
- DSP - Home
- DSP - Signals-Definition
- DSP - Basic CT Signals
- DSP - Basic DT Signals
- DSP - Classification of CT Signals
- DSP - Classification of DT Signals
- DSP - Miscellaneous Signals
- Operations Signals - Shifting
- Operations Signals - Scaling
- Operations Signals - Reversal
- Operations Signals - Differentiation
- Operations Signals - Integration
- Operations Signals - Convolution
- Basic System Properties
- DSP - Static Systems
- DSP - Dynamic Systems
- DSP - Causal Systems
- DSP - Non-Causal Systems
- DSP - Anti-Causal Systems
- DSP - Linear Systems
- DSP - Non-Linear Systems
- DSP - Time-Invariant Systems
- DSP - Time-Variant Systems
- DSP - Stable Systems
- DSP - Unstable Systems
- DSP - Solved Examples
- Z-Transform
- Z-Transform - Introduction
- Z-Transform - Properties
- Z-Transform - Existence
- Z-Transform - Inverse
- Z-Transform - Solved Examples
- Discrete Fourier Transform
- DFT - Introduction
- DFT - Time Frequency Transform
- DTF - Circular Convolution
- DFT - Linear Filtering
- DFT - Sectional Convolution
- DFT - Discrete Cosine Transform
- DFT - Solved Examples
- Fast Fourier Transform
- DSP - Fast Fourier Transform
- DSP - In-Place Computation
- DSP - Computer Aided Design
- Digital Signal Processing Resources
- DSP - Quick Guide
- DSP - Useful Resources
- DSP - Discussion
Digital Signal Processing - Basic CT Signals
To test a system, generally, standard or basic signals are used. These signals are the basic building blocks for many complex signals. Hence, they play a very important role in the study of signals and systems.
Unit Impulse or Delta Function
A signal, which satisfies the condition, $\delta(t) = \lim_{\epsilon \to \infty} x(t)$ is known as unit impulse signal. This signal tends to infinity when t = 0 and tends to zero when t ≠ 0 such that the area under its curve is always equals to one. The delta function has zero amplitude everywhere excunit_impulse.jpgept at t = 0.
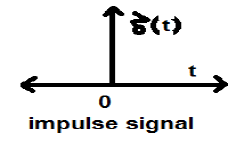
Properties of Unit Impulse Signal
- δ(t) is an even signal.
- δ(t) is an example of neither energy nor power (NENP) signal.
- Area of unit impulse signal can be written as; $$A = \int_{-\infty}^{\infty} \delta (t)dt = \int_{-\infty}^{\infty} \lim_{\epsilon \to 0} x(t) dt = \lim_{\epsilon \to 0} \int_{-\infty}^{\infty} [x(t)dt] = 1$$
- Weight or strength of the signal can be written as; $$y(t) = A\delta (t)$$
- Area of the weighted impulse signal can be written as − $$y (t) = \int_{-\infty}^{\infty} y (t)dt = \int_{-\infty}^{\infty} A\delta (t) = A[\int_{-\infty}^{\infty} \delta (t)dt ] = A = 1 = Wigthedimpulse$$
Unit Step Signal
A signal, which satisfies the following two conditions −
- $U(t) = 1(when\quad t \geq 0 )and$
- $U(t) = 0 (when\quad t < 0 )$
is known as a unit step signal.
It has the property of showing discontinuity at t = 0. At the point of discontinuity, the signal value is given by the average of signal value. This signal has been taken just before and after the point of discontinuity (according to Gibbs Phenomena).
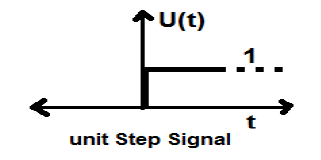
If we add a step signal to another step signal that is time scaled, then the result will be unity. It is a power type signal and the value of power is 0.5. The RMS (Root mean square) value is 0.707 and its average value is also 0.5
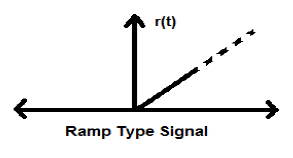
Ramp Signal
Integration of step signal results in a Ramp signal. It is represented by r(t). Ramp signal also satisfies the condition $r(t) = \int_{-\infty}^{t} U(t)dt = tU(t)$. It is neither energy nor power (NENP) type signal.
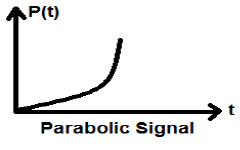
Parabolic Signal
Integration of Ramp signal leads to parabolic signal. It is represented by p(t). Parabolic signal also satisfies he condition $p(t) = \int_{-\infty}^{t} r(t)dt = (t^{2}/2)U(t)$ . It is neither energy nor Power (NENP) type signal.
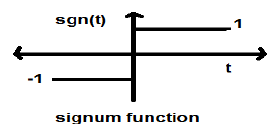
Signum Function
This function is represented as
$$sgn(t) = \begin{cases}1 & for\quad t >0\\-1 & for\quad t<0\end{cases}$$It is a power type signal. Its power value and RMS (Root mean square) values, both are 1. Average value of signum function is zero.
Sinc Function
It is also a function of sine and is written as −
$$SinC(t) = \frac{Sin\Pi t}{\Pi T} = Sa(\Pi t)$$Properties of Sinc function
It is an energy type signal.
$Sinc(0) = \lim_{t \to 0}\frac{\sin \Pi t}{\Pi t} = 1$
$Sinc(\infty) = \lim_{t \to \infty}\frac{\sin \Pi \infty}{\Pi \infty} = 0$ (Range of sinπ∞ varies between -1 to +1 but anything divided by infinity is equal to zero)
-
If $ \sin c(t) = 0 => \sin \Pi t = 0$
$\Rightarrow \Pi t = n\Pi$
$\Rightarrow t = n (n \neq 0)$
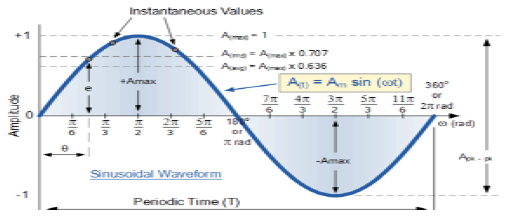
Sinusoidal Signal
A signal, which is continuous in nature is known as continuous signal. General format of a sinusoidal signal is
$$x(t) = A\sin (\omega t + \phi )$$Here,
A = amplitude of the signal
ω = Angular frequency of the signal (Measured in radians)
φ = Phase angle of the signal (Measured in radians)
The tendency of this signal is to repeat itself after certain period of time, thus is called periodic signal. The time period of signal is given as;
$$T = \frac{2\pi }{\omega }$$The diagrammatic view of sinusoidal signal is shown below.
Rectangular Function
A signal is said to be rectangular function type if it satisfies the following condition −
$$\pi(\frac{t}{\tau}) = \begin{cases}1, & for\quad t\leq \frac{\tau}{2}\\0, & Otherwise\end{cases}$$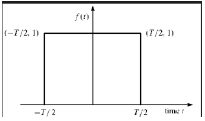
Being symmetrical about Y-axis, this signal is termed as even signal.
Triangular Pulse Signal
Any signal, which satisfies the following condition, is known as triangular signal.
$$\Delta(\frac{t}{\tau}) = \begin{cases}1-(\frac{2|t|}{\tau}) & for|t|<\frac{\tau}{2}\\0 & for|t|>\frac{\tau}{2}\end{cases}$$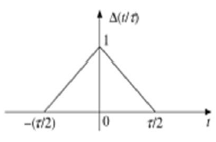
This signal is symmetrical about Y-axis. Hence, it is also termed as even signal.