
- Antenna Theory - Fundamentals
- Antenna Theory - Basic Parameters
- Antenna Theory - Parameters
- Antenna Theory - Near & Far Fields
- Antenna Theory - Radiation Pattern
- Isotropic Radiation
- Antenna - Beam & Polarization
- Antenna Theory - Beam Width
- Antenna Theory - Reciprocity
- Antenna Theory - Poynting Vector
- Types of Antennas
- Antenna Theory - Types of Antennas
- Antenna Theory - Wire
- Antenna - Half-Wave Dipole
- Antenna - Half-Wave Folded Dipole
- Antenna - Full-Wave Dipole
- Antenna Theory - Short Dipole
- Antenna Theory - Long Wire
- Antenna Theory - V-Antennas
- Inverted V-Antenna
- Antenna Theory - Rhombic
- Antenna Theory - Loop
- Antenna Theory - Helical
- Antenna Theory - Aperture
- Antenna Theory - Horn
- Antenna Theory - Slot
- Antenna Theory - Micro Strip
- Antenna Theory - Lens
- Parabolic Reflector
- Antenna Arrays
- Antenna Theory - Antenna Arrays
- Antenna Theory - Collinear Array
- Antenna Theory - Broad-side Array
- Antenna Theory - End-fire Array
- Antenna Theory - Parasitic Array
- Yagi-Uda Antenna Theory
- Log-periodic Antenna Theory
- Turnstile Antenna Theory
- Wave Propagation
- Antenna - Spectrum & Transmission
- Antenna - Types of Propagation
- Antenna - Lonosphere & its Layers
- Terms in Wave Propagation
- Antenna Theory Useful Resources
- Antenna Theory - Quick Guide
- Antenna Theory - Useful Resources
- Antenna Theory - Discussion
Antenna Theory - V-Antennas
A better version of long-wire antennas is the V-Antenna. This antenna is formed by arranging the long wire in a V-shaped pattern. The end wires are called as legs. This antenna is a bi-directional resonant antenna.
Frequency Range
The frequency range of operation of V-antenna is around 3 to 30 MHz. This antenna works in high frequency range.
Construction & Working of V-Antennas
Two long wires are connected in the shape of V to make a V-antenna. The two long wires are excited with 180 out of phase. As the length of these wires increases, the gain and directivity also increases.
The following figure shows a V-antenna with the transmission line impedance z and the lengh of the wire /2, making an angle Φm with the axis, which is called as apex angle.
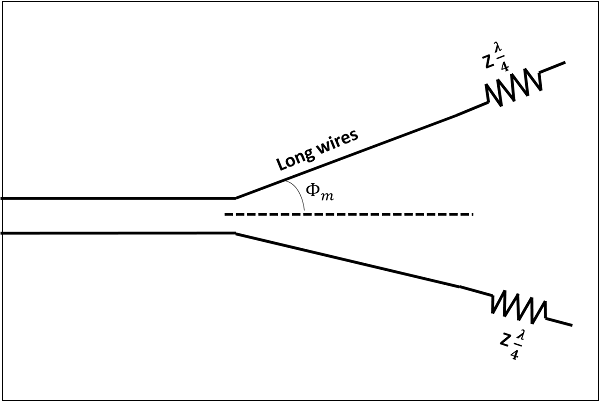
The gain achieved by V-antenna is higher than normal single long wire antenna. The gain in this V-formation is nearly twice compared to the single long wire antenna, which has a length equal to the legs of V-antenna. If wide range of radiation is to be achieved, the apex angle should have an average value between higher and lower frequencies in terms of the number of /2 in each leg.
Radiation Pattern
The radiation pattern of a V-antenna is bi-directional. The radiation obtained on each transmission line is added to obtain the resultant radiation pattern. This is well explained in the following figure −
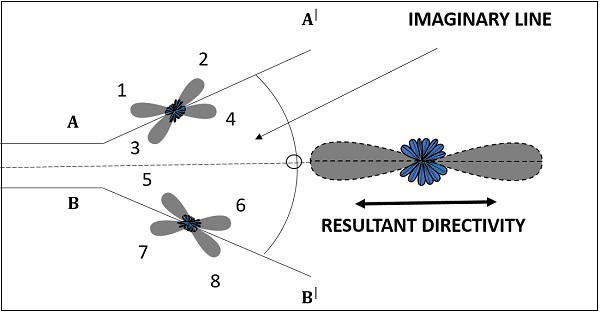
The figure shows the radiation pattern of V-antenna. The two transmission lines forming V-pattern are AA and BB. The patterns of individual transmission lines and the resultant pattern are shown in the figure. The resultant pattern is shown along the axis. This pattern resembles the broad-side array.
If another V-antenna is added to this antenna and fed with 90 phase difference, then the resultant pattern would be end-fire, doubling the power gain. The directivity is further increased by adding the array of V-antennas.
Advantages
The following are the advantages of V-antenna −
- Construction is simple
- High gain
- Low manufacturing cost
Disadvantages
The following are the disadvantages of V-antenna −
- Standing waves are formed
- The minor lobes occurred are also strong
- Used only for fixed frequency operations
Applications
The following are the applications of V-antenna −
- Used for commercial purposes
- Used in radio communications