Data Structure
Data Structure Networking
Networking RDBMS
RDBMS Operating System
Operating System Java
Java MS Excel
MS Excel iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C Programming
C Programming C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP
- Selected Reading
- UPSC IAS Exams Notes
- Developer's Best Practices
- Questions and Answers
- Effective Resume Writing
- HR Interview Questions
- Computer Glossary
- Who is Who
C++ Program to Represent Graph Using Adjacency Matrix
What is Adjacency Matrix?
Adjacency matrix is a square matrix that represent a finite graph data structure using a 2D array. The each elements in the matrix represent the edges of the graph. For example, if the graph has some edges from i to j vertices, then in the adjacency matrix at ith row and jth column it will be 1 (or some non-zero value for weighted graph), otherwise that place will hold 0.
Graph
The image below represent a simple undirected graph with 6 vertices and 8 edges.

Adjacency Matrix
The adjacency matrix of the above graph is shown below.
| 0 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
| 1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
| 2 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
| 3 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
| 4 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
| 5 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
Algorithm
The following are the steps to represent a graph using an adjacency matrix.
- Step 1: Start
- Step 2: Input the number of vertices V and number of edges E in the graph
- Step 3: Initialize a V x V matrix (adjMatrix) and set all values to 0.
- Step 4: For each edge, repeat step 5 to step 7.
- Step 5: Input the pair of vertices (u, v) that form an edge.
- Step 6: Set adjMatrix[u][v] = 1
- Step 7: If the graph is undirected, also set adjMatrix[v][u] = 1
- Step 8: Display the adjacency matrix.
- Step 9: End
C++ Program for Adjacency Matrix Representation of a Graph
The following C++ program demonstrates how to represent a graph using an adjacency matrix. The program allows the user to input the number of vertices and edges, and then it displays the adjacency matrix.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Graph {
private:
int vertices;
int **adjMatrix;
bool isDirected;
public:
Graph(int v, bool directed = false) {
vertices = v;
isDirected = directed;
// Allocate memory for adjacency matrix
adjMatrix = new int*[vertices];
for (int i = 0; i < vertices; ++i) {
adjMatrix[i] = new int[vertices];
for (int j = 0; j < vertices; ++j) {
adjMatrix[i][j] = 0; // Initialize with 0
}
}
}
void addEdge(int i, int j) {
adjMatrix[i][j] = 1;
if (!isDirected) {
adjMatrix[j][i] = 1;
}
}
void display() {
cout << "Adjacency Matrix:\n";
for (int i = 0; i < vertices; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < vertices; ++j) {
cout << adjMatrix[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
~Graph() {
for (int i = 0; i < vertices; ++i) {
delete[] adjMatrix[i];
}
delete[] adjMatrix;
}
};
int main() {
int V, E;
cout << "Enter number of vertices: ";
cin >> V;
Graph g(V); // Change to Graph g(V, true); for directed graph
cout << "Enter number of edges: ";
cin >> E;
cout << "Enter edges (format: from to):\n";
for (int i = 0; i < E; ++i) {
int from, to;
cin >> from >> to;
g.addEdge(from, to);
}
g.display();
return 0;
}
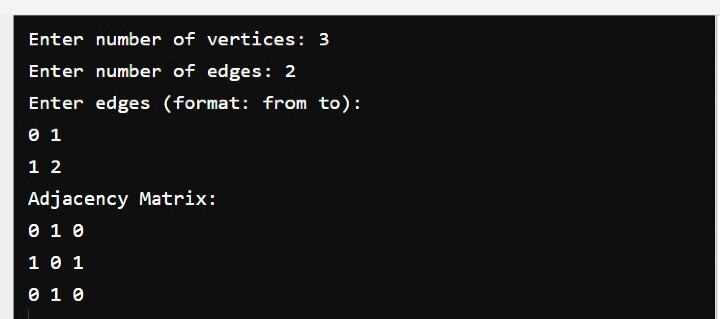
Sample Output
The output of the above program is as follows: