- PyGTK - Home
- PyGTK - Introduction
- PyGTK - Environment
- PyGTK - Hello World
- PyGTK - Important Classes
- PyGTK - Window Class
- PyGTK - Button Class
- PyGTK - Label CLass
- PyGTK - Entry Class
- PyGTK - Signal Handling
- PyGTK - Event Handling
- PyGTK - Containers
- PyGTK - Box Class
- PyGTK - ButtonBox Class
- PyGTK - Alignment Class
- PyGTK - EventBox Class
- PyGTK - Layout Class
- PyGTK - ComboBox Class
- PyGTK - ToggleButton Class
- PyGTK - CheckButton Class
- PyGTK - RadioButton Class
- PyGTK - MenuBar, Menu & MenuItem
- PyGTK - Toolbar Class
- PyGTK - Adjustment Class
- PyGTK - Range Class
- PyGTK - Scale Class
- PyGTK - Scrollbar Class
- PyGTK - Dialog Class
- PyGTK - MessageDialog Class
- PyGTK - AboutDialog Class
- PyGTK - Font Selection Dialog
- PyGTK - Color Selection Dialog
- PyGTK - File Chooser Dialog
- PyGTK - Notebook Class
- PyGTK - Frame Class
- PyGTK - AspectFrame Class
- PyGTK - TreeView Class
- PyGTK - Paned Class
- PyGTK - Statusbar Class
- PyGTK - ProgressBar Class
- PyGTK - Viewport Class
- PyGTK - Scrolledwindow Class
- PyGTK - Arrow Class
- PyGTK - Image Class
- PyGTK - DrawingArea Class
- PyGTK - SpinButton Class
- PyGTK - Calendar Class
- PyGTK - Clipboard Class
- PyGTK - Ruler Class
- PyGTK - Timeout
- PyGTK - Drag and Drop
PyGTK - Frame Class
Frame class is a subclass of the gtk.Bin class. It draws a decorative border around the child widget placed in it. The frame may contain a label whose position may be customized.
A gtk.Frame object is constructed with the help of the following constructor −
frame = gtk.Frame(label = None)
The following are the methods of the gtk.Frame() class −
set_label(text) − This sets the label as specified by text. If None, the current label is removed.
set_label_widget() − This sets a widget other than gtk.Label as label for frame.
set_label_align(x, y) − This sets the alignment of the frame's label widget and decoration (defaults are 0.0 and 0.5)
set_shadow_type() − This sets the frame's shadow type.
The possible values are −
- gtk.SHADOW_NONE
- gtk.SHADOW_IN
- gtk.SHADOW_OUT
- gtk.SHADOW_ETCHED_IN
- tk.SHADOW_ETCHED_OUT
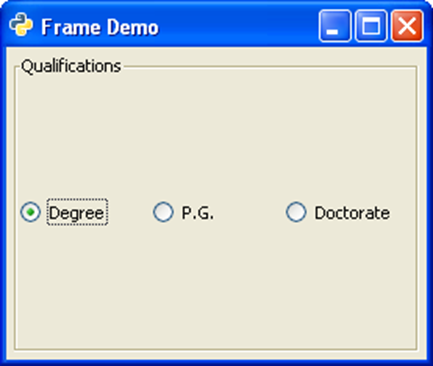
The following code demonstrates the functioning of the Frame widget. A group of three objects of gtk.RadioButton is placed in an HButtonBox.
btn1 = gtk.RadioButton(None,"Degree") btn2 = gtk.RadioButton(btn1,"P.G.") btn3 = gtk.RadioButton(btn1,"Doctorate") hb = gtk.HButtonBox() hb.add(btn1) hb.add(btn2) hb.add(btn3)
In order to draw border around the box, it is placed in a Frame widget, and it is added to the toplevel window.
frm = gtk.Frame() frm.add(hb) self.add(frm)
Example
Observe the following code −
import gtk
class PyApp(gtk.Window):
def __init__(self):
super(PyApp, self).__init__()
self.set_title("Frame Demo")
self.set_default_size(250, 200)
self.set_border_width(5)
frm = gtk.Frame()
hb = gtk.HButtonBox()
btn1 = gtk.RadioButton(None,"Degree")
hb.add(btn1)
btn2 = gtk.RadioButton(btn1,"P.G.")
hb.add(btn2)
btn3 = gtk.RadioButton(btn1,"Doctorate")
hb.add(btn3)
frm.add(hb)
frm.set_label("Qualifications")
self.add(frm)
self.connect("destroy", gtk.main_quit)
self.show_all()
if __name__ == '__main__':
PyApp()
gtk.main()
The above code will generate the following output −