
- VB.Net Basic Tutorial
- VB.Net - Home
- VB.Net - Overview
- VB.Net - Environment Setup
- VB.Net - Program Structure
- VB.Net - Basic Syntax
- VB.Net - Data Types
- VB.Net - Variables
- VB.Net - Constants
- VB.Net - Modifiers
- VB.Net - Statements
- VB.Net - Directives
- VB.Net - Operators
- VB.Net - Decision Making
- VB.Net - Loops
- VB.Net - Strings
- VB.Net - Date & Time
- VB.Net - Arrays
- VB.Net - Collections
- VB.Net - Functions
- VB.Net - Subs
- VB.Net - Classes & Objects
- VB.Net - Exception Handling
- VB.Net - File Handling
- VB.Net - Basic Controls
- VB.Net - Dialog Boxes
- VB.Net - Advanced Forms
- VB.Net - Event Handling
- VB.Net Advanced Tutorial
- VB.Net - Regular Expressions
- VB.Net - Database Access
- VB.Net - Excel Sheet
- VB.Net - Send Email
- VB.Net - XML Processing
- VB.Net - Web Programming
- VB.Net Useful Resources
- VB.Net - Quick Guide
- VB.Net - Useful Resources
- VB.Net - Discussion
VB.Net - Select Case Statement
A Select Case statement allows a variable to be tested for equality against a list of values. Each value is called a case, and the variable being switched on is checked for each select case.
Syntax
The syntax for a Select Case statement in VB.Net is as follows −
Select [ Case ] expression
[ Case expressionlist
[ statements ] ]
[ Case Else
[ elsestatements ] ]
End Select
Where,
expression − is an expression that must evaluate to any of the elementary data type in VB.Net, i.e., Boolean, Byte, Char, Date, Double, Decimal, Integer, Long, Object, SByte, Short, Single, String, UInteger, ULong, and UShort.
expressionlist − List of expression clauses representing match values for expression. Multiple expression clauses are separated by commas.
statements − statements following Case that run if the select expression matches any clause in expressionlist.
elsestatements − statements following Case Else that run if the select expression does not match any clause in the expressionlist of any of the Case statements.
Flow Diagram
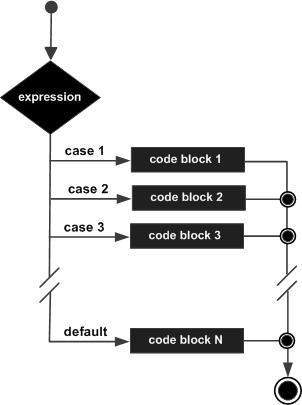
Example
Module decisions
Sub Main()
'local variable definition
Dim grade As Char
grade = "B"
Select grade
Case "A"
Console.WriteLine("Excellent!")
Case "B", "C"
Console.WriteLine("Well done")
Case "D"
Console.WriteLine("You passed")
Case "F"
Console.WriteLine("Better try again")
Case Else
Console.WriteLine("Invalid grade")
End Select
Console.WriteLine("Your grade is {0}", grade)
Console.ReadLine()
End Sub
End Module
When the above code is compiled and executed, it produces the following result −
Well done Your grade is B