
- PL/SQL - Home
- PL/SQL - Overview
- PL/SQL - Environment
- PL/SQL - Basic Syntax
- PL/SQL - Data Types
- PL/SQL - Variables
- PL/SQL - Constants and Literals
- PL/SQL - Operators
- PL/SQL - Conditions
- PL/SQL - Loops
- PL/SQL - Strings
- PL/SQL - Arrays
- PL/SQL - Procedures
- PL/SQL - Functions
- PL/SQL - Cursors
- PL/SQL - Records
- PL/SQL - Exceptions
- PL/SQL - Triggers
- PL/SQL - Packages
- PL/SQL - Collections
- PL/SQL - Transactions
- PL/SQL - Date & Time
- PL/SQL - DBMS Output
- PL/SQL - Object Oriented
PL/SQL - CASE Statement
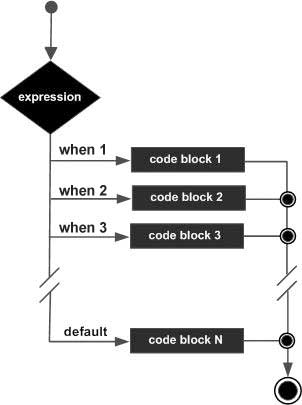
Like the IF statement, the CASE statement selects one sequence of statements to execute. However, to select the sequence, the CASE statement uses a selector rather than multiple Boolean expressions. A selector is an expression, the value of which is used to select one of several alternatives.
Syntax
The syntax for the case statement in PL/SQL is −
CASE selector WHEN 'value1' THEN S1; WHEN 'value2' THEN S2; WHEN 'value3' THEN S3; ... ELSE Sn; -- default case END CASE;
Flow Diagram
Example
DECLARE
grade char(1) := 'A';
BEGIN
CASE grade
when 'A' then dbms_output.put_line('Excellent');
when 'B' then dbms_output.put_line('Very good');
when 'C' then dbms_output.put_line('Well done');
when 'D' then dbms_output.put_line('You passed');
when 'F' then dbms_output.put_line('Better try again');
else dbms_output.put_line('No such grade');
END CASE;
END;
/
When the above code is executed at the SQL prompt, it produces the following result −
Excellent PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
plsql_conditional_control.htm
Advertisements