set to a non-empty string it is equivalent to specifying python -v command. It results in printing a message, showing the place (filename or built-in module) each time a module is initialized. If set to an integer â say 2, it is equivalent to specifying -v two times. (python --v).
PYTHONDONTWRITEBYTECODE
Normally, the imported modules are compiled to .pyc file. If this variable is set to a not null string,the .pyc files on the import of source modules are not created.
PYTHONWARNINGS
Pythonâs warning messages are redirected to the standard error stream, sys.stderr. This environment variable is equivalent to the python -W option. The following are allowed values of this variable −
PYTHONWARNINGS=default # Warn once per call location
PYTHONWARNINGS=error # Convert to exceptions
PYTHONWARNINGS=always # Warn every time
PYTHONWARNINGS=module # Warn once per calling module
PYTHONWARNINGS=once # Warn once per Python process
PYTHONWARNINGS=ignore # Never warn