
- DSA using Java - Home
- DSA using Java - Overview
- DSA using Java - Environment Setup
- DSA using Java - Algorithms
- DSA using Java - Data Structures
- DSA using Java - Array
- DSA using Java - Linked List
- DSA using Java - Doubly Linked List
- DSA using Java - Circular Linked List
- DSA using Java - Stack
- DSA - Parsing Expressions
- DSA using Java - Queue
- DSA using Java - Priority Queue
- DSA using Java - Tree
- DSA using Java - Hash Table
- DSA using Java - Heap
- DSA using Java - Graph
- DSA using Java - Search techniques
- DSA using Java - Sorting techniques
- DSA using Java - Recursion
- DSA using Java Useful Resources
- DSA using Java - Quick Guide
- DSA using Java - Useful Resources
- DSA using Java - Discussion
DSA using Java - Linked List
Linked List Basics
Linked List is a sequence of links which contains items. Each link contains a connection to another link. Linked list the second most used data structure after array. Following are important terms to understand the concepts of Linked List.
Link − Each Link of a linked list can store a data called an element.
Next − Each Link of a linked list contain a link to next link called Next.
LinkedList − A LinkedList contains the connection link to the first Link called First.
Linked List Representation
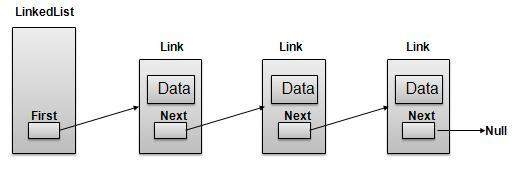
As per above shown illustration, following are the important points to be considered.
LinkedList contains an link element called first.
Each Link carries a data field(s) and a Link Field called next.
Each Link is linked with its next link using its next link.
Last Link carries a Link as null to mark the end of the list.
Types of Linked List
Following are the various flavours of linked list.
Simple Linked List − Item Navigation is forward only.
Doubly Linked List − Items can be navigated forward and backward way.
Circular Linked List − Last item contains link of the first element as next and and first element has link to last element as prev.
Basic Operations
Following are the basic operations supported by a list.
Insertion − add an element at the beginning of the list.
Deletion − delete an element at the beginning of the list.
Display − displaying complete list.
Search − search an element using given key.
Delete − delete an element using given key.
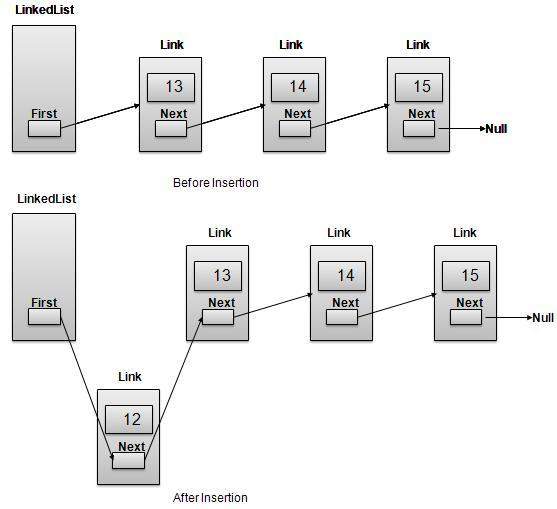
Insertion Operation
Insertion is a three step process:
Create a new Link with provided data.
Point New Link to old First Link.
Point First Link to this New Link.
//insert link at the first location
public void insertFirst(int key, int data){
//create a link
Link link = new Link(key,data);
//point it to old first node
link.next = first;
//point first to new first node
first = link;
}
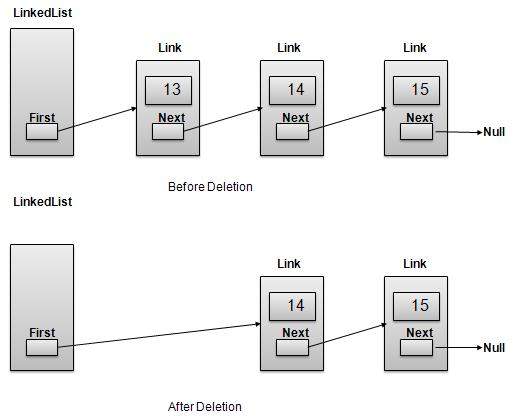
Deletion Operation
Deletion is a two step process:
Get the Link pointed by First Link as Temp Link.
Point First Link to Temp Link's Next Link.
//delete first item
public Link deleteFirst(){
//save reference to first link
Link tempLink = first;
//mark next to first link as first
first = first.next;
//return the deleted link
return tempLink;
}
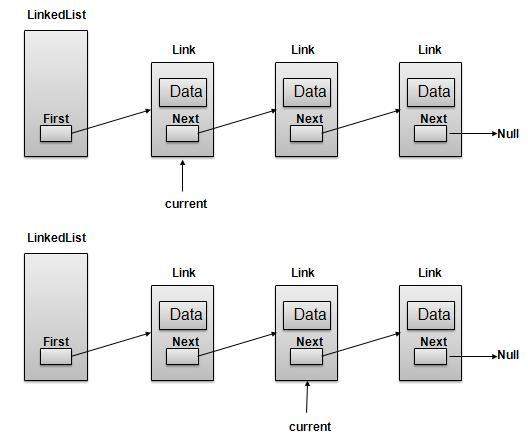
Navigation Operation
Navigation is a recursive step process and is basis of many operations like search, delete etc.:
Get the Link pointed by First Link as Current Link.
Check if Current Link is not null and display it.
Point Current Link to Next Link of Current Link and move to above step.
Note
//display the list
public void display(){
//start from the beginning
Link current = first;
//navigate till the end of the list
System.out.print("[ ");
while(current != null){
//print data
current.display();
//move to next item
current = current.next;
System.out.print(" ");
}
System.out.print(" ]");
}
Advanced Operations
Following are the advanced operations specified for a list.
Sort − sorting a list based on a particular order.
Reverse − reversing a linked list.
Concatenate − concatenate two lists.
Sort Operation
We've used bubble sort to sort a list.
public void sort(){
int i, j, k, tempKey, tempData ;
Link current,next;
int size = length();
k = size ;
for ( i = 0 ; i < size - 1 ; i++, k-- ) {
current = first ;
next = first.next ;
for ( j = 1 ; j < k ; j++ ) {
if ( current.data > next.data ) {
tempData = current.data ;
current.data = next.data;
next.data = tempData ;
tempKey = current.key;
current.key = next.key;
next.key = tempKey;
}
current = current.next;
next = next.next;
}
}
}
Reverse Operation
Following code demonstrate reversing a single linked list.
public LinkedList reverse() {
LinkedList reversedlist = new LinkedList();
Link nextLink = null;
reversedlist.insertFirst(first.key, first.data);
Link currentLink = first;
// Until no more data in list,
// insert current link before first and move ahead.
while(currentLink.next != null){
nextLink = currentLink.next;
// Insert at start of new list.
reversedlist.insertFirst(nextLink.key, nextLink.data);
//advance to next node
currentLink = currentLink.next;
}
return reversedlist;
}
Concatenate Operation
Following code demonstrate reversing a single linked list.
public void concatenate(LinkedList list){
if(first == null){
first = list.first;
}
if(list.first == null){
return;
}
Link temp = first;
while(temp.next !=null) {
temp = temp.next;
}
temp.next = list.first;
}
Demo
Link.java
package com.tutorialspoint;
public class Link {
public int key;
public int data;
public Link next;
public Link(int key, int data){
this.key = key;
this.data = data;
}
public void display(){
System.out.print("{"+key+","+data+"}");
}
}
LinkedList.java
package com.tutorialspoint;
public class LinkedList {
//this link always point to first Link
//in the Linked List
private Link first;
// create an empty linked list
public LinkedList(){
first = null;
}
//insert link at the first location
public void insertFirst(int key, int data){
//create a link
Link link = new Link(key,data);
//point it to old first node
link.next = first;
//point first to new first node
first = link;
}
//delete first item
public Link deleteFirst(){
//save reference to first link
Link tempLink = first;
//mark next to first link as first
first = first.next;
//return the deleted link
return tempLink;
}
//display the list
public void display(){
//start from the beginning
Link current = first;
//navigate till the end of the list
System.out.print("[ ");
while(current != null){
//print data
current.display();
//move to next item
current = current.next;
System.out.print(" ");
}
System.out.print(" ]");
}
//find a link with given key
public Link find(int key){
//start from the first link
Link current = first;
//if list is empty
if(first == null){
return null;
}
//navigate through list
while(current.key != key){
//if it is last node
if(current.next == null){
return null;
}else{
//go to next link
current = current.next;
}
}
//if data found, return the current Link
return current;
}
//delete a link with given key
public Link delete(int key){
//start from the first link
Link current = first;
Link previous = null;
//if list is empty
if(first == null){
return null;
}
//navigate through list
while(current.key != key){
//if it is last node
if(current.next == null){
return null;
}else{
//store reference to current link
previous = current;
//move to next link
current = current.next;
}
}
//found a match, update the link
if(current == first) {
//change first to point to next link
first = first.next;
}else {
//bypass the current link
previous.next = current.next;
}
return current;
}
//is list empty
public boolean isEmpty(){
return first == null;
}
public int length(){
int length = 0;
for(Link current = first; current!=null;
current = current.next){
length++;
}
return length;
}
public void sort(){
int i, j, k, tempKey, tempData ;
Link current,next;
int size = length();
k = size ;
for ( i = 0 ; i < size - 1 ; i++, k-- ) {
current = first ;
next = first.next ;
for ( j = 1 ; j < k ; j++ ) {
if ( current.data > next.data ) {
tempData = current.data ;
current.data = next.data;
next.data = tempData ;
tempKey = current.key;
current.key = next.key;
next.key = tempKey;
}
current = current.next;
next = next.next;
}
}
}
public LinkedList reverse() {
LinkedList reversedlist = new LinkedList();
Link nextLink = null;
reversedlist.insertFirst(first.key, first.data);
Link currentLink = first;
// Until no more data in list,
// insert current link before first and move ahead.
while(currentLink.next != null){
nextLink = currentLink.next;
// Insert at start of new list.
reversedlist.insertFirst(nextLink.key, nextLink.data);
//advance to next node
currentLink = currentLink.next;
}
return reversedlist;
}
public void concatenate(LinkedList list){
if(first == null){
first = list.first;
}
if(list.first == null){
return;
}
Link temp = first;
while(temp.next !=null) {
temp = temp.next;
}
temp.next = list.first;
}
}
LinkedListDemo.java
package com.tutorialspoint;
public class LinkedListDemo {
public static void main(String args[]){
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
list.insertFirst(1, 10);
list.insertFirst(2, 20);
list.insertFirst(3, 30);
list.insertFirst(4, 1);
list.insertFirst(5, 40);
list.insertFirst(6, 56);
System.out.print("\nOriginal List: ");
list.display();
System.out.println("");
while(!list.isEmpty()){
Link temp = list.deleteFirst();
System.out.print("Deleted value:");
temp.display();
System.out.println("");
}
System.out.print("List after deleting all items: ");
list.display();
System.out.println("");
list.insertFirst(1, 10);
list.insertFirst(2, 20);
list.insertFirst(3, 30);
list.insertFirst(4, 1);
list.insertFirst(5, 40);
list.insertFirst(6, 56);
System.out.print("Restored List: ");
list.display();
System.out.println("");
Link foundLink = list.find(4);
if(foundLink != null){
System.out.print("Element found: ");
foundLink.display();
System.out.println("");
}else{
System.out.println("Element not found.");
}
list.delete(4);
System.out.print("List after deleting an item: ");
list.display();
System.out.println("");
foundLink = list.find(4);
if(foundLink != null){
System.out.print("Element found: ");
foundLink.display();
System.out.println("");
}else{
System.out.print("Element not found. {4,1}");
}
System.out.println("");
list.sort();
System.out.print("List after sorting the data: ");
list.display();
System.out.println("");
System.out.print("Reverse of the list: ");
LinkedList list1 = list.reverse();
list1.display();
System.out.println("");
LinkedList list2 = new LinkedList();
list2.insertFirst(9, 50);
list2.insertFirst(8, 40);
list2.insertFirst(7, 20);
list.concatenate(list2);
System.out.print("List after concatenation: ");
list.display();
System.out.println("");
}
}
class LinkedList {
//this link always point to first Link
//in the Linked List
private Link first;
// create an empty linked list
public LinkedList(){
first = null;
}
//insert link at the first location
public void insertFirst(int key, int data){
//create a link
Link link = new Link(key,data);
//point it to old first node
link.next = first;
//point first to new first node
first = link;
}
//delete first item
public Link deleteFirst(){
//save reference to first link
Link tempLink = first;
//mark next to first link as first
first = first.next;
//return the deleted link
return tempLink;
}
//display the list
public void display(){
//start from the beginning
Link current = first;
//navigate till the end of the list
System.out.print("[ ");
while(current != null){
//print data
current.display();
//move to next item
current = current.next;
System.out.print(" ");
}
System.out.print(" ]");
}
//find a link with given key
public Link find(int key){
//start from the first link
Link current = first;
//if list is empty
if(first == null){
return null;
}
//navigate through list
while(current.key != key){
//if it is last node
if(current.next == null){
return null;
}else{
//go to next link
current = current.next;
}
}
//if data found, return the current Link
return current;
}
//delete a link with given key
public Link delete(int key){
//start from the first link
Link current = first;
Link previous = null;
//if list is empty
if(first == null){
return null;
}
//navigate through list
while(current.key != key){
//if it is last node
if(current.next == null){
return null;
}else{
//store reference to current link
previous = current;
//move to next link
current = current.next;
}
}
//found a match, update the link
if(current == first) {
//change first to point to next link
first = first.next;
}else {
//bypass the current link
previous.next = current.next;
}
return current;
}
//is list empty
public boolean isEmpty(){
return first == null;
}
public int length(){
int length = 0;
for(Link current = first; current!=null;
current = current.next){
length++;
}
return length;
}
public void sort(){
int i, j, k, tempKey, tempData ;
Link current,next;
int size = length();
k = size ;
for ( i = 0 ; i < size - 1 ; i++, k-- ) {
current = first ;
next = first.next ;
for ( j = 1 ; j < k ; j++ ) {
if ( current.data > next.data ) {
tempData = current.data ;
current.data = next.data;
next.data = tempData ;
tempKey = current.key;
current.key = next.key;
next.key = tempKey;
}
current = current.next;
next = next.next;
}
}
}
public LinkedList reverse() {
LinkedList reversedlist = new LinkedList();
Link nextLink = null;
reversedlist.insertFirst(first.key, first.data);
Link currentLink = first;
// Until no more data in list,
// insert current link before first and move ahead.
while(currentLink.next != null){
nextLink = currentLink.next;
// Insert at start of new list.
reversedlist.insertFirst(nextLink.key, nextLink.data);
//advance to next node
currentLink = currentLink.next;
}
return reversedlist;
}
public void concatenate(LinkedList list){
if(first == null){
first = list.first;
}
if(list.first == null){
return;
}
Link temp = first;
while(temp.next !=null) {
temp = temp.next;
}
temp.next = list.first;
}
}
class Link {
public int key;
public int data;
public Link next;
public Link(int key, int data){
this.key = key;
this.data = data;
}
public void display(){
System.out.print("{"+key+","+data+"}");
}
}
Output
If we compile and run the above program then it would produce following result:
Original List: [ {6,56} {5,40} {4,1} {3,30} {2,20} {1,10} ]
Deleted value:{6,56}
Deleted value:{5,40}
Deleted value:{4,1}
Deleted value:{3,30}
Deleted value:{2,20}
Deleted value:{1,10}
List after deleting all items: [ ]
Restored List: [ {6,56} {5,40} {4,1} {3,30} {2,20} {1,10} ]
Element found: {4,1}
List after deleting an item: [ {6,56} {5,40} {3,30} {2,20} {1,10} ]
Element not found. {4,1}
List after sorting the data: [ {1,10} {2,20} {3,30} {5,40} {6,56} ]
Reverse of the list: [ {6,56} {5,40} {3,30} {2,20} {1,10} ]
List after concatenation: [ {1,10} {2,20} {3,30} {5,40} {6,56} {7,20} {8,40} {9,50} ]