
- C - Home
- C - Overview
- C - Features
- C - History
- C - Standards
- C - Environment Setup
- C - Program Structure
- C - Hello World
- C - Compilation Process
- C - Comments
- C - Basic Syntax
- C - User Input
- C - printf Function
- C - Format Specifiers
- Lexical Elements in C
- C - Tokens
- C - Keywords
- C - Identifiers
- Variables and Constants
- C - Variables
- C - Constants
- C - Const Qualifier
- C - Linkage
- Data Types and Type Conversions
- C - Data Types
- C - Literals
- C - Escape Sequences
- C - Booleans
- C - Integer Promotions
- C - Character Arithmetic
- C - Type Conversion
- C - Type Casting
- Operators in C
- C - Operators
- C - Arithmetic Operators
- C - Unary Operators
- C - Relational Operators
- C - Logical Operators
- C - Bitwise Operators
- C - Assignment Operators
- C - Increment and Decrement Operators
- C - Ternary Operator
- C - sizeof Operator
- C - Operator Precedence
- C - Miscellaneous Operators
- Decision Making & Control Statements
- C - Decision Making
- C - if Statement
- C - if...else Statement
- C - if...else if Ladder
- C - Nested if Statements
- C - Switch Statement
- C - Nested Switch Statements
- C - Switch Case Using Range
- Loops in C
- C - Loops
- C - For Loop
- C - While Loop
- C - Do...while Loop
- C - For Loop vs While Loop
- C - Nested Loop
- C - Infinite Loop
- C - Break Statement
- C - Continue Statement
- C - Goto Statement
- Functions in C
- C - Functions
- C - Function Prototype
- C - Main Function
- C - Function call by Value
- C - Function call by reference
- C - Nested Functions
- C - Variadic Functions
- C - User-Defined Functions
- C - Callback Function
- C - Return Statement
- C - Recursion
- C - Predefined Identifier __func__
- Scope Rules in C
- C - Scope Rules
- C - Static Variables
- C - Global Variables
- Arrays in C
- C - Arrays
- C - Properties of Array
- C - Multi-Dimensional Arrays
- C - Passing Arrays to Function
- C - Return Array from Function
- C - Variable Length Arrays
- C - Dynamic Arrays
- Strings in C
- C - Strings
- C - Array of Strings
- C - Character Arrays
- C - Special Characters
- Pointers in C
- C - Pointers
- C - Initialization of Pointer Arrays
- C - Applications of Pointers
- C - Dereference Pointer
- C - NULL Pointer
- C - void Pointer
- C - Const Pointers & Pointer to Const
- C - Dangling Pointers
- C - Pointer Arithmetics
- C - Pointers and Arrays
- C - Pointer vs Array
- C - Pointer to an Array
- C - Array of Pointers
- C - Pointers vs. Multi-dimensional Arrays
- C - Pointer to Pointer
- C - Chain of Pointers
- C - Character Pointers and Functions
- C - Passing Pointers to Functions
- C - Return Pointer from Functions
- C - Function Pointers
- C - Array of Function Pointers
- C - Pointers to Structures
- C - Near, Far and Huge Pointers
- C - Restrict Keyword
- User-Defined Data Types
- C - Structures
- C - Structures and Functions
- C - Arrays of Structures
- C - Self-Referential Structures
- C - Dot (.) Operator
- C - Lookup Tables
- C - Enumeration (or enum)
- C - Structure Padding and Packing
- C - Nested Structures
- C - Anonymous Structure and Union
- C - Unions
- C - Bit Fields
- C - Typedef
- C - Flexible Array Members in Structures
- C - Structures vs Unions
- Memory Management in C
- C - Memory Layout
- C - Memory Management
- C - Memory Address
- C - Storage Classes
- C - Dynamic Array Resizing
- C - Memory Leaks
- File Handling in C
- C - File Handling
- C - Input & Output
- C - File Operations
- C - Formatted Output
- C - getc, getchar, getch, getche
- Preprocessors in C
- C - Preprocessors
- C - Pragmas
- C - Macros
- C - Working of Preprocessor
- C - Preprocessor Operators
- C - Header Files
- C - Custom Header Files
- Miscellaneous Topics
- C - Error Handling
- C - Variable Arguments
- C - Command Execution
- C - Math Functions
- C - Static Keyword
- C - Random Number Generation
- C - Command Line Arguments
- C Programming Resources
- C - Questions & Answers
- C - Quick Guide
- C - Cheat Sheet
- C - Useful Resources
- C - Discussion
- C - Online Compiler
Switch Statement in C
A switch statement allows a variable to be tested for equality against a list of values. Each value is called a case, and the variable being switched on is checked for each switch case.
C switch-case Statement
The switch-case statement is a decision-making statement in C. The if-else statement provides two alternative actions to be performed, whereas the switch-case construct is a multi-way branching statement. A switch statement in C simplifies multi-way choices by evaluating a single variable against multiple values, executing specific code based on the match. It allows a variable to be tested for equality against a list of values.
Syntax of switch-case Statement
The flow of the program can switch the line execution to a branch that satisfies a given case. The schematic representation of the usage of switch-case construct is as follows −
switch (Expression){
// if expr equals Value1
case Value1:
Statement1;
Statement2;
break;
// if expr equals Value2
case Value2:
Statement1;
Statement2;
break;
.
.
// if expr is other than the specific values above
default:
Statement1;
Statement2;
}
How switch-case Statement Work?
The parenthesis in front of the switch keyword holds an expression. The expression should evaluate to an integer or a character. Inside the curly brackets after the parenthesis, different possible values of the expression form the case labels.
One or more statements after a colon(:) in front of the case label forms a block to be executed when the expression equals the value of the label.
You can literally translate a switch-case as "in case the expression equals value1, execute the block1", and so on.
C checks the expression with each label value, and executes the block in front of the first match. Each case block has a break as the last statement. The break statement takes the control out of the scope of the switch construct.
You can also define a default case as the last option in the switch construct. The default case block is executed when the expression doesnt match with any of the earlier case values.
Flowchart of switch-case Statement
The flowchart that represents the switch-case construct in C is as follows −
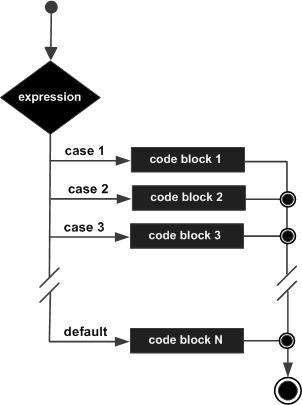
Rules for Using the switch-case Statement
The following rules apply to a switch statement −
The expression used in a switch statement must have an integral or enumerated type, or be of a class type in which the class has a single conversion function to an integral or enumerated type.
You can have any number of case statements within a switch. Each case is followed by the value to be compared to and a colon.
The constant-expression for a case must be the same data type as the variable in the switch, and it must be a constant or a literal.
When the variable being switched on is equal to a case, the statements following that case will execute until a break statement is reached.
When a break statement is reached, the switch terminates, and the flow of control jumps to the next line following the switch statement.
Not every case needs to contain a break. If no break appears, the flow of control will fall through to subsequent cases until a break is reached.
A switch statement can have an optional default case, which must appear at the end of the switch. The default case can be used for performing a task when none of the cases is true. No break is needed in the default case.
The switch-case statement acts as a compact alternative to cascade of if-else statements, particularly when the Boolean expression in "if" is based on the "=" operator.
If there are more than one statements in an if (or else) block, you must put them inside curly brackets. Hence, if your code has many if and else statements, the code with that many opening and closing curly brackets appears clumsy. The switch-case alternative is a compact and clutter-free solution.
C switch-case Statement Examples
Practice the following examples to learn the switch case statements in C programming language −
Example 1
In the following code, a series of if-else statements print three different greeting messages based on the value of a "ch" variable ("m", "a" or "e" for morning, afternoon or evening).
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
/* local variable definition */
char ch = 'e';
printf("Time code: %c\n\n", ch);
if (ch == 'm')
printf("Good Morning");
else if (ch == 'a')
printf("Good Afternoon");
else
printf("Good Evening");
return 0;
}
The if-else logic in the above code is replaced by the switch-case construct in the code below −
#include <stdio.h>
int main (){
// local variable definition
char ch = 'm';
printf("Time code: %c\n\n", ch);
switch (ch){
case 'a':
printf("Good Afternoon\n");
break;
case 'e':
printf("Good Evening\n");
break;
case 'm':
printf("Good Morning\n");
}
return 0;
}
Output
Change the value of "ch" variable and check the output. For ch = 'm', we get the following output −
Time code: m Good Morning
The use of break is very important here. The block of statements corresponding to each case ends with a break statement. What if the break statement is not used?
The switch-case works like this: As the program enters the switch construct, it starts comparing the value of switching expression with the cases, and executes the block of its first match. The break causes the control to go out of the switch scope. If break is not found, the subsequent block also gets executed, leading to incorrect result.
Example 2: Switch Statement without using Break
Let us comment out all the break statements in the above code.
#include <stdio.h>
int main (){
/* local variable definition */
char ch = 'a';
printf("Time code: %c\n\n", ch);
switch (ch){
case 'a':
printf("Good Afternoon\n");
// break;
case 'e':
printf("Good Evening\n");
// break;
case 'm':
printf("Good Morning\n");
}
return 0;
}
Output
You expect the "Good Morning" message to be printed, but you find all the three messages printed!
Time code: a Good Afternoon Good Evening Good Morning
This is because C falls through the subsequent case blocks in the absence of break statements at the end of the blocks.
Example 3: Grade Checker Program using Switch Statement
In the following program, "grade" is the switching variable. For different cases of grades, the corresponding result messages will be printed.
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
/* local variable definition */
char grade = 'B';
switch(grade){
case 'A' :
printf("Outstanding!\n" );
break;
case 'B':
printf("Excellent!\n");
break;
case 'C':
printf("Well Done\n" );
break;
case 'D':
printf("You passed\n" );
break;
case 'F':
printf("Better try again\n" );
break;
default :
printf("Invalid grade\n" );
}
printf("Your grade is %c\n", grade);
return 0;
}
Output
Run the code and check its output −
Excellent! Your grade is B
Now change the value of "grade" (it is a "char" variable) and check the outputs.
Example 4: Menu-based Calculator for Arithmetic Operations using Switch
The following example displays a menu for arithmetic operations. Based on the value of the operator code (1, 2, 3, or 4), addition, subtraction, multiplication or division of two values is done. If the operation code is something else, the default case is executed.
#include <stdio.h>
int main (){
// local variable definition
int a = 10, b = 5;
// Run the program with other values 2, 3, 4, 5
int op = 1;
float result;
printf("1: addition\n");
printf("2: subtraction\n");
printf("3: multiplication\n");
printf("4: division\n");
printf("\na: %d b: %d : op: %d\n", a, b, op);
switch (op){
case 1:
result = a + b;
break;
case 2:
result = a - b;
break;
case 3:
result = a * b;
break;
case 4:
result = a / b;
break;
default:
printf("Invalid operation\n");
}
if (op >= 1 && op <= 4)
printf("Result: %6.2f", result);
return 0;
}
Output
1: addition 2: subtraction 3: multiplication 4: division a: 10 b: 5 : op: 1 Result: 15.00
For other values of "op" (2, 3, and 4), you will get the following outputs −
a: 10 b: 5 : op: 2 Result: 5.00 a: 10 b: 5 : op: 3 Result: 50.00 a: 10 b: 5 : op: 4 Result: 2.00 a: 10 b: 5 : op: 5 Invalid operation
Switch Statement by Combining Multiple Cases
Multiple cases can be written together to execute one block of code. When any of them case value matches, the body of these combined cases executes. If you have a situation where the same code block is to be executed for more than one case labels of an expression, you can combine them by putting the two cases one below the other, as shown below −
Syntax
switch (exp) {
case 1:
case 2:
statements;
break;
case 3:
statements;
break;
default:
printf("%c is a non-alphanumeric character\n", ch);
}
You can also use the ellipsis () to combine a range of values for an expression. For example, to match the value of switching variable with any number between 1 to 10, you can use "case 1 10"
Example 1
#include <stdio.h>
int main (){
// local variable definition
int number = 5;
switch (number){
case 1 ... 10:
printf("The number is between 1 and 10\n");
break;
default:
printf("The number is not between 1 and 10\n");
}
return 0;
}
Output
Run the code and check its output. For "number = 5", we get the following output −
The number is between 1 and 10
Example 2
The following program checks whether the value of the given char variable stores a lowercase alphabet, an uppercase alphabet, a digit, or any other key.
#include <stdio.h>
int main (){
char ch = 'g';
switch (ch){
case 'a' ... 'z':
printf("%c is a lowercase alphabet\n", ch);
break;
case 'A' ... 'Z':
printf("%c is an uppercase alphabet\n", ch);
break;
case 48 ... 57:
printf("%c is a digit\n", ch);
break;
default:
printf("%c is a non-alphanumeric character\n", ch);
}
return 0;
}
Output
For ch = 'g', we get the following output −
g is a lowercase alphabet
Test the code output with different values of "ch".