
- C++ Home
- C++ Overview
- C++ Environment Setup
- C++ Basic Syntax
- C++ Comments
- C++ Hello World
- C++ Omitting Namespace
- C++ Tokens
- C++ Constants/Literals
- C++ Keywords
- C++ Identifiers
- C++ Data Types
- C++ Numeric Data Types
- C++ Character Data Type
- C++ Boolean Data Type
- C++ Variable Types
- C++ Variable Scope
- C++ Multiple Variables
- C++ Input Output Operations
- C++ Basic Input/Output
- C++ Cin
- C++ Cout
- C++ Manipulators
- Type System & Data Representation
- C++ Modifier Types
- C++ Storage Classes
- C++ Constexpr Specifier
- C++ Numbers
- C++ Enumeration
- C++ Enum Class
- C++ References
- C++ Date & Time
- C++ Operators
- C++ Operators
- C++ Arithmetic Operators
- C++ Relational Operators
- C++ Logical Operators
- C++ Bitwise Operators
- C++ Assignment Operators
- C++ sizeof Operator
- C++ Conditional Operator
- C++ Comma Operator
- C++ Member Operators
- C++ Casting Operators
- C++ Pointer Operators
- C++ Operators Precedence
- C++ Unary Operators
- C++ Scope Resolution Operator
- C++ Control Statements
- C++ Decision Making
- C++ if Statement
- C++ if else Statement
- C++ Nested if Statements
- C++ switch Statement
- C++ Nested switch Statements
- C++ Loop Types
- C++ while Loop
- C++ for Loop
- C++ do while Loop
- C++ Foreach Loop
- C++ Nested Loops
- C++ Jump Statements
- C++ break Statement
- C++ continue Statement
- C++ goto Statement
- C++ Return Values
- C++ Strings
- C++ Strings
- C++ Loop Through a String
- C++ String Length
- C++ String Concatenation
- C++ String Comparison
- C++ Functions
- C++ Functions
- C++ Multiple Function Parameters
- C++ Recursive Function
- C++ Function Overloading
- C++ Function Overriding
- C++ Default Arguments
- C++ Arrays
- C++ Arrays
- C++ Multidimensional Arrays
- C++ Pointer to an Array
- C++ Passing Arrays to Functions
- C++ Return Array from Functions
- C++ Array Decay
- C++ Structure & Union
- C++ Structures
- C++ Unions
- C++ Class and Objects
- C++ Object Oriented
- C++ Classes & Objects
- C++ Class Member Functions
- C++ Class Access Modifiers
- C++ Static Class Members
- C++ Static Data Members
- C++ Static Member Function
- C++ Inline Functions
- C++ this Pointer
- C++ Friend Functions
- C++ Pointer to Classes
- C++ Constructors
- C++ Constructor & Destructor
- C++ Default Constructors
- C++ Parameterized Constructors
- C++ Copy Constructor
- C++ Constructor Overloading
- C++ Constructor with Default Arguments
- C++ Delegating Constructors
- C++ Constructor Initialization List
- C++ Dynamic Initialization Using Constructors
- C++ Destructors
- C++ Virtual Destructor
- C++ Inheritance
- C++ Inheritance
- C++ Multiple Inheritance
- C++ Multilevel Inheritance
- C++ Object-oriented
- C++ Overloading
- C++ Polymorphism
- C++ Abstraction
- C++ Encapsulation
- C++ Interfaces
- C++ Virtual Function
- C++ Pure Virtual Functions & Abstract Classes
- C++ Override Specifiers
- C++ Final Specifiers
- C++ Design Patterns
- C++ Creational Design Patterns
- C++ Singleton Design Pattern
- C++ Factory Method Design Pattern
- C++ Abstract Factory Pattern
- C++ Prototype Design Pattern
- C++ Structural Design Patterns
- C++ Facade Design Pattern
- C++ Iterator Design Pattern
- C++ Mediator Design Pattern
- C++ Memento Design Pattern
- C++ Observer Design Pattern
- C++ State Design Pattern
- C++ Strategy Design Pattern
- C++ Template Method Design Pattern
- C++ Visitor Design Pattern
- C++ Behavioural Design Pattern
- C++ File Handling
- C++ Files and Streams
- C++ Reading From File
- C++ Advanced
- C++ Exception Handling
- C++ Dynamic Memory
- C++ Move Semantics
- C++ Namespaces
- C++ Templates
- C++ Preprocessor
- C++ Signal Handling
- C++ Multithreading
- C++ Web Programming
- C++ Socket Programming
- C++ Concurrency
- C++ Advanced Concepts
- C++ Lambda Expression
- C++ nullptr
- C++ unordered_multiset
- C++ Chain of Responsibility
- C++ Structural Design Patterns
- C++ Adapter Pattern
- C++ Bridge Pattern
- C++ Composite Pattern
- C++ Decorator Pattern
- C++ Flyweight Pattern
- C++ Command Pattern
- C++ Proxy Pattern
C++ Loop Types
There may be a situation, when you need to execute a block of code several number of times. In general, statements are executed sequentially: The first statement in a function is executed first, followed by the second, and so on.
Programming languages provide various control structures that allow for more complicated execution paths.
A loop statement allows us to execute a statement or group of statements multiple times and following is the general from of a loop statement in most of the programming languages −
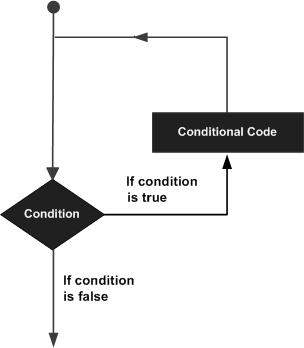
C++ programming language provides the following type of loops to handle looping requirements.
| Sr.No | Loop Type & Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | while loop
Repeats a statement or group of statements while a given condition is true. It tests the condition before executing the loop body. |
| 2 | for loop
Execute a sequence of statements multiple times and abbreviates the code that manages the loop variable. |
| 3 | do...while loop
Like a while statement, except that it tests the condition at the end of the loop body. |
| 4 | nested loops
You can use one or more loop inside any another while, for or do..while loop. |
Loop Control Statements
Loop control statements change execution from its normal sequence. When execution leaves a scope, all automatic objects that were created in that scope are destroyed.
C++ supports the following control statements.
| Sr.No | Control Statement & Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | break statement
Terminates the loop or switch statement and transfers execution to the statement immediately following the loop or switch. |
| 2 | continue statement
Causes the loop to skip the remainder of its body and immediately retest its condition prior to reiterating. |
| 3 | goto statement
Transfers control to the labeled statement. Though it is not advised to use goto statement in your program. |
The Infinite Loop
A loop becomes infinite loop if a condition never becomes false. The for loop is traditionally used for this purpose. Since none of the three expressions that form the for loop are required, you can make an endless loop by leaving the conditional expression empty.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main () {
for( ; ; ) {
printf("This loop will run forever.\n");
}
return 0;
}
When the conditional expression is absent, it is assumed to be true. You may have an initialization and increment expression, but C++ programmers more commonly use the for (;;) construct to signify an infinite loop.
NOTE − You can terminate an infinite loop by pressing Ctrl + C keys.