
- DSA - Home
- DSA - Overview
- DSA - Environment Setup
- DSA - Algorithms Basics
- DSA - Asymptotic Analysis
- Data Structures
- DSA - Data Structure Basics
- DSA - Data Structures and Types
- DSA - Array Data Structure
- DSA - Skip List Data Structure
- Linked Lists
- DSA - Linked List Data Structure
- DSA - Doubly Linked List Data Structure
- DSA - Circular Linked List Data Structure
- Stack & Queue
- DSA - Stack Data Structure
- DSA - Expression Parsing
- DSA - Queue Data Structure
- DSA - Circular Queue Data Structure
- DSA - Priority Queue Data Structure
- DSA - Deque Data Structure
- Searching Algorithms
- DSA - Searching Algorithms
- DSA - Linear Search Algorithm
- DSA - Binary Search Algorithm
- DSA - Interpolation Search
- DSA - Jump Search Algorithm
- DSA - Exponential Search
- DSA - Fibonacci Search
- DSA - Sublist Search
- DSA - Hash Table
- Sorting Algorithms
- DSA - Sorting Algorithms
- DSA - Bubble Sort Algorithm
- DSA - Insertion Sort Algorithm
- DSA - Selection Sort Algorithm
- DSA - Merge Sort Algorithm
- DSA - Shell Sort Algorithm
- DSA - Heap Sort Algorithm
- DSA - Bucket Sort Algorithm
- DSA - Counting Sort Algorithm
- DSA - Radix Sort Algorithm
- DSA - Quick Sort Algorithm
- Matrices Data Structure
- DSA - Matrices Data Structure
- DSA - Lup Decomposition In Matrices
- DSA - Lu Decomposition In Matrices
- Graph Data Structure
- DSA - Graph Data Structure
- DSA - Depth First Traversal
- DSA - Breadth First Traversal
- DSA - Spanning Tree
- DSA - Topological Sorting
- DSA - Strongly Connected Components
- DSA - Biconnected Components
- DSA - Augmenting Path
- DSA - Network Flow Problems
- DSA - Flow Networks In Data Structures
- DSA - Edmonds Blossom Algorithm
- DSA - Maxflow Mincut Theorem
- Tree Data Structure
- DSA - Tree Data Structure
- DSA - Tree Traversal
- DSA - Binary Search Tree
- DSA - AVL Tree
- DSA - Red Black Trees
- DSA - B Trees
- DSA - B+ Trees
- DSA - Splay Trees
- DSA - Range Queries
- DSA - Segment Trees
- DSA - Fenwick Tree
- DSA - Fusion Tree
- DSA - Hashed Array Tree
- DSA - K-Ary Tree
- DSA - Kd Trees
- DSA - Priority Search Tree Data Structure
- Recursion
- DSA - Recursion Algorithms
- DSA - Tower of Hanoi Using Recursion
- DSA - Fibonacci Series Using Recursion
- Divide and Conquer
- DSA - Divide and Conquer
- DSA - Max-Min Problem
- DSA - Strassen's Matrix Multiplication
- DSA - Karatsuba Algorithm
- Greedy Algorithms
- DSA - Greedy Algorithms
- DSA - Travelling Salesman Problem (Greedy Approach)
- DSA - Prim's Minimal Spanning Tree
- DSA - Kruskal's Minimal Spanning Tree
- DSA - Dijkstra's Shortest Path Algorithm
- DSA - Map Colouring Algorithm
- DSA - Fractional Knapsack Problem
- DSA - Job Sequencing with Deadline
- DSA - Optimal Merge Pattern Algorithm
- Dynamic Programming
- DSA - Dynamic Programming
- DSA - Matrix Chain Multiplication
- DSA - Floyd Warshall Algorithm
- DSA - 0-1 Knapsack Problem
- DSA - Longest Common Sub-sequence Algorithm
- DSA - Travelling Salesman Problem (Dynamic Approach)
- Hashing
- DSA - Hashing Data Structure
- DSA - Collision In Hashing
- Disjoint Set
- DSA - Disjoint Set
- DSA - Path Compression And Union By Rank
- Heap
- DSA - Heap Data Structure
- DSA - Binary Heap
- DSA - Binomial Heap
- DSA - Fibonacci Heap
- Tries Data Structure
- DSA - Tries
- DSA - Standard Tries
- DSA - Compressed Tries
- DSA - Suffix Tries
- Treaps
- DSA - Treaps Data Structure
- Bit Mask
- DSA - Bit Mask In Data Structures
- Bloom Filter
- DSA - Bloom Filter Data Structure
- Approximation Algorithms
- DSA - Approximation Algorithms
- DSA - Vertex Cover Algorithm
- DSA - Set Cover Problem
- DSA - Travelling Salesman Problem (Approximation Approach)
- Randomized Algorithms
- DSA - Randomized Algorithms
- DSA - Randomized Quick Sort Algorithm
- DSA - Karger’s Minimum Cut Algorithm
- DSA - Fisher-Yates Shuffle Algorithm
- Miscellaneous
- DSA - Infix to Postfix
- DSA - Bellmon Ford Shortest Path
- DSA - Maximum Bipartite Matching
- DSA Useful Resources
- DSA - Questions and Answers
- DSA - Selection Sort Interview Questions
- DSA - Merge Sort Interview Questions
- DSA - Insertion Sort Interview Questions
- DSA - Heap Sort Interview Questions
- DSA - Bubble Sort Interview Questions
- DSA - Bucket Sort Interview Questions
- DSA - Radix Sort Interview Questions
- DSA - Cycle Sort Interview Questions
- DSA - Quick Guide
- DSA - Useful Resources
- DSA - Discussion
Binomial Heaps
A binomial Heap is a collection of Binomial Trees. A binomial tree Bk is an ordered tree defined recursively. A binomial Tree B0 consists of a single node.
A binomial tree is an ordered tree defined recursively. A binomial tree Bk consists of two binomial trees Bk-1 that are linked together. The root of one is the leftmost child of the root of the other.
Binomial trees are defined recursively. A binomial tree Bk is defined as follows
B0 is a single node.
Bk is formed by linking two binomial trees Bk-1 such that the root of one is the leftmost child of the root of the other.
Some properties of binomial trees are
Binomial tree with Bk has 2k nodes.
Height of the tree is k
There are exactly j! / (i! * (j-i)!) nodes at depth i for all i in range 0 to k.
What is Binomial Heap?
As mentioned above, a binomial heap is a collection of binomial trees. These binomial trees are linked together in a specific way. The binomial heap has the following properties
Each binomial tree in the heap follows the min-heap property.
No two binomial trees in the heap can have the same number of nodes.
There is at most one binomial tree of any order.
Representation of Binomial Heap
Following is a representation of binomial heap, where Bk is a binomial heap of order k.
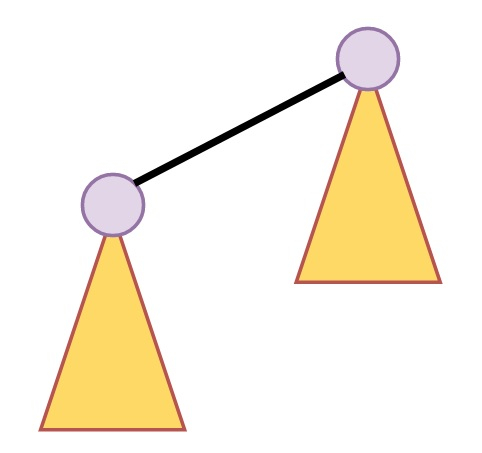
Some binomial heaps are like below
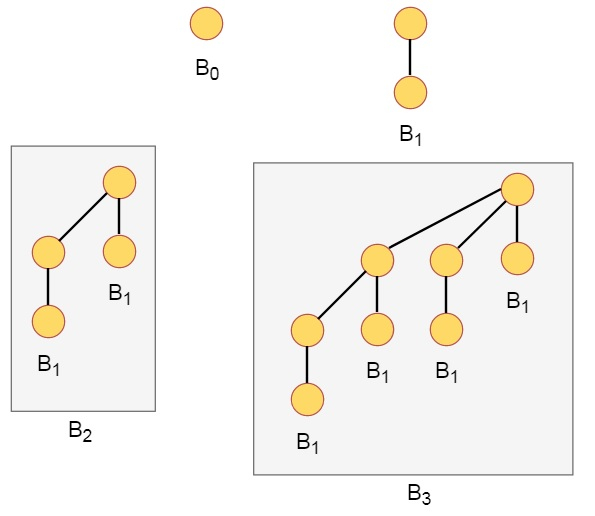
Example of Binomial Heap
This binomial Heap H consists of binomial trees B0, B2 and B3. Which have 1, 4 and 8 nodes respectively. And in total n = 13 nodes. The root of binomial trees are linked by a linked list in order of increasing degree
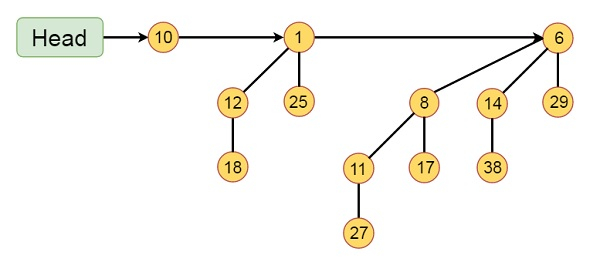
Operations on Binomial Heap
Following are the operations that can be performed on a binomial heap
Insert: As name suggests, it is used to insert a node into the heap.
Union: It is used to merge two binomial heaps into a single binomial heap.
Extract-Min: This operation removes the node with the smallest key from the heap.
Decrease-Key: This operation decreases the key of a node in the heap.
Delete: Simply put, it deletes a node from the heap.
Implementation of Binomial Heap
We can implement a binomial heap using a linked list of binomial trees. Each node in the linked list is a binomial tree. The root of each binomial tree is the head of the linked list. The linked list is ordered by the order of the binomial trees. The binomial heap is the head of the linked list.
Implementation of binomial heap using following steps
1. Create a new node with the given key. 2. Merge the new node with the binomial heap. 3. Adjust the binomial heap to maintain the heap property. 4. Insert the new node into the binomial heap. 5. Print the binomial heap.
Code for Binomial Heap
Following is the implementation of binomial heap in C, C++, Java and Python.
In the following code, first we create a structure Node to represent a node in the binomial heap. The structure contains the data, degree, child, sibling, and parent of the node. We then define functions to create a new node, merge two binomial trees, union two binomial heaps, adjust the heap, and insert a new node into the heap. Finally, we print the binomial heap.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <limits.h>
struct Node {
int data, degree;
struct Node *child, *sibling, *parent;
};
struct Node *newNode(int key) {
struct Node *temp = (struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
temp->data = key;
temp->degree = 0;
temp->child = temp->parent = temp->sibling = NULL;
return temp;
}
struct Node *mergeBinomialTrees(struct Node *b1, struct Node *b2) {
if (b1->data > b2->data) {
struct Node *temp = b1;
b1 = b2;
b2 = temp;
}
b2->parent = b1;
b2->sibling = b1->child;
b1->child = b2;
b1->degree++;
return b1;
}
struct Node *unionBinomialHeap(struct Node *h1, struct Node *h2) {
if (!h1) return h2;
if (!h2) return h1;
struct Node *newHeap = NULL, **pos = &newHeap;
struct Node *curr1 = h1, *curr2 = h2;
while (curr1 && curr2) {
if (curr1->degree <= curr2->degree) {
*pos = curr1;
curr1 = curr1->sibling;
} else {
*pos = curr2;
curr2 = curr2->sibling;
}
pos = &((*pos)->sibling);
}
*pos = (curr1) ? curr1 : curr2;
return newHeap;
}
struct Node *adjustHeap(struct Node *head) {
if (!head) return NULL;
struct Node *prev = NULL, *curr = head, *next = head->sibling;
while (next) {
if (curr->degree != next->degree || (next->sibling && next->sibling->degree == curr->degree)) {
prev = curr;
curr = next;
} else {
if (curr->data <= next->data) {
curr->sibling = next->sibling;
curr = mergeBinomialTrees(curr, next);
} else {
if (!prev) head = next;
else prev->sibling = next;
curr = mergeBinomialTrees(next, curr);
}
}
next = curr->sibling;
}
return head;
}
struct Node *insert(struct Node *heap, int key) {
struct Node *temp = newNode(key);
return adjustHeap(unionBinomialHeap(heap, temp));
}
void printTree(struct Node *h) {
while (h) {
printf("%d ", h->data);
printTree(h->child);
h = h->sibling;
}
}
void printHeap(struct Node *h) {
printf("Binomial Heap: \n");
while (h) {
printf("B%d: ", h->degree);
printTree(h);
printf("\n");
h = h->sibling;
}
}
int main() {
struct Node *hp = NULL;
hp = insert(hp, 10);
hp = insert(hp, 20);
hp = insert(hp, 30);
hp = insert(hp, 40);
printHeap(hp);
return 0;
}
Output
Following is the output of the above C code
10 20 30 40
#include <iostream>
#include <limits.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int data, degree;
Node *child, *sibling, *parent;
};
Node *newNode(int key) {
Node *temp = new Node;
temp->data = key;
temp->degree = 0;
temp->child = temp->parent = temp->sibling = NULL;
return temp;
}
Node *mergeBinomialTrees(Node *b1, Node *b2) {
if (b1->data > b2->data) {
Node *temp = b1;
b1 = b2;
b2 = temp;
}
b2->parent = b1;
b2->sibling = b1->child;
b1->child = b2;
b1->degree++;
return b1;
}
Node *unionBinomialHeap(Node *h1, Node *h2) {
if (!h1) return h2;
if (!h2) return h1;
Node *newHeap = NULL, **pos = &newHeap;
Node *curr1 = h1, *curr2 = h2;
while (curr1 && curr2) {
if (curr1->degree <= curr2->degree) {
*pos = curr1;
curr1 = curr1->sibling;
} else {
*pos = curr2;
curr2 = curr2->sibling;
}
pos = &((*pos)->sibling);
}
*pos = (curr1) ? curr1 : curr2;
return newHeap;
}
Node *adjustHeap(Node *head) {
if (!head) return NULL;
Node *prev = NULL, *curr = head, *next = head->sibling;
while (next) {
if (curr->degree != next->degree || (next->sibling && next->sibling->degree == curr->degree)) {
prev = curr;
curr = next;
} else {
if (curr->data <= next->data) {
curr->sibling = next->sibling;
curr = mergeBinomialTrees(curr, next);
} else {
if (!prev) head = next;
else prev->sibling = next;
curr = mergeBinomialTrees(next, curr);
}
}
next = curr->sibling;
}
return head;
}
Node *insert(Node *heap, int key) {
Node *temp = newNode(key);
return adjustHeap(unionBinomialHeap(heap, temp));
}
void printTree(Node *h) {
while (h) {
cout << h->data << " ";
printTree(h->child);
h = h->sibling;
}
}
void printHeap(Node *h) {
cout << "Binomial Heap: " << endl;
while (h) {
cout << "B" << h->degree << ": ";
printTree(h);
cout << endl;
h = h->sibling;
}
}
int main() {
Node *hp = NULL;
hp = insert(hp, 10);
hp = insert(hp, 20);
hp = insert(hp, 30);
hp = insert(hp, 40);
printHeap(hp);
return 0;
}
Output
Following is the output of the above C++ code
10 20 30 40
import java.util.*;
class Node {
int data, degree;
Node child, parent, sibling;
}
public class BinomialHeap {
Node newNode(int key) {
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = key;
temp.degree = 0;
temp.child = temp.parent = temp.sibling = null;
return temp;
}
Node mergeBinomialTrees(Node b1, Node b2) {
if (b1.data > b2.data) {
Node temp = b1;
b1 = b2;
b2 = temp;
}
b2.parent = b1;
b2.sibling = b1.child;
b1.child = b2;
b1.degree++;
return b1;
}
Node unionBinomialHeap(Node h1, Node h2) {
if (h1 == null) return h2;
if (h2 == null) return h1;
Node dummy = new Node(); // Dummy node to track newHeap
Node tail = dummy;
Node curr1 = h1, curr2 = h2;
while (curr1 != null && curr2 != null) {
if (curr1.degree <= curr2.degree) {
tail.sibling = curr1;
curr1 = curr1.sibling;
} else {
tail.sibling = curr2;
curr2 = curr2.sibling;
}
tail = tail.sibling;
}
tail.sibling = (curr1 != null) ? curr1 : curr2;
return dummy.sibling; // Return merged heap without dummy node
}
Node adjustHeap(Node head) {
if (head == null) return null;
Node prev = null, curr = head, next = head.sibling;
while (next != null) {
if (curr.degree != next.degree ||
(next.sibling != null && next.sibling.degree == curr.degree)) {
prev = curr;
curr = next;
} else {
if (curr.data <= next.data) {
curr.sibling = next.sibling;
curr = mergeBinomialTrees(curr, next);
} else {
if (prev == null) head = next;
else prev.sibling = next;
curr = mergeBinomialTrees(next, curr);
}
}
next = curr.sibling;
}
return head;
}
Node insert(Node heap, int key) {
Node temp = newNode(key);
return adjustHeap(unionBinomialHeap(heap, temp));
}
void printTree(Node h) {
while (h != null) {
System.out.print(h.data + " ");
printTree(h.child);
h = h.sibling;
}
}
void printHeap(Node h) {
System.out.println("Binomial Heap: ");
while (h != null) {
System.out.print("B" + h.degree + ": ");
printTree(h);
System.out.println();
h = h.sibling;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinomialHeap bh = new BinomialHeap();
Node hp = null;
hp = bh.insert(hp, 10);
hp = bh.insert(hp, 20);
hp = bh.insert(hp, 30);
hp = bh.insert(hp, 40);
bh.printHeap(hp);
}
}
Output
Following is the output of the above Java code
Binomial Heap: B2 : 10 20 30 40
class Node:
def __init__(self, key):
self.data = key
self.degree = 0
self.child = self.parent = self.sibling = None
def mergeBinomialTrees(b1, b2):
if b1.data > b2.data:
b1, b2 = b2, b1
b2.parent = b1
b2.sibling = b1.child
b1.child = b2
b1.degree += 1
return b1
def unionBinomialHeap(h1, h2):
if not h1: return h2
if not h2: return h1
dummy = Node(-1) # Dummy node to track merged heap
tail = dummy
curr1, curr2 = h1, h2
while curr1 and curr2:
if curr1.degree <= curr2.degree:
tail.sibling = curr1
curr1 = curr1.sibling
else:
tail.sibling = curr2
curr2 = curr2.sibling
tail = tail.sibling
tail.sibling = curr1 if curr1 else curr2
return dummy.sibling # Return merged heap without dummy node
def adjustHeap(head):
if not head: return None
prev, curr, next = None, head, head.sibling
while next:
if curr.degree != next.degree or (next.sibling and next.sibling.degree == curr.degree):
prev, curr = curr, next
else:
if curr.data <= next.data:
curr.sibling = next.sibling
curr = mergeBinomialTrees(curr, next)
else:
if prev: prev.sibling = next
else: head = next
curr = mergeBinomialTrees(next, curr)
next = curr.sibling
return head
def insert(heap, key):
temp = Node(key)
return adjustHeap(unionBinomialHeap(heap, temp))
def printTree(h):
while h:
print(h.data, end=" ")
printTree(h.child)
h = h.sibling
def printHeap(h):
print("Binomial Heap:")
while h:
print("B" + str(h.degree) + ": ", end="")
printTree(h)
print()
h = h.sibling
# Testing the fixed binomial heap
hp = None
hp = insert(hp, 10)
hp = insert(hp, 20)
hp = insert(hp, 30)
hp = insert(hp, 40)
printHeap(hp)
Output
Following is the output of the above Python code
Binomial Heap: B2: 10 20 30 40
Extract-Min Operation in Binomial Heap
The extract-min operation removes the node with the smallest key from the binomial heap. The extract-min operation is performed as follows
1. Find the node with the smallest key in the binomial heap. 2. Remove the node from the binomial heap. 3. Now, Let's Merge the children of the node with the binomial heap. 4. Adjust the binomial heap to maintain the heap property. 5. Return the new binomial heap.
Code for Extract-Min Operation
Following is the implementation of extract-min operation in C, C++, Java and Python.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <limits.h>
struct Node {
int data, degree;
struct Node *child, *sibling, *parent;
};
struct Node *newNode(int key) {
struct Node *temp = (struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
temp->data = key;
temp->degree = 0;
temp->child = temp->parent = temp->sibling = NULL;
return temp;
}
struct Node *mergeBinomialTrees(struct Node *b1, struct Node *b2) {
if (b1->data > b2->data) {
struct Node *temp = b1;
b1 = b2;
b2 = temp;
}
b2->parent = b1;
b2->sibling = b1->child;
b1->child = b2;
b1->degree++;
return b1;
}
struct Node *unionBinomialHeap(struct Node *h1, struct Node *h2) {
if (!h1) return h2;
if (!h2) return h1;
struct Node *newHeap = NULL, **pos = &newHeap;
struct Node *curr1 = h1, *curr2 = h2;
while (curr1 && curr2) {
if (curr1->degree <= curr2->degree) {
*pos = curr1;
curr1 = curr1->sibling;
} else {
*pos = curr2;
curr2 = curr2->sibling;
}
pos = &((*pos)->sibling);
}
*pos = (curr1) ? curr1 : curr2;
return newHeap;
}
struct Node *adjustHeap(struct Node *head) {
if (!head) return NULL;
struct Node *prev = NULL, *curr = head, *next = head->sibling;
while (next) {
if (curr->degree != next->degree || (next->sibling && next->sibling->degree == curr->degree)) {
prev = curr;
curr = next;
} else {
if (curr->data <= next->data) {
curr->sibling = next->sibling;
curr = mergeBinomialTrees(curr, next);
} else {
if (!prev) head = next;
else prev->sibling = next;
curr = mergeBinomialTrees(next, curr);
}
}
next = curr->sibling;
}
return head;
}
struct Node *insert(struct Node *heap, int key) {
struct Node *temp = newNode(key);
return adjustHeap(unionBinomialHeap(heap, temp));
}
struct Node *getMin(struct Node *heap) {
if (!heap) return NULL;
struct Node *min = heap;
struct Node *curr = heap->sibling;
while (curr) {
if (curr->data < min->data) min = curr;
curr = curr->sibling;
}
return min;
}
struct Node *extractMin(struct Node *heap) {
if (!heap) return NULL;
struct Node *min = getMin(heap);
struct Node *prev = NULL, *curr = heap;
while (curr != min) {
prev = curr;
curr = curr->sibling;
}
if (prev) prev->sibling = min->sibling;
else heap = min->sibling;
struct Node *child = min->child;
struct Node *newHeap = NULL;
while (child) {
struct Node *next = child->sibling;
child->sibling = newHeap;
child->parent = NULL;
newHeap = child;
child = next;
}
newHeap = adjustHeap(newHeap);
return newHeap;
}
void printTree(struct Node *h) {
while (h) {
printf("%d ", h->data);
printTree(h->child);
h = h->sibling;
}
}
void printHeap(struct Node *h) {
printf("Binomial Heap: \n");
while (h) {
printf("B%d: ", h->degree);
printTree(h);
printf("\n");
h = h->sibling;
}
}
int main() {
struct Node *hp = NULL;
hp = insert(hp, 10);
hp = insert(hp, 20);
hp = insert(hp, 30);
hp = insert(hp, 40);
printHeap(hp);
struct Node *min = getMin(hp);
printf("Min: %d\n", min->data);
hp = extractMin(hp);
printHeap(hp);
return 0;
}
Output
Following is the output of the above C code
Binomial Heap: B0: 10 B1: 20 B2: 30 B3: 40 Min: 10 Binomial Heap: B1: 20 B2: 30 B3: 40
#include <iostream>
#include <limits.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int data, degree;
Node *child, *sibling, *parent;
};
Node *newNode(int key) {
Node *temp = new Node;
temp->data = key;
temp->degree = 0;
temp->child = temp->parent = temp->sibling = NULL;
return temp;
}
Node *mergeBinomialTrees(Node *b1, Node *b2) {
if (b1->data > b2->data) {
Node *temp = b1;
b1 = b2;
b2 = temp;
}
b2->parent = b1;
b2->sibling = b1->child;
b1->child = b2;
b1->degree++;
return b1;
}
Node *unionBinomialHeap(Node *h1, Node *h2) {
if (!h1) return h2;
if (!h2) return h1;
Node *newHeap = NULL, **pos = &newHeap;
Node *curr1 = h1, *curr2 = h2;
while (curr1 && curr2) {
if (curr1->degree <= curr2->degree) {
*pos = curr1;
curr1 = curr1->sibling;
} else {
*pos = curr2;
curr2 = curr2->sibling;
}
pos = &((*pos)->sibling);
}
*pos = (curr1) ? curr1 : curr2;
return newHeap;
}
Node *adjustHeap(Node *head) {
if (!head) return NULL;
Node *prev = NULL, *curr = head, *next = head->sibling;
while (next) {
if (curr->degree != next->degree || (next->sibling && next->sibling->degree == curr->degree)) {
prev = curr;
curr = next;
} else {
if (curr->data <= next->data) {
curr->sibling = next->sibling;
curr = mergeBinomialTrees(curr, next);
} else {
if (!prev) head = next;
else prev->sibling = next;
curr = mergeBinomialTrees(next, curr);
}
}
next = curr->sibling;
}
return head;
}
Node *insert(Node *heap, int key) {
Node *temp = newNode(key);
return adjustHeap(unionBinomialHeap(heap, temp));
}
Node *getMin(Node *heap) {
if (!heap) return NULL;
Node *min = heap;
Node *curr = heap->sibling;
while (curr) {
if (curr->data < min->data) min = curr;
curr = curr->sibling;
}
return min;
}
Node *extractMin(Node *heap) {
if (!heap) return NULL;
Node *min = getMin(heap);
Node *prev = NULL, *curr = heap;
while (curr != min) {
prev = curr;
curr = curr->sibling;
}
if (prev) prev->sibling = min->sibling;
else heap = min->sibling;
Node *child = min->child;
Node *newHeap = NULL;
while (child) {
Node *next = child->sibling;
child->sibling = newHeap;
child->parent = NULL;
newHeap = child;
child = next;
}
newHeap = adjustHeap(newHeap);
return newHeap;
}
void printTree(Node *h) {
while (h) {
cout << h->data << " ";
printTree(h->child);
h = h->sibling;
}
}
void printHeap(Node *h) {
cout << "Binomial Heap: " << endl;
while (h) {
cout << "B" << h->degree << ": ";
printTree(h);
cout << endl;
h = h->sibling;
}
}
int main() {
Node *hp = NULL;
hp = insert(hp, 10);
hp = insert(hp, 20);
hp = insert(hp, 30);
hp = insert(hp, 40);
printHeap(hp);
Node *min = getMin(hp);
cout << "Min: " << min->data << endl;
hp = extractMin(hp);
printHeap(hp);
return 0;
}
Output
Following is the output of the above C++ code
Binomial Heap: B0: 10 B1: 20 B2: 30 B3: 40 Min: 10 Binomial Heap: B1: 20 B2: 30 B3: 40
import java.util.*;
class Node {
int data, degree;
Node child, parent, sibling;
}
public class BinomialHeap {
Node newNode(int key) {
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = key;
temp.degree = 0;
temp.child = temp.parent = temp.sibling = null;
return temp;
}
Node mergeBinomialTrees(Node b1, Node b2) {
if (b1.data > b2.data) {
Node temp = b1;
b1 = b2;
b2 = temp;
}
b2.parent = b1;
b2.sibling = b1.child;
b1.child = b2;
b1.degree++;
return b1;
}
Node unionBinomialHeap(Node h1, Node h2) {
if (h1 == null) return h2;
if (h2 == null) return h1;
Node dummy = new Node();
Node tail = dummy;
Node curr1 = h1, curr2 = h2;
while (curr1 != null && curr2 != null) {
if (curr1.degree <= curr2.degree) {
tail.sibling = curr1;
curr1 = curr1.sibling;
} else {
tail.sibling = curr2;
curr2 = curr2.sibling;
}
tail = tail.sibling;
}
tail.sibling = (curr1 != null) ? curr1 : curr2;
return dummy.sibling;
}
Node adjustHeap(Node head) {
if (head == null) return null;
Node prev = null, curr = head, next = head.sibling;
while (next != null) {
if (curr.degree != next.degree ||
(next.sibling != null && next.sibling.degree == curr.degree)) {
prev = curr;
curr = next;
} else {
if (curr.data <= next.data) {
curr.sibling = next.sibling;
curr = mergeBinomialTrees(curr, next);
} else {
if (prev == null) head = next;
else prev.sibling = next;
curr = mergeBinomialTrees(next, curr);
}
}
next = curr.sibling;
}
return head;
}
Node insert(Node heap, int key) {
Node temp = newNode(key);
return adjustHeap(unionBinomialHeap(heap, temp));
}
Node getMin(Node heap) {
if (heap == null) return null;
Node min = heap;
Node curr = heap.sibling;
while (curr != null) {
if (curr.data < min.data) min = curr;
curr = curr.sibling;
}
return min;
}
Node extractMin(Node heap) {
if (heap == null) return null;
Node min = getMin(heap);
Node prev = null, curr = heap;
while (curr != min) {
prev = curr;
curr = curr.sibling;
}
if (prev != null) prev.sibling = min.sibling;
else heap = min.sibling;
// Reverse child list
Node child = min.child;
Node newHeap = null;
while (child != null) {
Node next = child.sibling;
child.sibling = newHeap;
child.parent = null;
newHeap = child;
child = next;
}
return adjustHeap(unionBinomialHeap(heap, newHeap));
}
void printTree(Node h) {
while (h != null) {
System.out.print(h.data + " ");
printTree(h.child);
h = h.sibling;
}
}
void printHeap(Node h) {
System.out.println("Binomial Heap: ");
while (h != null) {
System.out.print("B" + h.degree + ": ");
printTree(h);
System.out.println();
h = h.sibling;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinomialHeap bh = new BinomialHeap();
Node hp = null;
hp = bh.insert(hp, 10);
hp = bh.insert(hp, 20);
hp = bh.insert(hp, 30);
hp = bh.insert(hp, 40);
bh.printHeap(hp);
Node min = bh.getMin(hp);
System.out.println("Min: " + min.data);
hp = bh.extractMin(hp);
bh.printHeap(hp);
}
}
Output
Following is the output of the above Java code
Binomial Heap: B0: 10 B1: 20 B2: 30 B3: 40 Min: 10 Binomial Heap: B1: 20 B2: 30 B3: 40
class Node:
def __init__(self, key):
self.data = key
self.degree = 0
self.child = self.parent = self.sibling = None
def mergeBinomialTrees(b1, b2):
if b1.data > b2.data:
temp = b1
b1 = b2
b2 = temp
b2.parent = b1
b2.sibling = b1.child
b1.child = b2
b1.degree += 1
return b1
def unionBinomialHeap(h1, h2):
if not h1: return h2
if not h2: return h1
newHeap = None
if h1.degree <= h2.degree:
newHeap = h1
h1 = h1.sibling
else:
newHeap = h2
h2 = h2.sibling
pos = newHeap
while h1 and h2:
if h1.degree <= h2.degree:
pos.sibling = h1
h1 = h1.sibling
else:
pos.sibling = h2
h2 = h2.sibling
pos = pos.sibling
if h1:
pos.sibling = h1
else:
pos.sibling = h2
return newHeap
def adjustHeap(head):
if not head: return None
prev = None
curr = head
next = head.sibling
while next:
if curr.degree != next.degree or (next.sibling and next.sibling.degree == curr.degree):
prev = curr
curr = next
else:
if curr.data <= next.data:
curr.sibling = next.sibling
curr = mergeBinomialTrees(curr, next)
else:
if not prev: head = next
else: prev.sibling = next
curr = mergeBinomialTrees(next, curr)
next = curr.sibling
return head
def insert(heap, key):
temp = Node(key)
return adjustHeap(unionBinomialHeap(heap, temp))
def getMin(heap):
if not heap: return None
min = heap
curr = heap.sibling
while curr:
if curr.data < min.data: min = curr
curr = curr.sibling
return min
def extractMin(heap):
if not heap: return None
min = getMin(heap)
prev = None
curr = heap
while curr != min:
prev = curr
curr = curr.sibling
if prev: prev.sibling = min.sibling
else: heap = min.sibling
child = min.child
newHeap = None
while child:
next = child.sibling
child.sibling = newHeap
child.parent = None
newHeap = child
child = next
newHeap = adjustHeap(newHeap)
return newHeap
def printTree(h):
while h:
print(h.data, end=" ")
printTree(h.child)
h = h.sibling
def printHeap(h):
print("Binomial Heap: ")
while h:
print("B" + str(h.degree) + ": ", end="")
printTree(h)
print()
h = h.sibling
hp = None
hp = insert(hp, 10)
hp = insert(hp, 20)
hp = insert(hp, 30)
hp = insert(hp, 40)
printHeap(hp)
min = getMin(hp)
print("Min: " + str(min.data))
hp = extractMin(hp)
printHeap(hp)
Output
Following is the output of the above Python code
Binomial Heap: B0: 10 B1: 20 B2: 30 B3: 40 Min: 10 Binomial Heap: B1: 20 B2: 30 B3: 40
Decrease-Key Operation in Binomial Heap
Decrease-key is a important operation in the binomial heap. It is used to decrease the value of a key in the binomial heap. The decrease-key operation is performed as follows
Algorithm for Decrease-Key Operation
Follow the steps below to decrease-key.
1. Decrease the value of the key to a new value. 2. If the new value is greater than the parent of the node, then return. 3. If the new value is less than the parent of the node, then swap the values of the node and its parent. 4. Repeat the above step until the node reaches the root or the parent of the node is less than the node.
Code for Decrease-Key Operation in Binomial Heap
Following is the implementation of decrease-key operation in C, C++, Java and Python.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <limits.h>
struct Node {
int data, degree;
struct Node *child, *sibling, *parent;
};
struct Node *newNode(int key) {
struct Node *temp = (struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
temp->data = key;
temp->degree = 0;
temp->child = temp->parent = temp->sibling = NULL;
return temp;
}
struct Node *mergeBinomialTrees(struct Node *b1, struct Node *b2) {
if (b1->data > b2->data) {
struct Node *temp = b1;
b1 = b2;
b2 = temp;
}
b2->parent = b1;
b2->sibling = b1->child;
b1->child = b2;
b1->degree++;
return b1;
}
struct Node *unionBinomialHeap(struct Node *h1, struct Node *h2) {
if (!h1) return h2;
if (!h2) return h1;
struct Node *newHeap = NULL, **pos = &newHeap;
struct Node *curr1 = h1, *curr2 = h2;
while (curr1 && curr2) {
if (curr1->degree <= curr2->degree) {
*pos = curr1;
curr1 = curr1->sibling;
} else {
*pos = curr2;
curr2 = curr2->sibling;
}
pos = &((*pos)->sibling);
}
*pos = (curr1) ? curr1 : curr2;
return newHeap;
}
struct Node *adjustHeap(struct Node *head) {
if (!head) return NULL;
struct Node *prev = NULL, *curr = head, *next = head->sibling;
while (next) {
if (curr->degree != next->degree || (next->sibling && next->sibling->degree == curr->degree)) {
prev = curr;
curr = next;
} else {
if (curr->data <= next->data) {
curr->sibling = next->sibling;
curr = mergeBinomialTrees(curr, next);
} else {
if (!prev) head = next;
else prev->sibling = next;
curr = mergeBinomialTrees(next, curr);
}
}
next = curr->sibling;
}
return head;
}
struct Node *insert(struct Node *heap, int key) {
struct Node *temp = newNode(key);
return adjustHeap(unionBinomialHeap(heap, temp));
}
struct Node *getMin(struct Node *heap) {
if (!heap) return NULL;
struct Node *min = heap;
struct Node *curr = heap->sibling;
while (curr) {
if (curr->data < min->data) min = curr;
curr = curr->sibling;
}
return min;
}
struct Node *extractMin(struct Node *heap) {
if (!heap) return NULL;
struct Node *min = getMin(heap);
struct Node *prev = NULL, *curr = heap;
while (curr != min) {
prev = curr;
curr = curr->sibling;
}
if (prev) prev->sibling = min->sibling;
else heap = min->sibling;
struct Node *child = min->child;
struct Node *newHeap = NULL;
while (child) {
struct Node *next = child->sibling;
child->sibling = newHeap;
child->parent = NULL;
newHeap = child;
child = next;
}
newHeap = adjustHeap(newHeap);
return newHeap;
}
void decreaseKey(struct Node *heap, struct Node *node, int key) {
if (!heap || !node) return;
if (key > node->data) return;
node->data = key;
struct Node *parent = node->parent;
while (parent && node->data < parent->data) {
int temp = node->data;
node->data = parent->data;
parent->data = temp;
node = parent;
parent = node->parent;
}
}
void printTree(struct Node *h) {
while (h) {
printf("%d ", h->data);
printTree(h->child);
h = h->sibling;
}
}
void printHeap(struct Node *h) {
while (h) {
printf("B%d: ", h->degree);
printTree(h);
printf("\n");
h = h->sibling;
}
}
int main() {
struct Node *hp = NULL;
hp = insert(hp, 10);
hp = insert(hp, 20);
hp = insert(hp, 30);
hp = insert(hp, 40);
printf("Binomial Heap: \n");
printHeap(hp);
struct Node *min = getMin(hp);
printf("Min: %d\n", min->data);
decreaseKey(hp, hp->sibling, 5);
printf("Binomial Heap after Decrease-Key operation\n");
printHeap(hp);
return 0;
}
Output
Following is the output of the above C code
Binomial Heap: B2: 10 30 40 20 Min: 10 Binomial Heap after Decrease-Key operation B2: 10 30 40 20
#include <iostream>
#include <limits.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int data, degree;
Node *child, *sibling, *parent;
};
Node *newNode(int key) {
Node *temp = new Node;
temp->data = key;
temp->degree = 0;
temp->child = temp->parent = temp->sibling = NULL;
return temp;
}
Node *mergeBinomialTrees(Node *b1, Node *b2) {
if (b1->data > b2->data) {
Node *temp = b1;
b1 = b2;
b2 = temp;
}
b2->parent = b1;
b2->sibling = b1->child;
b1->child = b2;
b1->degree++;
return b1;
}
Node *unionBinomialHeap(Node *h1, Node *h2) {
if (!h1) return h2;
if (!h2) return h1;
Node *newHeap = NULL, **pos = &newHeap;
Node *curr1 = h1, *curr2 = h2;
while (curr1 && curr2) {
if (curr1->degree <= curr2->degree) {
*pos = curr1;
curr1 = curr1->sibling;
} else {
*pos = curr2;
curr2 = curr2->sibling;
}
pos = &((*pos)->sibling);
}
*pos = (curr1) ? curr1 : curr2;
return newHeap;
}
Node *adjustHeap(Node *head) {
if (!head) return NULL;
Node *prev = NULL, *curr = head, *next = head->sibling;
while (next) {
if (curr->degree != next->degree || (next->sibling && next->sibling->degree == curr->degree)) {
prev = curr;
curr = next;
} else {
if (curr->data <= next->data) {
curr->sibling = next->sibling;
curr = mergeBinomialTrees(curr, next);
} else {
if (!prev) head = next;
else prev->sibling = next;
curr = mergeBinomialTrees(next, curr);
}
}
next = curr->sibling;
}
return head;
}
Node *insert(Node *heap, int key) {
Node *temp = newNode(key);
return adjustHeap(unionBinomialHeap(heap, temp));
}
Node *getMin(Node *heap) {
if (!heap) return NULL;
Node *min = heap;
Node *curr = heap->sibling;
while (curr) {
if (curr->data < min->data) min = curr;
curr = curr->sibling;
}
return min;
}
Node *extractMin(Node *heap) {
if (!heap) return NULL;
Node *min = getMin(heap);
Node *prev = NULL, *curr = heap;
while (curr != min) {
prev = curr;
curr = curr->sibling;
}
if (prev) prev->sibling = min->sibling;
else heap = min->sibling;
Node *child = min->child;
Node *newHeap = NULL;
while (child) {
Node *next = child->sibling;
child->sibling = newHeap;
child->parent = NULL;
newHeap = child;
child = next;
}
newHeap = adjustHeap(newHeap);
return newHeap;
}
void decreaseKey(Node *heap, Node *node, int key) {
if (!heap || !node) return;
if (key > node->data) return;
node->data = key;
Node *parent = node->parent;
while (parent && node->data < parent->data) {
int temp = node->data;
node->data = parent->data;
parent->data = temp;
node = parent;
parent = node->parent;
}
}
void printTree(Node *h) {
while (h) {
cout << h->data << " ";
printTree(h->child);
h = h->sibling;
}
}
void printHeap(Node *h) {
while (h) {
cout << "B" << h->degree << ": ";
printTree(h);
cout << endl;
h = h->sibling;
}
}
int main() {
Node *hp = NULL;
hp = insert(hp, 10);
hp = insert(hp, 20);
hp = insert(hp, 30);
hp = insert(hp, 40);
cout << "Binomial Heap:" << endl;
printHeap(hp);
Node *min = getMin(hp);
cout << "Min: " << min->data << endl;
decreaseKey(hp, hp->sibling, 5);
cout << "Binomial Heap after Decrease-Key operation" << endl;
printHeap(hp);
return 0;
}
Output
Following is the output of the above C++ code
Binomial Heap: B2: 10 30 40 20 Min: 10 Binomial Heap after Decrease-Key operation B2: 10 30 40 20
import java.util.*;
class Node {
int data, degree;
Node child, parent, sibling;
}
public class BinomialHeap {
Node newNode(int key) {
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = key;
temp.degree = 0;
temp.child = temp.parent = temp.sibling = null;
return temp;
}
Node mergeBinomialTrees(Node b1, Node b2) {
if (b1.data > b2.data) {
Node temp = b1;
b1 = b2;
b2 = temp;
}
b2.parent = b1;
b2.sibling = b1.child;
b1.child = b2;
b1.degree++;
return b1;
}
Node unionBinomialHeap(Node h1, Node h2) {
if (h1 == null) return h2;
if (h2 == null) return h1;
Node newHeap = null, tail = null;
Node curr1 = h1, curr2 = h2;
// Merging two heaps by linking nodes in increasing order of degree
while (curr1 != null && curr2 != null) {
Node smaller;
if (curr1.degree <= curr2.degree) {
smaller = curr1;
curr1 = curr1.sibling;
} else {
smaller = curr2;
curr2 = curr2.sibling;
}
if (newHeap == null) {
newHeap = smaller;
tail = newHeap;
} else {
tail.sibling = smaller;
tail = tail.sibling;
}
}
if (curr1 != null) tail.sibling = curr1;
if (curr2 != null) tail.sibling = curr2;
return newHeap;
}
Node adjustHeap(Node head) {
if (head == null) return null;
Node prev = null, curr = head, next = head.sibling;
while (next != null) {
if (curr.degree != next.degree ||
(next.sibling != null && next.sibling.degree == curr.degree)) {
prev = curr;
curr = next;
} else {
if (curr.data <= next.data) {
curr.sibling = next.sibling;
curr = mergeBinomialTrees(curr, next);
} else {
if (prev == null) head = next;
else prev.sibling = next;
curr = mergeBinomialTrees(next, curr);
}
}
next = curr.sibling;
}
return head;
}
Node insert(Node heap, int key) {
Node temp = newNode(key);
return adjustHeap(unionBinomialHeap(heap, temp));
}
Node getMin(Node heap) {
if (heap == null) return null;
Node min = heap;
Node curr = heap.sibling;
while (curr != null) {
if (curr.data < min.data) min = curr;
curr = curr.sibling;
}
return min;
}
Node extractMin(Node heap) {
if (heap == null) return null;
Node min = getMin(heap);
Node prev = null, curr = heap;
while (curr != min) {
prev = curr;
curr = curr.sibling;
}
if (prev != null) prev.sibling = min.sibling;
else heap = min.sibling;
Node child = min.child;
Node newHeap = null;
while (child != null) {
Node next = child.sibling;
child.sibling = newHeap;
child.parent = null;
newHeap = child;
child = next;
}
return adjustHeap(unionBinomialHeap(heap, newHeap));
}
void decreaseKey(Node heap, Node node, int key) {
if (heap == null || node == null) return;
if (key > node.data) return;
node.data = key;
Node parent = node.parent;
while (parent != null && node.data < parent.data) {
int temp = node.data;
node.data = parent.data;
parent.data = temp;
node = parent;
parent = node.parent;
}
}
void printTree(Node h) {
while (h != null) {
System.out.print(h.data + " ");
printTree(h.child);
h = h.sibling;
}
}
void printHeap(Node h) {
while (h != null) {
System.out.print("B" + h.degree + ": ");
printTree(h);
System.out.println();
h = h.sibling;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinomialHeap bh = new BinomialHeap();
Node hp = null;
hp = bh.insert(hp, 10);
hp = bh.insert(hp, 20);
hp = bh.insert(hp, 30);
hp = bh.insert(hp, 40);
System.out.println("Binomial Heap:");
bh.printHeap(hp);
Node min = bh.getMin(hp);
System.out.println("Min: " + min.data);
// Find node with value 30 and decrease its key to 5
Node nodeToDecrease = hp.child != null ? hp.child.sibling : null; // Assuming 30 is at this position
if (nodeToDecrease != null) {
bh.decreaseKey(hp, nodeToDecrease, 5);
}
System.out.println("Binomial Heap after Decrease-Key operation:");
bh.printHeap(hp);
}
}
Output
Following is the output of the above Java code
Binomial Heap: B2: 10 30 40 20 Min: 10 Binomial Heap after Decrease-Key operation: B2: 5 30 40 10
class Node:
def __init__(self, key):
self.data = key
self.degree = 0
self.child = self.parent = self.sibling = None
def mergeBinomialTrees(b1, b2):
if b1.data > b2.data:
b1, b2 = b2, b1 # Ensure b1 is the root
b2.parent = b1
b2.sibling = b1.child
b1.child = b2
b1.degree += 1
return b1
def unionBinomialHeap(h1, h2):
if not h1: return h2
if not h2: return h1
head, tail = None, None
while h1 and h2:
if h1.degree <= h2.degree:
node = h1
h1 = h1.sibling
else:
node = h2
h2 = h2.sibling
if not head:
head = node
tail = node
else:
tail.sibling = node
tail = node
tail.sibling = h1 if h1 else h2
return head
def adjustHeap(head):
if not head: return None
prev, curr, next = None, head, head.sibling
while next:
if curr.degree != next.degree or (next.sibling and next.sibling.degree == curr.degree):
prev = curr
curr = next
else:
if curr.data <= next.data:
curr.sibling = next.sibling
curr = mergeBinomialTrees(curr, next)
else:
if prev:
prev.sibling = next
else:
head = next
curr = mergeBinomialTrees(next, curr)
next = curr.sibling
return head
def insert(heap, key):
temp = Node(key)
return adjustHeap(unionBinomialHeap(heap, temp))
def getMin(heap):
if not heap: return None
minNode = heap
curr = heap.sibling
while curr:
if curr.data < minNode.data:
minNode = curr
curr = curr.sibling
return minNode
def extractMin(heap):
if not heap: return None
minNode = getMin(heap)
prev, curr = None, heap
while curr != minNode:
prev = curr
curr = curr.sibling
if prev:
prev.sibling = minNode.sibling
else:
heap = minNode.sibling
child = minNode.child
newHeap = None
while child:
nextChild = child.sibling
child.sibling = newHeap
child.parent = None
newHeap = child
child = nextChild
return adjustHeap(unionBinomialHeap(heap, newHeap))
def decreaseKey(heap, node, key):
if not node or key > node.data:
return
node.data = key
parent = node.parent
while parent and node.data < parent.data:
node.data, parent.data = parent.data, node.data
node = parent
parent = node.parent
def printTree(h):
while h:
print(h.data, end=" ")
printTree(h.child)
h = h.sibling
def printHeap(h):
while h:
print(f"B{h.degree}: ", end="")
printTree(h)
print()
h = h.sibling
# Testing the heap
hp = None
hp = insert(hp, 10)
hp = insert(hp, 20)
hp = insert(hp, 30)
hp = insert(hp, 40)
print("Binomial Heap:")
printHeap(hp)
minNode = getMin(hp)
print("Min:", minNode.data)
if hp.child:
decreaseKey(hp, hp.child, 5)
print("Binomial Heap after Decrease-Key operation:")
printHeap(hp)
Output
Following is the output of the above Python code
Binomial Heap: B2: 10 30 40 20 Min: 10 Binomial Heap after Decrease-Key operation: B2: 5 10 40 20
Delete Operation in Binomial Heap
Delete operation is used for deleting a key from a binomial heap.
Algorithm for Delete Operation
1. Decrease the key value to minus infinity. 2. Now extract the minimum value from the heap.
Code for Delete Operation in Binomial Heap
Following is the implementation of delete operation in C, C++, Java and Python.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <limits.h>
struct Node {
int data, degree;
struct Node *child, *sibling, *parent;
};
struct Node *newNode(int key) {
struct Node *temp = (struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
temp->data = key;
temp->degree = 0;
temp->child = temp->parent = temp->sibling = NULL;
return temp;
}
struct Node *mergeBinomialTrees(struct Node *b1, struct Node *b2) {
if (b1->data > b2->data) {
struct Node *temp = b1;
b1 = b2;
b2 = temp;
}
b2->parent = b1;
b2->sibling = b1->child;
b1->child = b2;
b1->degree++;
return b1;
}
struct Node *unionBinomialHeap(struct Node *h1, struct Node *h2) {
if (!h1) return h2;
if (!h2) return h1;
struct Node *newHeap = NULL, **pos = &newHeap;
struct Node *curr1 = h1, *curr2 = h2;
while (curr1 && curr2) {
if (curr1->degree <= curr2->degree) {
*pos = curr1;
curr1 = curr1->sibling;
} else {
*pos = curr2;
curr2 = curr2->sibling;
}
pos = &((*pos)->sibling);
}
*pos = (curr1) ? curr1 : curr2;
return newHeap;
}
struct Node *adjustHeap(struct Node *head) {
if (!head) return NULL;
struct Node *prev = NULL, *curr = head, *next = head->sibling;
while (next) {
if (curr->degree != next->degree || (next->sibling && next->sibling->degree == curr->degree)) {
prev = curr;
curr = next;
} else {
if (curr->data <= next->data) {
curr->sibling = next->sibling;
curr = mergeBinomialTrees(curr, next);
} else {
if (!prev) head = next;
else prev->sibling = next;
curr = mergeBinomialTrees(next, curr);
}
}
next = curr->sibling;
}
return head;
}
struct Node *insert(struct Node *heap, int key) {
struct Node *temp = newNode(key);
return adjustHeap(unionBinomialHeap(heap, temp));
}
struct Node *getMin(struct Node *heap) {
if (!heap) return NULL;
struct Node *min = heap;
struct Node *curr = heap->sibling;
while (curr) {
if (curr->data < min->data) min = curr;
curr = curr->sibling;
}
return min;
}
struct Node *extractMin(struct Node *heap) {
if (!heap) return NULL;
struct Node *min = getMin(heap);
struct Node *prev = NULL, *curr = heap;
while (curr != min) {
prev = curr;
curr = curr->sibling;
}
if (prev) prev->sibling = min->sibling;
else heap = min->sibling;
struct Node *child = min->child;
struct Node *newHeap = NULL;
while (child) {
struct Node *next = child->sibling;
child->sibling = newHeap;
child->parent = NULL;
newHeap = child;
child = next;
}
newHeap = adjustHeap(newHeap);
return newHeap;
}
void deleteKey(struct Node **heap, struct Node *node) {
if (!*heap || !node) return;
node->data = INT_MIN;
struct Node *parent = node->parent;
while (parent && node->data < parent->data) {
int temp = node->data;
node->data = parent->data;
parent->data = temp;
node = parent;
parent = node->parent;
}
*heap = extractMin(*heap);
}
void printTree(struct Node *h) {
while (h) {
printf("%d ", h->data);
printTree(h->child);
h = h->sibling;
}
}
void printHeap(struct Node *h) {
printf("Binomial Heap: \n");
while (h) {
printf("B%d: ", h->degree);
printTree(h);
printf("\n");
h = h->sibling;
}
}
int main() {
struct Node *hp = NULL;
hp = insert(hp, 10);
hp = insert(hp, 20);
hp = insert(hp, 30);
hp = insert(hp, 40);
printHeap(hp);
struct Node *min = getMin(hp);
printf("Min: %d\n", min->data);
deleteKey(&hp, hp->sibling);
printf("Binomial Heap after Delete operation\n");
printHeap(hp);
return 0;
}
Output
Following is the output of the above C code
Binomial Heap: B0: 10 B1: 20 B2: 30 B3: 40 Min: 10 Binomial Heap after Delete operation B0: 10 B1: 30 B2: 40
#include <iostream>
#include <limits.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int data, degree;
Node *child, *sibling, *parent;
};
Node *newNode(int key) {
Node *temp = new Node;
temp->data = key;
temp->degree = 0;
temp->child = temp->parent = temp->sibling = NULL;
return temp;
}
Node *mergeBinomialTrees(Node *b1, Node *b2) {
if (b1->data > b2->data) {
Node *temp = b1;
b1 = b2;
b2 = temp;
}
b2->parent = b1;
b2->sibling = b1->child;
b1->child = b2;
b1->degree++;
return b1;
}
Node *unionBinomialHeap(Node *h1, Node *h2) {
if (!h1) return h2;
if (!h2) return h1;
Node *newHeap = NULL, **pos = &newHeap;
Node *curr1 = h1, *curr2 = h2;
while (curr1 && curr2) {
if (curr1->degree <= curr2->degree) {
*pos = curr1;
curr1 = curr1->sibling;
} else {
*pos = curr2;
curr2 = curr2->sibling;
}
pos = &((*pos)->sibling);
}
*pos = (curr1) ? curr1 : curr2;
return newHeap;
}
Node *adjustHeap(Node *head) {
if (!head) return NULL;
Node *prev = NULL, *curr = head, *next = head->sibling;
while (next) {
if (curr->degree != next->degree || (next->sibling && next->sibling->degree == curr->degree)) {
prev = curr;
curr = next;
} else {
if (curr->data <= next->data) {
curr->sibling = next->sibling;
curr = mergeBinomialTrees(curr, next);
} else {
if (!prev) head = next;
else prev->sibling = next;
curr = mergeBinomialTrees(next, curr);
}
}
next = curr->sibling;
}
return head;
}
Node *insert(Node *heap, int key) {
Node *temp = newNode(key);
return adjustHeap(unionBinomialHeap(heap, temp));
}
Node *getMin(Node *heap) {
if (!heap) return NULL;
Node *min = heap;
Node *curr = heap->sibling;
while (curr) {
if (curr->data < min->data) min = curr;
curr = curr->sibling;
}
return min;
}
Node *extractMin(Node *heap) {
if (!heap) return NULL;
Node *min = getMin(heap);
Node *prev = NULL, *curr = heap;
while (curr != min) {
prev = curr;
curr = curr->sibling;
}
if (prev) prev->sibling = min->sibling;
else heap = min->sibling;
Node *child = min->child;
Node *newHeap = NULL;
while (child) {
Node *next = child->sibling;
child->sibling = newHeap;
child->parent = NULL;
newHeap = child;
child = next;
}
newHeap = adjustHeap(newHeap);
return newHeap;
}
void deleteKey(Node *heap, Node *node) {
if (!heap || !node) return;
node->data = INT_MIN;
Node *parent = node->parent;
while (parent && node->data < parent->data) {
int temp = node->data;
node->data = parent->data;
parent->data = temp;
node = parent;
parent = node->parent;
}
extractMin(heap);
}
void printTree(Node *h) {
while (h) {
cout << h->data << " ";
printTree(h->child);
h = h->sibling;
}
}
void printHeap(Node *h) {
cout << "Binomial Heap: " << endl;
while (h) {
cout << "B" << h->degree << ": ";
printTree(h);
cout << endl;
h = h->sibling;
}
}
int main() {
Node *hp = NULL;
hp = insert(hp, 10);
hp = insert(hp, 20);
hp = insert(hp, 30);
hp = insert(hp, 40);
printHeap(hp);
Node *min = getMin(hp);
cout << "Min: " << min->data << endl;
deleteKey(hp, hp->sibling);
cout << "Binomial Heap after Delete operation" << endl;
printHeap(hp);
return 0;
}
Output
Following is the output of the above C++ code
Binomial Heap: B0: 10 B1: 20 B2: 30 B3: 40 Min: 10 Binomial Heap after Delete operation B0: 10 B1: 30 B2: 40
import java.util.*;
class Node {
int data, degree;
Node child, parent, sibling;
}
public class BinomialHeap {
Node newNode(int key) {
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = key;
temp.degree = 0;
temp.child = temp.parent = temp.sibling = null;
return temp;
}
Node mergeBinomialTrees(Node b1, Node b2) {
if (b1.data > b2.data) {
Node temp = b1;
b1 = b2;
b2 = temp;
}
b2.parent = b1;
b2.sibling = b1.child;
b1.child = b2;
b1.degree++;
return b1;
}
Node unionBinomialHeap(Node h1, Node h2) {
if (h1 == null) return h2;
if (h2 == null) return h1;
Node newHeap = null, pos = newHeap;
Node curr1 = h1, curr2 = h2;
while (curr1 != null && curr2 != null) {
if (curr1.degree <= curr2.degree) {
if (newHeap == null) {
newHeap = curr1;
pos = curr1;
} else {
pos.sibling = curr1;
pos = curr1;
}
curr1 = curr1.sibling;
} else {
if (newHeap == null) {
newHeap = curr2;
pos = curr2;
} else {
pos.sibling = curr2;
pos = curr2;
}
curr2 = curr2.sibling;
}
}
if (curr1 != null) pos.sibling = curr1;
if (curr2 != null) pos.sibling = curr2;
return newHeap;
}
Node adjustHeap(Node head) {
if (head == null) return null;
Node prev = null, curr = head, next = head.sibling;
while (next != null) {
if (curr.degree != next.degree || (next.sibling != null && next.sibling.degree == curr.degree)) {
prev = curr;
curr = next;
} else {
if (curr.data <= next.data) {
curr.sibling = next.sibling;
curr = mergeBinomialTrees(curr, next);
} else {
if (prev == null) head = next;
else prev.sibling = next;
curr = mergeBinomialTrees(next, curr);
}
}
next = curr.sibling;
}
return head;
}
Node insert(Node heap, int key) {
Node temp = newNode(key);
return adjustHeap(unionBinomialHeap(heap, temp));
}
Node getMin(Node heap) {
if (heap == null) return null;
Node min = heap;
Node curr = heap.sibling;
while (curr != null) {
if (curr.data < min.data) min = curr;
curr = curr.sibling;
}
return min;
}
Node extractMin(Node heap) {
if (heap == null) return null;
Node min = getMin(heap);
Node prev = null, curr = heap;
while (curr != min) {
prev = curr;
curr = curr.sibling;
}
if (prev != null) prev.sibling = min.sibling;
else heap = min.sibling;
Node child = min.child;
Node newHeap = null;
while (child != null) {
Node next = child.sibling;
child.sibling = newHeap;
child.parent = null;
newHeap = child;
child = next;
}
newHeap = adjustHeap(newHeap);
return newHeap;
}
void deleteKey(Node heap, Node node) {
if (heap == null || node == null) return;
node.data = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
Node parent = node.parent;
while (parent != null && node.data < parent.data) {
int temp = node.data;
node.data = parent.data;
parent.data = temp;
node = parent;
parent = node.parent;
}
extractMin(heap);
}
void printTree(Node h) {
while (h != null) {
System.out.print(h.data + " ");
printTree(h.child);
h = h.sibling;
}
}
void printHeap(Node h) {
System.out.println("Binomial Heap: ");
while (h != null) {
System.out.print("B" + h.degree + ": ");
printTree(h);
System.out.println();
h = h.sibling;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinomialHeap bh = new BinomialHeap();
Node hp = null;
hp = bh.insert(hp, 10);
hp = bh.insert(hp, 20);
hp = bh.insert(hp, 30);
hp = bh.insert(hp, 40);
bh.printHeap(hp);
Node min = bh.getMin(hp);
System.out.println("Min: " + min.data);
bh.deleteKey(hp, hp.child);
System.out.println("Binomial Heap after Delete operation");
bh.printHeap(hp);
}
}
Output
Following is the output of the above Java code
Binomial Heap: B0: 10 B1: 20 B2: 30 B3: 40 Min: 10 Binomial Heap after Delete operation B0: 10 B1: 30 B2: 40
class Node:
def __init__(self, key):
self.data = key
self.degree = 0
self.child = self.parent = self.sibling = None
def mergeBinomialTrees(b1, b2):
if b1.data > b2.data:
b1, b2 = b2, b1 # Ensure b1 is the root
b2.parent = b1
b2.sibling = b1.child
b1.child = b2
b1.degree += 1
return b1
def unionBinomialHeap(h1, h2):
if not h1: return h2
if not h2: return h1
head, tail = None, None
while h1 and h2:
if h1.degree <= h2.degree:
node = h1
h1 = h1.sibling
else:
node = h2
h2 = h2.sibling
if not head:
head = node
tail = node
else:
tail.sibling = node
tail = node
tail.sibling = h1 if h1 else h2
return head
def adjustHeap(head):
if not head: return None
prev, curr, next = None, head, head.sibling
while next:
if curr.degree != next.degree or (next.sibling and next.sibling.degree == curr.degree):
prev = curr
curr = next
else:
if curr.data <= next.data:
curr.sibling = next.sibling
curr = mergeBinomialTrees(curr, next)
else:
if prev:
prev.sibling = next
else:
head = next
curr = mergeBinomialTrees(next, curr)
next = curr.sibling
return head
def insert(heap, key):
temp = Node(key)
return adjustHeap(unionBinomialHeap(heap, temp))
def getMin(heap):
if not heap: return None
minNode = heap
curr = heap.sibling
while curr:
if curr.data < minNode.data:
minNode = curr
curr = curr.sibling
return minNode
def extractMin(heap):
if not heap: return None
minNode = getMin(heap)
prev, curr = None, heap
while curr != minNode:
prev = curr
curr = curr.sibling
if prev:
prev.sibling = minNode.sibling
else:
heap = minNode.sibling
child = minNode.child
newHeap = None
while child:
nextChild = child.sibling
child.sibling = newHeap
child.parent = None
newHeap = child
child = nextChild
return adjustHeap(unionBinomialHeap(heap, newHeap))
def decreaseKey(heap, node, key):
if not node or key > node.data:
return
node.data = key
parent = node.parent
while parent and node.data < parent.data:
node.data, parent.data = parent.data, node.data
node = parent
parent = node.parent
def printTree(h):
while h:
print(h.data, end=" ")
printTree(h.child)
h = h.sibling
def printHeap(h):
while h:
print(f"B{h.degree}: ", end="")
printTree(h)
print()
h = h.sibling
# Testing the heap
def deleteKey(heap, node):
if not heap or not node: return
node.data = float('-inf')
parent = node.parent
while parent and node.data < parent.data:
node.data, parent.data = parent.data, node.data
node = parent
parent = node.parent
extractMin(heap)
hp = None
hp = insert(hp, 10)
hp = insert(hp, 20)
hp = insert(hp, 30)
hp = insert(hp, 40)
printHeap(hp)
min_node = getMin(hp)
print("Min:", min_node.data)
deleteKey(hp, hp.child)
print("Binomial Heap after Delete operation:")
printHeap(hp)
Output
Following is the output of the above Python code
Binomial Heap: B0: 10 B1: 20 B2: 30 B3: 40 Min: 10 Binomial Heap after Delete operation B0: 10 B1: 30 B2: 40
Time Complexity of Binomial Heap
Following are the time complexities of the Binomial Heap
- Insertion: O(log n)
- Deletion: O(log n)
- Decrease-Key: O(log n)
- Extract-Min: O(log n)
- Get-Min: O(1)
Applications of Binomial Heap
Binomial heaps are used in plenty of applications. Some of them are listed below
- Used in implementing priority queues.
- Dijkstra's shortest path algorithm.
- Prim's minimum spanning tree algorithm.
- Used in garbage collection.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we have learned about Binomial Heap, its operations, and its implementation in C, C++, Java, and Python. We also discussed the time complexity of the Binomial Heap and its applications.