
- Kivy - Home
- Kivy Basics
- Kivy - Getting Started
- Kivy - Installation
- Kivy - Architecture
- Kivy - File Syntax
- Kivy - Applications
- Kivy - Hello World
- Kivy - App Life Cycle
- Kivy - Events
- Kivy - Properties
- Kivy - Inputs
- Kivy - Behaviors
- Kivy Buttons
- Kivy - Buttons
- Kivy - Button Events
- Kivy - Button Colors
- Kivy - Button Size
- Kivy - Button Position
- Kivy - Round Buttons
- Kivy - Disabled Buttons
- Kivy - Image Button
- Kivy Widgets
- Kivy - Widgets
- Kivy - Label
- Kivy - Text Input
- Kivy - Canvas
- Kivy - Line
- Kivy - Checkbox
- Kivy - Dropdown List
- Kivy - Windows
- Kivy - ScrollView
- Kivy - Carousel
- Kivy - Slider
- Kivy - Images
- Kivy - Popup
- Kivy - Switch
- Kivy - Spinner
- Kivy - Splitter
- Kivy - Progress Bar
- Kivy - Bubble
- Kivy - Tabbed Panel
- Kivy - Scatter
- Kivy - Accordion
- Kivy - File Chooser
- Kivy - Color Picker
- Kivy - Code Input
- Kivy - Modal View
- Kivy - Toggle Button
- Kivy - Camera
- Kivy - Tree View
- Kivy - reStructuredText
- Kivy - Action Bar
- Kivy - Video Player
- Kivy - Stencil View
- Kivy - VKeyboard
- Kivy - Touch Ripple
- Kivy - Audio
- Kivy - Videos
- Kivy - Spelling
- Kivy - Effects
- Kivy - Input Recorder
- Kivy - OpenGL
- Kivy - Text
- Kivy - Text Markup
- Kivy - Settings
- Kivy Layouts
- Kivy - Layouts
- Kivy - Float Layout
- Kivy - Grid Layouts
- Kivy - Box Layouts
- Kivy - Stack Layout
- Kivy - Anchor Layout
- Kivy - Relative Layout
- Kivy - Page Layout
- Kivy - Recycle Layout
- Kivy - Layouts in Layouts
- Kivy Advanced Concepts
- Kivy - Configuration Object
- Kivy - Atlas
- Kivy - Data Loader
- Kivy - Cache Manager
- Kivy - Console
- Kivy - Animation
- Kivy - Multistroke
- Kivy - Clock
- Kivy - SVGs
- Kivy - UrlRequest
- Kivy - Clipboard
- Kivy - Factory
- Kivy - Gesture
- Kivy - Language
- Kivy - Graphics
- Kivy - Drawing
- Kivy - Packaging
- Kivy - Garden
- Kivy - Storage
- Kivy - Vector
- Kivy - Utils
- Kivy - Inspector
- Kivy - Tools
- Kivy - Logger
- Kivy - Framebuffer
- Kivy Applications and Projects
- Kivy - Drawing App
- Kivy - Calculator App
- Kivy - Stopwatch App
- Kivy - Camera Handling
- Kivy - Image Viewer
- Kivy - Bezier
- Kivy - Canvas Stress
- Kivy - Circle Drawing
- Kivy - Widget Animation
- Kivy - Miscellaneous
- Kivy Useful Resources
- Kivy - Quick Guide
- Kivy - Useful Resources
- Kivy - Discussion
Kivy - Code Input
The CodeInput widget in the Kivy framework is a specialized TextInput box, capable of displaying editable text that is highlighted as per the syntax of the language lexer chosen.
The CodeInput widget requires the pygments package to be installed.
The pygments package is a Python syntax highlighter.
It is used in applications that need to prettify source code.
Pygments supports almost all the languages, including programming, scripting languages and even capable of providing syntax highlighting as per the framework and library syntax.
The support comes in the form of Lexer classes. For example, to pickup Python syntax for highlighting the language elements, we need to import Python3Lexer, for C++ code, the CppLexer class needs to be imported. Specifically the Kivy code is highlighted with KivyLexer.
If your current working environment doesn't have pygments installed, run the following command −
pip3 install pygments
The CodeInput class is defined in the "kivy.uix.codeinput" module.
from kivy.uix.codeinput import CodeInput codewidget = CodeInput(**kwargs)
The CodeInput class inherits the TextInput class, as well as CodeNavigationBehaviou mixin. Just as a TextInput object, the CodeInput widget is a multiline text box, which can be added to other layout classes. It can be instantiated by specifying following properties −
lexer − This holds the selected Lexer used by pygments to highlight the code. It is an ObjectProperty and defaults to PythonLexer.
style − The pygments style object to use for formatting. When style_name is set, this will be changed to the corresponding style object.
style_name − Name of the pygments style to use for formatting. style_name is an OptionProperty and defaults to 'default'. There are a number of styles available in pygments. Some of the examples are emacs, xcode, vs, bw, colorful and many more.
In addition to these, the properties are also inherited from TextInput class. The CodeNavigationBehavior mixin modifies navigation behavior in the TextInput, making it work like an IDE instead of a word processor.
Example
In the following code, the CodeInput widget uses PythonLexer to perform syntax highlighting of a Python source code. A "code.py" file is read using Python's file object and the data is assigned to the text property of CodeInput object.
from kivy.app import App
from kivy.uix.gridlayout import GridLayout
from kivy.uix.codeinput import CodeInput
from pygments.lexers.python import Python3Lexer
from kivy.uix.scrollview import ScrollView
from kivy.uix.codeinput import CodeInput
from kivy.core.window import Window
Window.size = (720,400)
class codeinputdemoapp(App):
def build(self):
scr = ScrollView(size=Window.size)
codinp = CodeInput(style='emacs')
codinp.height = max(codinp.minimum_height, scr.height)
file=open('code.py')
text=file.read()
codinp.text=text
scr.add_widget(codinp)
return scrx
codeinputdemoapp().run()

To highlight the code which uses Kivy related keywords and functions, load the KivyLexer. You can also experiment with the "pigment" style, changing it to "colorful" or any of the available styles.
from kivy.extras.highlight import KivyLexer
Read the "kivycode.py" file and load it in the CodeInput box.
file=open('kivycode.py')
text=file.read()
codinp.text=text
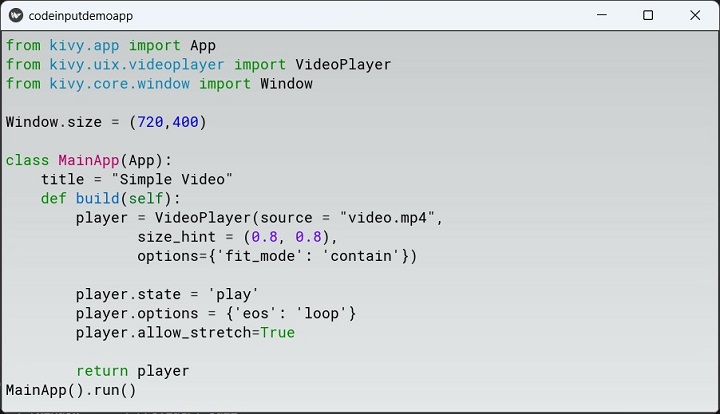
You can also try and display a C++ code with CppLexer −
from pygments.lexers.c_cpp import CppLexer
This time, change the style to "friendly".
file=open('test.cpp')
text=file.read()
codinp.text=text
